The Wireless Infrastructure Market is estimated to be valued at USD 195.7 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 463.2 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.0% over the forecast period.
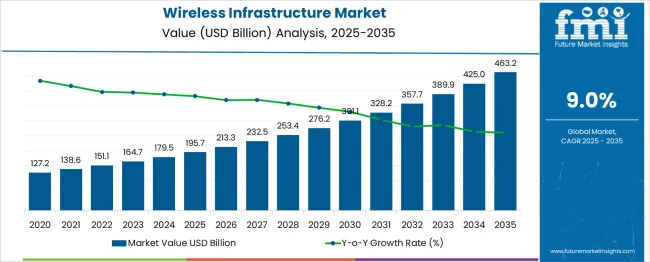
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Wireless Infrastructure Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 195.7 billion |
| Wireless Infrastructure Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 463.2 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 9.0% |
The wireless infrastructure market is evolving rapidly in response to surging demand for high-speed connectivity, expanded mobile network coverage, and enhanced data capacity. Increasing reliance on mobile communication and the accelerated rollout of 5G infrastructure have positioned wireless systems as essential components in global connectivity strategies.
Governments and private enterprises are investing heavily in network upgrades, rural connectivity, and smart city initiatives, creating long-term growth opportunities. Additionally, the rise in connected devices, IoT expansion, and remote work models continues to drive deployment of advanced infrastructure solutions.
As network demands increase, the integration of AI-based network optimization, energy-efficient systems, and small cell deployments is expected to further enhance service quality. The future of the wireless infrastructure market is set to be defined by its ability to support real-time applications, dense data environments, and critical connectivity across various industry verticals.
The wireless infrastructure market is segmented by component, technology, and end use and geographic regions. By component of the wireless infrastructure market is divided into Hardware, Software, and Services. In terms of technology of the wireless infrastructure market is classified into 4G/LTE, 2G/3G, 5G, and Satellite. Based on end use of the wireless infrastructure market is segmented into Defense, Government, and Commercial. Regionally, the wireless infrastructure industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
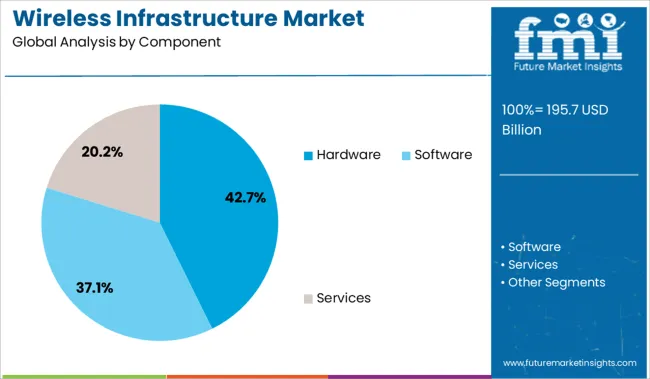
The hardware segment holds a commanding 42.7% share within the component category, highlighting its foundational role in wireless infrastructure deployment. This segment encompasses essential physical elements such as base stations, antennas, remote radio units, and routers that form the backbone of wireless communication networks.
Increased investments in macro and micro cell deployment, driven by the need for network densification, continue to support segment expansion. Hardware upgrades are essential for accommodating evolving standards like 4G, 5G, and beyond, pushing telecom providers to modernize existing assets.
Demand is also rising from enterprises building private networks for localized, high-reliability communication. Continued enhancements in hardware durability, signal strength, and integration capability are expected to secure this segment’s growth, especially as emerging economies expand rural and urban network infrastructures.
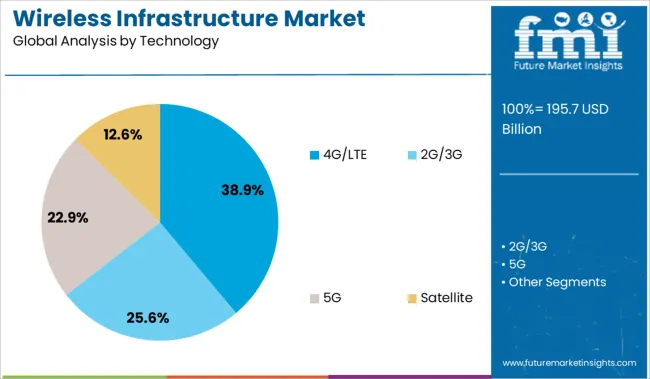
The 4G/LTE segment leads the wireless infrastructure market’s technology category with a 38.9% share, reflecting its extensive global adoption and ongoing relevance. Despite growing investments in 5G, 4G/LTE continues to provide critical support for mobile voice, broadband data, and IoT applications, particularly in regions where 5G deployment remains limited.
Telecom operators rely on 4G networks to bridge coverage gaps, maintain quality service, and extend connectivity to underserved areas. The maturity of 4G/LTE technology, along with its compatibility with existing devices and infrastructure, has cemented its role as a cost-effective and reliable solution for wide-scale communication needs.
Future upgrades, such as LTE Advanced and carrier aggregation, will continue to enhance performance and efficiency. The segment is expected to retain a stable market share as it coexists with next-gen technologies, ensuring connectivity during transitional phases of network modernization.
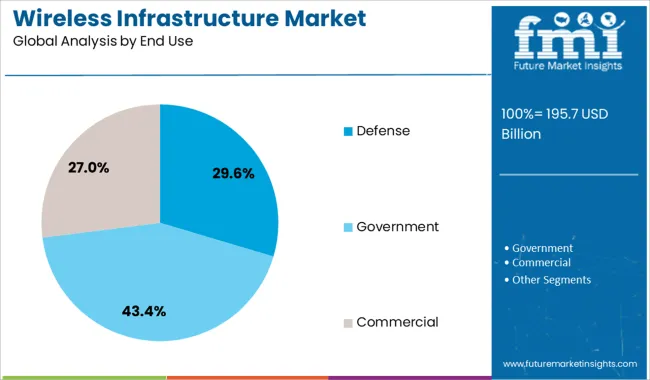
The defense segment commands a notable 29.6% share within the end use category, underscoring the critical importance of secure and resilient wireless communication systems in military operations. Defense agencies prioritize robust infrastructure to support mission-critical applications, including battlefield coordination, remote surveillance, and unmanned systems control.
The growing adoption of software-defined radios, encrypted networks, and satellite-linked systems has driven consistent investment in wireless infrastructure tailored to defense requirements. As defense organizations modernize communication networks to enable real-time data exchange and interoperability across land, air, and naval forces, demand for high-performance and ruggedized wireless systems remains strong.
The rise in asymmetric warfare, cybersecurity threats, and border surveillance has further highlighted the strategic role of advanced wireless connectivity. This segment is expected to experience sustained growth due to continued defense modernization efforts and the integration of next-generation communication technologies in national security frameworks.
Wireless infrastructure growth is driven by surging mobile data traffic, prompting investments in base stations, small-cell networks, and fiber backhaul for improved capacity and low latency. Spectrum scarcity and high licensing costs have increased financial pressures, encouraging modular solutions, shared networks, and cost-optimized deployments
The growth of wireless infrastructure is influenced by the rapid expansion of mobile data traffic caused by streaming services, cloud-based applications, and remote work environments. Service providers have invested heavily in upgrading base stations and small-cell networks to address congestion and enhance capacity. Demand for low-latency connections has driven large-scale deployment of advanced radio access technologies, particularly in densely populated regions. Operators are expanding fiber backhaul integration to support spectrum efficiency, which ensures consistent network performance. The emphasis on rural connectivity has led to broader coverage obligations, creating new infrastructure contracts. Increased capital expenditure from telecom firms has been observed as competitive pressures intensify for reliable connectivity solutions across consumer and enterprise segments.
The wireless infrastructure market has been influenced significantly by the scarcity of spectrum and the rising costs associated with licensing and equipment procurement. Governments have implemented spectrum auctions that increase financial pressure on network operators, limiting budget allocation for network expansion. Vendors have responded by developing modular hardware to reduce total cost of ownership for telecom carriers. Competition among infrastructure providers has been strong, resulting in strategic partnerships for network sharing and joint deployment to manage expenditure. Price sensitivity in emerging economies has created opportunities for cost-optimized solutions that deliver efficiency without compromising service quality. Regulatory mandates concerning network resiliency have reinforced the need for long-term infrastructure investments, particularly for mission-critical connectivity in public and private networks.
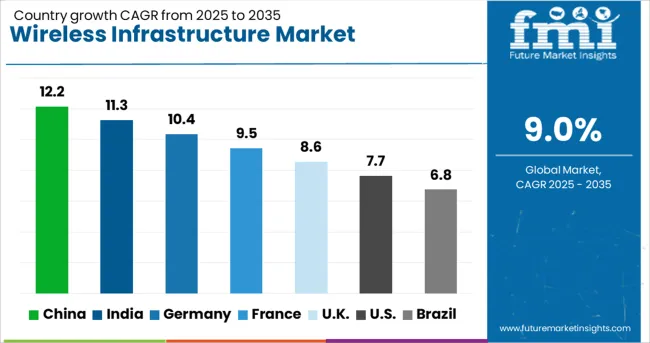
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 12.2% |
| India | 11.3% |
| Germany | 10.4% |
| France | 9.5% |
| UK | 8.6% |
| USA | 7.7% |
| Brazil | 6.8% |
The wireless infrastructure sector, projected to grow at a global CAGR of 9.0% from 2025 to 2035, shows diverse growth patterns across major economies. A 12.2% CAGR is being led by China, a BRICS member, supported by aggressive network rollouts and spectrum utilization. India follows with an 11.3% CAGR, also a BRICS member, driven by rural connectivity initiatives and expanding 5G adoption.
Among OECD members, France is witnessing a 9.5% CAGR as operators prioritize advanced network deployments, while the United Kingdom is recording an 8.6% CAGR through urban coverage enhancement and enterprise connectivity solutions. The United States shows a 7.7% CAGR, attributed to ongoing investments in fiber backhaul and private network infrastructure. The report includes in-depth insights for 40+ countries, with these top five highlighted as key benchmarks.
The CAGR in China rose from about 7.8% during 2020-2024 to 12.2% in the 2025-2035 period, driven by extensive 5G rollout programs and aggressive rural connectivity initiatives. Provincial infrastructure subsidies supported local carriers in deploying fiber backhaul and small-cell networks across tier-2 and tier-3 cities. Network densification projects became critical as data traffic surged due to expanded adoption of video streaming and cloud gaming platforms.
Vendor partnerships with domestic handset manufacturers allowed faster integration of 5G-ready equipment. The introduction of private enterprise networks in industrial zones further stimulated equipment procurement and service upgrades. China’s push for digital manufacturing under national connectivity strategies has ensured robust capital investments in next-generation wireless infrastructure deployments.
The CAGR in India moved from approximately 8.2% during 2020-2024 to 11.3% for the 2025-2035 phase, supported by rural broadband penetration and government-driven network modernization schemes. Affordable spectrum auctions in 2025 provided operators with favorable conditions for the rapid deployment of high-capacity wireless networks. The surge in mobile data consumption from OTT platforms and fintech ecosystems created demand for low-latency backhaul systems. Domestic telecom manufacturers expanded production of radio units and base station equipment to reduce import reliance.
Cloud-based core network deployments were accelerated in enterprise clusters, with edge data centers complementing connectivity upgrades. Private 5G adoption in manufacturing and logistics added another growth vector, as companies pursued automation-enabled solutions requiring reliable connectivity infrastructure.
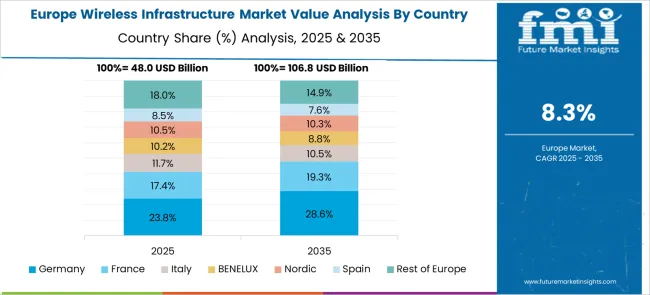
France increased from nearly 6.7% CAGR in 2020-2024 to 9.5% during 2025-2035, driven by the nationwide expansion of 5G corridors for industrial automation and smart cities. Operators implemented energy-optimized base stations across urban and suburban networks to meet quality of service requirements. The French government allocated dedicated funds under digital economy initiatives to improve rural coverage and connectivity resilience.
Adoption of private LTE and enterprise-grade 5G systems accelerated in sectors such as automotive manufacturing and transportation logistics. Strategic collaborations between telecom operators and hyperscale cloud providers enhanced the rollout of edge computing-based solutions for real-time applications in healthcare and mobility sectors.
The CAGR in the United Kingdom climbed from 3.4% during 2020-2024 to 8.6% across 2025-2035 as policy reforms addressed spectrum efficiency and infrastructure resiliency gaps. Increased competition among major operators spurred network-sharing agreements and joint ventures for small-cell deployment in dense urban centers. Enterprise adoption of wireless connectivity for logistics and manufacturing created demand for customized private networks.
Public sector-driven smart mobility and e-health initiatives necessitated broader low-latency network coverage, supporting 5G and edge-based deployments. Regulatory efforts to streamline site acquisition and mast installation shortened project timelines, helping carriers invest aggressively in nationwide connectivity upgrades for both consumer and industrial use cases.
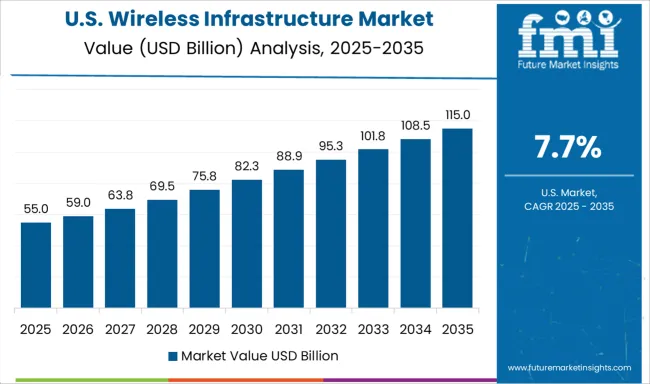
The United States grew from about a 4.5% CAGR during 2020-2024 to 7.7% for 2025-2035, influenced by high investments in fiber backhaul and small-cell networks to meet surging data demand. Enterprise demand for low-latency applications in manufacturing, healthcare, and defense drove infrastructure upgrades, especially in private 5G deployment. Federal funding initiatives targeted coverage in underserved rural areas, providing opportunities for domestic and regional infrastructure suppliers.
Telecom operators implemented spectrum refarming strategies to optimize mid-band utilization, improving efficiency without additional licensing costs. Strategic alliances with cloud providers advanced edge integration, supporting IoT and mission-critical systems. These developments strengthened the ecosystem for scalable, high-capacity wireless infrastructure throughout the USA market.
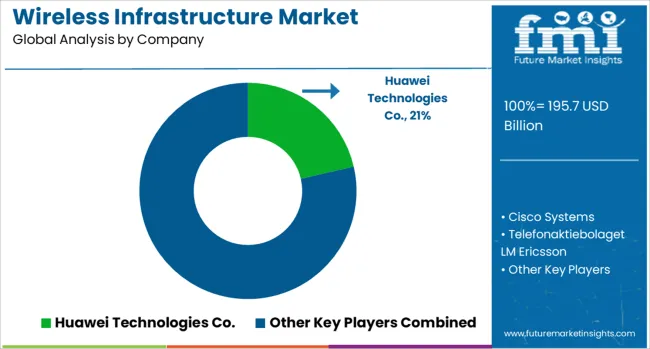
In the wireless infrastructure market, dominant players are advancing network reliability and scalability to address the explosive surge in data traffic. Huawei Technologies Co. has strengthened its leadership through comprehensive 5G deployment strategies, enabling robust connectivity in both urban and rural regions. Cisco Systems focuses on software-defined networking and cloud-based orchestration tools, providing telecom operators with cost-optimized solutions for high-capacity networks. Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson continues to deliver next-generation radio access systems, supported by its global expertise in spectrum efficiency and edge computing integration.
D-Link Corporation emphasizes affordable networking hardware for enterprise and residential sectors, expanding its presence in emerging economies. Juniper Networks is driving secure, AI-enabled network automation to enhance operational efficiency across service provider networks. Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP targets carrier-grade edge solutions with cloud-native infrastructure, while Mavenir specializes in open RAN technology, reducing dependency on proprietary hardware. These companies collectively shape the transition toward disaggregated, flexible, and software-driven wireless ecosystems.
In 2024, Huawei announced plans to launch commercial 5.5G network equipment, marking the commercial debut of what it terms the 5G-A or 5G-Advanced era, with initial availability expected during the year.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 195.7 Billion |
| Component | Hardware, Software, and Services |
| Technology | 4G/LTE, 2G/3G, 5G, and Satellite |
| End Use | Defense, Government, and Commercial |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Huawei Technologies Co., Cisco Systems, Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson, D-Link Corporation, Juniper Networks, Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP, and Mavenir |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales, share by technology and region, spectrum licensing impact, vendor strategies, base station deployment trends, 5G adoption rates, pricing benchmarks, competitive positioning, and regulatory drivers shaping global connectivity demand. |
The global wireless infrastructure market is estimated to be valued at USD 195.7 billion in 2025.
The market size for the wireless infrastructure market is projected to reach USD 463.2 billion by 2035.
The wireless infrastructure market is expected to grow at a 9.0% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in wireless infrastructure market are hardware, _small cells, _radio access network (ran), _macro cells, _backhaul, _mobile core, _others, software, _network management tools, _optimization solutions, services, _installation & deployment, _maintenance & support and _consulting & integration.
In terms of technology, 4g/lte segment to command 38.9% share in the wireless infrastructure market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Wireless EEG Monitoring System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Wireless Refrigerant Charging Scale Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Wireless Hydrometer Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Wireless HDMI Transmitter and Receiver Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Wireless Access Point Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Wireless Video - 2.4/5GHz Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Wireless Polysomnography Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Wireless Audio Devices Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Wireless Communication Technologies In Healthcare Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Wireless Mesh Network Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Wireless Sensor Tags Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Wireless Sensor Network Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Wireless Power Transmission Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Wireless Home Security Camera Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Wireless Testing Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Wireless Power Bank Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Wireless Battery Monitoring System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Wireless Printer Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Wireless Headphones Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Wireless Sensors Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA