The Japan babesiosis treatment demand is valued at USD 72.3 million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 105.3 million by 2035, reflecting a CAGR of 3.8%. Demand is influenced by increased tick-borne infection surveillance, early diagnostic adoption, and clinical interventions among high-risk demographics including elderly individuals and immunocompromised patients. Improved reporting systems and public-health initiatives targeting vector control contribute to sustained uptake of prescription therapies. Generic drugs represent the leading treatment category due to cost-efficiency and established clinical protocols that combine antimicrobial and antiparasitic agents. Treatment regimens typically include atovaquone-based combinations used to achieve effective pathogen clearance and limit relapse risk. Continued emphasis on clinical guideline standardization and availability of oral formulations supports broader treatment accessibility across healthcare facilities.
Higher utilization is concentrated in Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, and Kansai. These regions report greater incidence rates linked to favourable tick habitats, larger populations of outdoor and agricultural workers, and wider diagnostic coverage. Healthcare networks in these areas maintain better availability of infectious-disease specialists and treatment infrastructure. Key suppliers include Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Pfizer Japan Inc., Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, Daiichi Sankyo Company, Limited, and Meiji Seika Pharma Co., Ltd. These companies support distribution of generic therapies aligned with clinical recommendations for babesiosis management within hospital and outpatient settings.
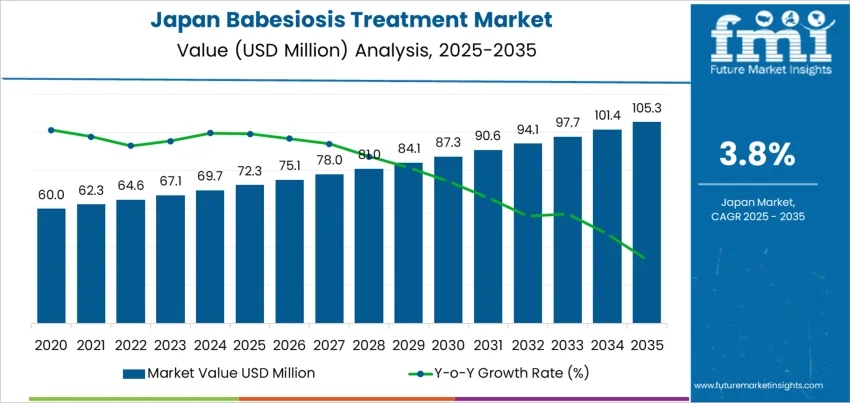
Demand for babesiosis treatment in Japan shows controlled acceleration linked to improved diagnostics and increased clinical awareness. Early acceleration is driven by better detection of tick-borne infections in regions where vector exposure has risen due to climate and land-use changes. Hospitals refine screening protocols for at-risk populations, which supports a steady increase in treatment demand.
Deceleration phases appear because babesiosis remains a low-incidence infectious disease in Japan. Limited patient volumes restrict rapid expansion, and therapeutic protocols typically rely on established drug regimens with long replacement cycles. Public-health interventions and vector-control programs can further slow growth by reducing transmission opportunities. Seasonal case variability also influences fluctuations, producing softer demand outside peak exposure periods.
The pattern reflects medical-need responsiveness rather than broad expansion. Acceleration occurs when awareness, detection capability, and exposure converge, while deceleration follows as incidence stabilizes and preventive strategies strengthen. This results in a measured trajectory where treatment demand expands gradually but remains restricted by epidemiological scale within Japan.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Japan Babesiosis Treatment Sales Value (2025) | USD 72.3 million |
| Japan Babesiosis Treatment Forecast Value (2035) | USD 105.3 million |
| Japan Babesiosis Treatment Forecast CAGR (2025-2035) | 3.8% |
Demand for babesiosis treatment in Japan is increasing because clinicians are identifying more tickborne infections during warmer seasons and in regions with expanding tick populations. Travel-related exposure also contributes, as international visitors and returning residents may acquire the parasite in endemic areas abroad. Hospitals and diagnostic centers improve screening capabilities through blood smears, PCR testing and antibody assays, which increases confirmed case numbers and guides more targeted treatment. Patients with compromised immunity, including older adults and individuals receiving immunosuppressive therapy, often require early medical intervention, strengthening treatment demand in tertiary care settings.
Awareness efforts by local healthcare providers encourage prompt medical evaluation after tick bites, leading to earlier diagnosis and reduced complication risk. The blood transfusion sector also monitors for transfusion-related pathogen transmission, which supports preventive measures and treatment readiness.
Constraints include limited familiarity with the disease among some primary care practitioners, variable symptom presentation that may delay diagnosis and the need for combination therapy in severe cases. Low overall prevalence slows widespread availability of specialized medications, and treatment plans may require infectious-disease consultation that is not evenly accessible in rural locations.
Demand for babesiosis treatment in Japan is influenced by increased diagnostic awareness, improved reporting of tick-borne infections, and better preventive monitoring in high-risk regions. Treatment decisions prioritize clinical severity, patient age, and co-existing conditions, particularly among elderly populations. Hospitals lead prescriptions for severe infections requiring rapid therapeutic response, while home-based recovery is growing through oral regimens. Market uptake aligns with antimicrobial stewardship, reimbursement considerations, and availability of approved therapeutic protocols.
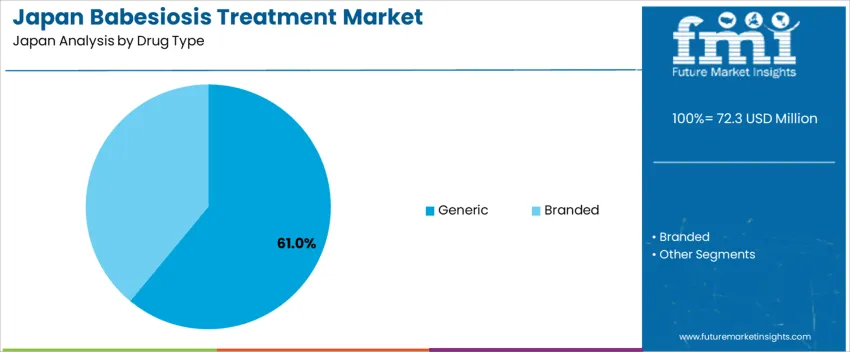
Generic medications account for 61.0%, driven by affordability, wide availability, and physician confidence in standard regimens such as atovaquone-azithromycin combinations used for mild to moderate cases. Japan’s healthcare priorities emphasize cost-effective antimicrobial therapy where clinical equivalence of generics supports broader patient access. Branded drugs represent 39.0%, primarily applied in complicated or resistant cases, and in treatment settings where branded formulations offer better dosing precision or tolerability. Hospital formularies and national insurance coverage influence drug selection, creating higher penetration for generics in outpatient care.
Key Points:
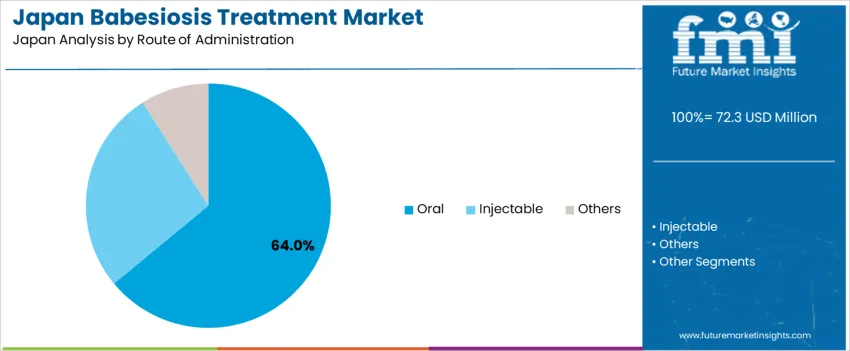
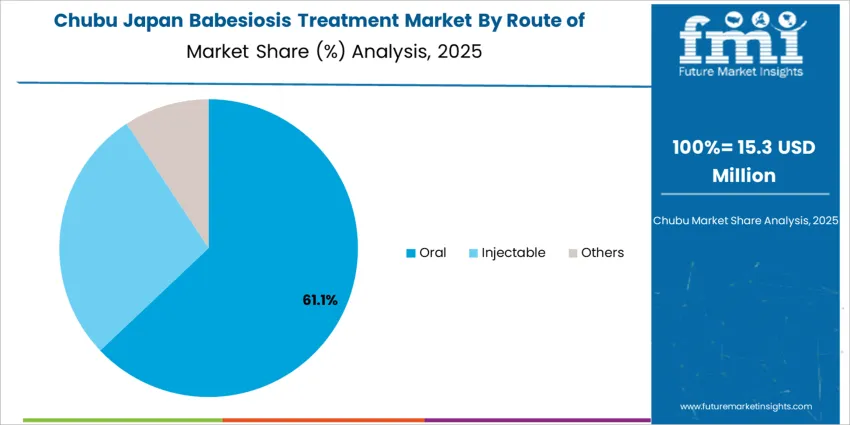
Oral treatments represent 64.0%, supporting outpatient and home-care protocols where babesiosis manifests in mild or early-detected cases. Oral regimens enable simplified dosing and sustained compliance across Japan’s extensive senior demographic. Injectable therapies account for 27.0%, required for hospitalized patients experiencing severe symptoms or co-infections such as Lyme disease. “Other” routes represent 9.0%, limited to investigational or supportive therapies. Administration trends reflect clinical severity classification and resource allocation, ensuring hospitalization only when necessary.
Key Points:
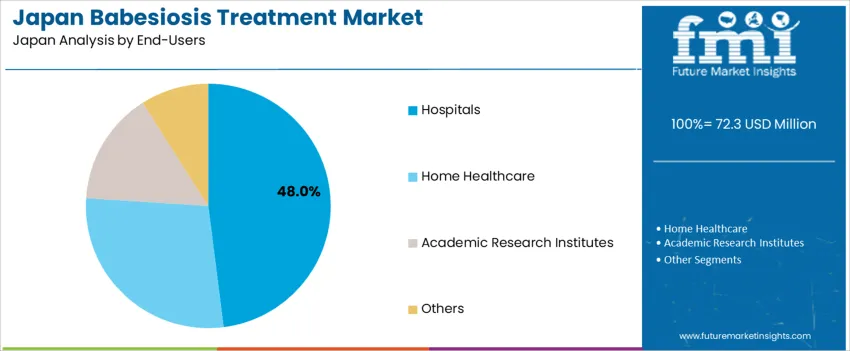
Hospitals hold 48.0%, due to centralized diagnosis, acute infection control, and inpatient treatment for severe or immunocompromised individuals. Home healthcare accounts for 28.0%, supported by oral therapy usage and shorter recovery pathways. Academic research institutes represent 15.0%, reflecting Japan’s focus on infectious disease surveillance and tick-related pathogen studies. “Others” comprise 9.0%, including private clinics and travel-related specialty centers. End-user distribution aligns with Japan’s healthcare structure emphasizing rapid clinical assessment and prevention of complications in vulnerable patients.
Key Points:
Increased surveillance of tick-borne diseases, rising exposure through outdoor recreation and expanded veterinary detection that improves human awareness are driving demand.
In Japan, demand for babesiosis treatment is shaped by tick exposure in rural and forested areas where hiking, farming and pet ownership remain common. Public health programs in prefectures such as Hokkaido and Nagano monitor tick-borne infections and encourage earlier diagnostic testing when febrile illness follows outdoor activity. Veterinarians diagnose babesiosis in dogs more frequently as owners travel to endemic areas, which raises awareness about human infection risk and promotes caution. Hospitals handling seasonal tick-related illnesses rely on antiparasitic agents and supportive therapies for suspected cases. These vigilance measures sustain limited but necessary treatment readiness in infectious disease networks.
Low incidence in humans, delayed diagnosis because of nonspecific symptoms and limited physician familiarity restrain demand.
Human babesiosis remains rare in Japan, so most medical facilities do not maintain dedicated treatment pathways. Symptoms often resemble influenza or other vector-borne diseases, which can delay correct identification and reduce treatment initiation speed. Infectious disease specialists may focus more on conditions with higher domestic prevalence, leading to limited clinical familiarity outside reference hospitals. Public health budgets emphasize higher-priority illnesses, which keeps procurement of specialized medications modest. These epidemiological realities contribute to small and irregular demand patterns.
Shift toward improved diagnostic access, increased coordination between veterinary and human health systems and rising attention from aging-population risk groups define key trends.
Clinics are adopting broader pathogen screening panels that detect parasitic infections more quickly when patients present after tick exposure. Collaboration between veterinarians and regional health centers strengthens early notification when zoonotic cases increase among domestic animals. Older adults with weakened immunity are recognized as a population requiring faster intervention, leading to cautious stocking of essential antiparasitic treatments in specific hospitals. Travel medicine services for residents visiting endemic countries also support training on prompt recognition. These trends indicate low but steadily maintained preparedness for babesiosis treatment needs within Japan’s public health and clinical care systems.
Demand for babesiosis treatment in Japan relates to vector-borne disease surveillance, diagnostic availability, and treatment readiness in both hospital and veterinary settings. Regional growth reflects differences in zoonotic-disease management and outdoor exposure patterns. Forecasts indicate Kyushu & Okinawa leads at 4.8% CAGR, followed by Kanto (4.4%), Kansai (3.9%), Chubu (3.4%), Tohoku (3.0%), and the Rest of Japan (2.8%). Adoption patterns are shaped by early diagnostic recognition and clinical access in each area.
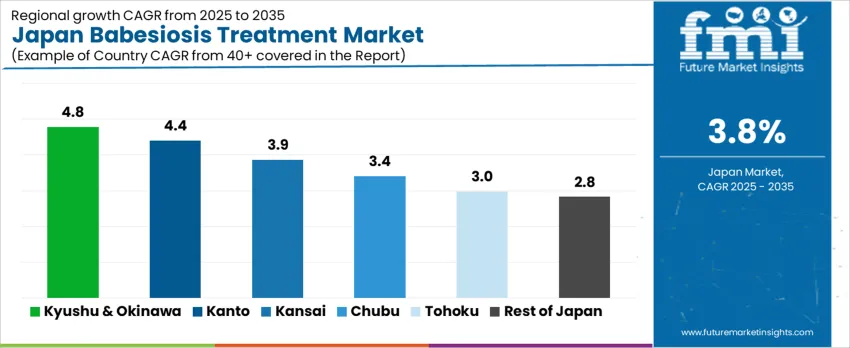
| Region | CAGR (2025-2035) |
|---|---|
| Kyushu & Okinawa | 4.8% |
| Kanto | 4.4% |
| Kansai | 3.9% |
| Chubu | 3.4% |
| Tohoku | 3.0% |
| Rest of Japan | 2.8% |
Kyushu & Okinawa posts a 4.8% compound annual growth rate, reflecting higher tick-borne disease monitoring due to warmer climates that support vector activity across extended seasons. Hospitals improve diagnostic workflows using PCR and serological methods to detect Babesia infections in early clinical stages. Public health networks conduct awareness programs addressing infection sources among outdoor workers, forest industry personnel, and pet owners. Veterinary facilities coordinate with human-health authorities because pet exposure increases household risk. Procurement focuses on reliable antiprotozoal medications that align with established treatment protocols. Physicians consider patient travel history between islands and inland forestry zones to shorten diagnostic delays. Local academic research supports monitoring programs tracking infection clusters in wildlife. Enhanced clinician familiarity with differential diagnosis ensures testing triggers when febrile illness does not resolve through first-line therapies. These efforts maintain rising treatment utilization as reporting accuracy improves.
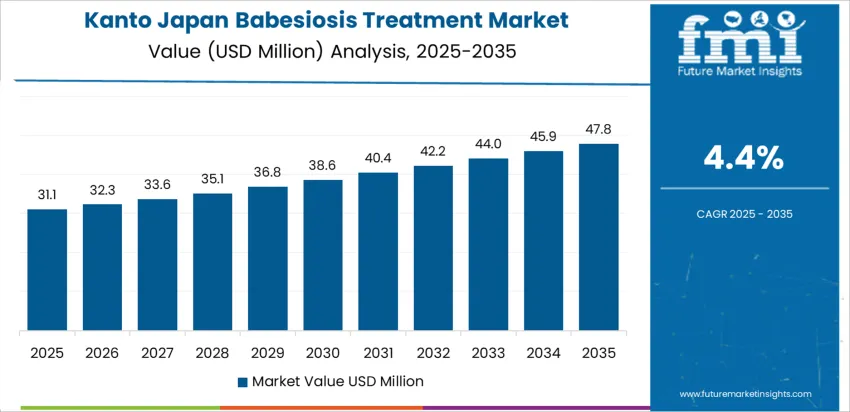
In Kanto, treatment demand is rising roughly 4.4% per year as clinicians respond to increased testing for tick-borne pathogens in peri-urban recreation zones and mountainous hiking regions near Tokyo and Kanagawa. Hospitals update diagnostic pathways that include babesiosis in evaluations for persistent fever and hemolytic symptoms. Laboratories provide higher-frequency confirmatory tests, improving case accuracy. Public-health offices monitor exposure associated with outdoor leisure activities and animal contact near residential areas. Pharmacies coordinate steady supply of antiprotozoals compatible with treatment guidelines. Healthcare providers emphasize patient education about bite prevention and post-exposure symptom monitoring. Integration of travel and activity history into triage enables earlier intervention. Suburban medical centers streamline referral networks with infectious-disease specialists to support accurate and timely therapy decisions, ensuring continuity of care.
Kansai shows 3.9% CAGR as Osaka and surrounding prefectures strengthen infectious-disease evaluation protocols. Hospitals integrate babesiosis into rule-out testing for hemolytic anemia cases linked to outdoor work in forest boundaries and rural townships. Veterinary interactions heighten exposure awareness for households with companion animals. Healthcare facilities adopt structured standard operating procedures covering symptom documentation and test ordering criteria. Regional blood-safety guidelines ensure screening measures remain aligned with national recommendations to reduce transmission risks in transfusion settings. Training modules highlight atypical presentations in older adults living in suburban retirement areas. Improved patient screening contributes to balanced medication-inventory planning. As clinicians refine recognition of vector-related febrile illnesses, therapeutic demand rises gradually but consistently across the Kansai region.
Chubu registers about 3.4% annual growth, driven by treatment readiness in Nagoya and broader mountainous jurisdictions where tick encounters are more frequent. Hospitals engage infectious-disease experts to support complex hemolytic cases requiring monitoring of organ functions during treatment. Health departments provide educational outreach for seasonal outdoor workers in construction and agriculture, where exposure risk averages remain measurable. Diagnostic services assess Babesia infection through rapid laboratory coordination when symptoms persist after initial assessment. Procurement priorities include medicine stability and compatibility with routine therapeutic protocols. As blood-donation oversight expands, transfusion-linked surveillance strengthens case detection. These mechanisms build a stable base for continued adoption without sharp spikes in resource requirements.
Tohoku’s demand rises at approximately 3.0% CAGR, reflecting dispersed populations with outdoor occupational exposure in forestry and farming. Regional hospitals refine triage processes for tick-associated illness, ensuring blood-smear evaluations and targeted PCR are considered when anemia and fever persist. Public-health messaging encourages early medical visits following suspected tick bites. Rural healthcare facilities maintain supply planning for necessary antiprotozoals to avoid treatment delays. Partnerships with veterinary services strengthen environmental surveillance since canine infections can indicate local vector presence. Cold-climate resilience in ticks during warmer months keeps monitoring requirements consistent year to year. Gradual expansion of diagnostic familiarity maintains controlled but positive treatment demand trends.
Across the remaining prefectures, demand is increasing near 2.8% annually, supported by emerging diagnostic alerts and clinical caution applied to unexplained hemolytic presentations. Facilities adopt incremental improvements in electronic medical records to document exposure history, enabling faster test ordering. Smaller clinics rely on referral networks to infectious-disease units for complex management when needed. Information campaigns reinforce household protection practices and prompt reporting of symptomatic cases. Procurement strategies focus on maintaining adequate treatment reserves without large inventory buildup, aligning with measured case frequency. These regions experience fewer confirmed cases but maintain preparedness to ensure timely therapeutic response when Babesia infections are identified.
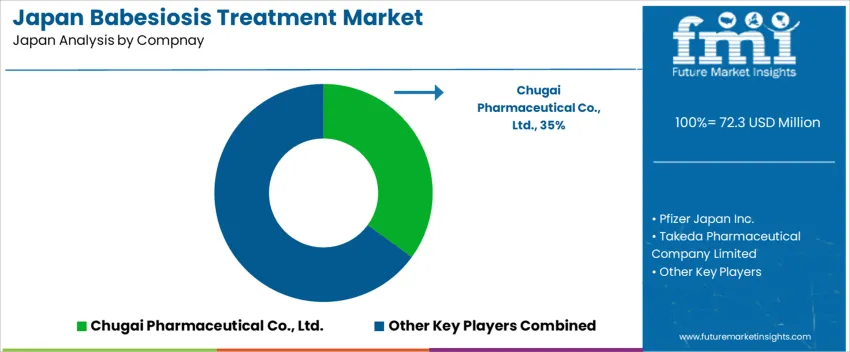
Human babesiosis incidence in Japan remains extremely low, with treatment supplied through broad-spectrum antiparasitic and antimicrobial products used for case-based response rather than structured procurement. Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. holds an estimated 35% share, supported by stable access to azithromycin products distributed through domestic hospital channels. Case management emphasizes assured supply continuity for acute parasitic infections requiring rapid intervention.
Pfizer Japan Inc. contributes through availability of antiparasitic agents considered in clinical response protocols, including atovaquone-based therapy used internationally. Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited supports demand through controlled antibiotic supply where inpatient management and differential parasitic diagnosis are required. Daiichi Sankyo Company, Limited remains active in infectious-disease product distribution within clinics and regional hospitals. Meiji Seika Pharma Co., Ltd. adds supplementary coverage for antimicrobial regimens suited to specialist infectious-disease care.
Competition in Japan focuses on reliable distribution, pharmaceutical-grade quality control, and alignment with hospital infectious-disease protocols. Demand remains limited due to low incidence, yet suppliers maintain readiness through portfolio-level availability of treatments consistent with clinical standards for tick-borne parasitic infections.
| Items | Values |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD million |
| Drug Type | Generic, Branded |
| Route of Administration | Oral, Injectable, Others |
| End-Users | Hospitals, Home Healthcare, Academic Research Institutes, Others |
| Regions Covered | Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, Kansai, Chubu, Tohoku, Rest of Japan |
| Key Companies Profiled | Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Pfizer Japan Inc., Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, Daiichi Sankyo Company, Limited, Meiji Seika Pharma Co., Ltd. |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by administration route, drug type, and healthcare provider segments; incidence concentration among tick-exposed regions; availability of azithromycin-atovaquone and clindamycin-quinine therapies; diagnostic support capacity in Japanese hospitals; integration with vector-borne disease surveillance programs and expansion of awareness in primary care settings. |
The demand for babesiosis treatment in Japan is estimated to be valued at USD 72.3 million in 2025.
The market size for the babesiosis treatment in Japan is projected to reach USD 105.3 million by 2035.
The demand for babesiosis treatment in Japan is expected to grow at a 3.8% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in babesiosis treatment in Japan are generic and branded.
In terms of route of administration, oral segment is expected to command 64.0% share in the babesiosis treatment in Japan in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Babesiosis Treatment Market Analysis - Trends, Demand & Growth 2025 to 2035
Japan Axillary Hyperhidrosis Treatment Market Insights – Size, Share & Trends 2025-2035
Demand for Babesiosis Treatment in USA Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Biliary Tract Cancers (BTCs) Treatment Market Growth – Demand, Trends & Forecast 2025-2035
Demand for Burns Treatment in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand for Water Treatment System in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand for Endometriosis Treatment in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand for Yeast Infection Treatment in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand for Cannabis Use Disorder Treatment in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand for Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Treatment in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Faith-based Tourism Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Sports Tourism Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Respiratory Inhaler Devices Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Halal Tourism Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Automated People Mover Industry Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Automotive Load Floor Industry Analysis Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Food Cling Film Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Polypropylene Packaging Films Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Treatment-Resistant Hypertension Management Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Treatment-Resistant Depression Treatment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA