The Japan canned legumes demand is valued at USD 180.7 million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 248.2 million by 2035, reflecting a CAGR of 3.2%. Consumption is shaped by increased use of plant-based protein sources in household cooking, steady uptake of ready-to-cook ingredients, and growing reliance on shelf-stable foods for convenience. The expansion of home-meal preparation, wider distribution through supermarkets and convenience stores, and the suitability of canned legumes for salads, curries, and ready-made meal kits support continued demand across consumer groups.
Chickpeas lead utilisation due to their versatility in Japanese and international dishes, stable texture under retort processing, and suitability for expanded applications in salads, hummus, and home-cooking formats. Their rising inclusion in health-oriented and protein-rich meal options reinforces segment preference and supports sustained procurement by retail and food-service channels.
Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, and Kansai record the highest demand because of their concentration of supermarkets, urban households with high convenience-food usage, and diversified distribution networks. These regions also support consistent rotation of canned bean varieties in both domestic and commercial kitchens. Key suppliers include Imuraya Group Co., Ltd., Hagoromo Foods Corporation, Maruha Nichiro Corporation, Hotei Foods Corporation, and Kokubu Group Corp. (K&K brand). These companies distribute chickpeas, kidney beans, mixed legumes, and other canned variants across retail, wholesale, and food-service supply chains.
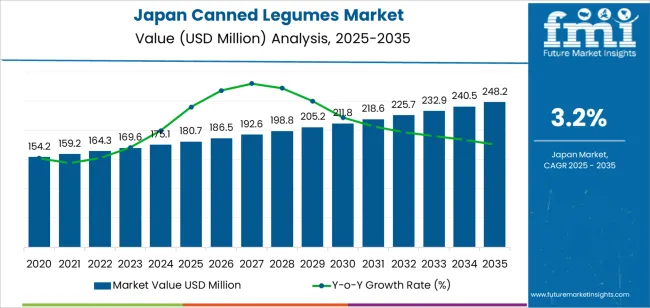
A 10-year comparison for Japan’s canned-legumes segment shows steady but modest expansion shaped by stable dietary habits and gradual adoption of convenient plant-protein options. In the early years, growth is driven by consistent household use of legumes in traditional dishes and increased interest in ready-to-use ingredients for time-saving meal preparation. Early growth remains moderate because canned legumes serve as a complement to fresh and dried varieties rather than a substitute, keeping annual increases controlled.
Across the later years, the segment continues to expand at a measured pace as convenience cooking gains broader acceptance among working households and smaller family units. Growth also benefits from incremental use in salads, ready meals, and home-meal-replacement offerings, supported by retailers promoting shelf-stable protein sources. However, the pace remains contained because culinary preferences favour fresh preparation in many households, limiting rapid adoption.
Comparing both periods, early growth reflects traditional consumption patterns and steady convenience uptake, while late growth gains modest support from meal-solution trends and diversified product formats. The 10-year pattern shows consistent expansion, characterized by slow acceleration and limited volatility within Japan’s packaged-legume landscape.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Japan Canned Legumes Sales Value (2025) | USD 180.7 million |
| Japan Canned Legumes Forecast Value (2035) | USD 248.2 million |
| Japan Canned Legumes Forecast CAGR (2025-2035) | 3.2% |
Demand for canned legumes in Japan is increasing because consumers seek convenient, nutritious and shelf-stable foods that fit busy routines and small household sizes. Canned beans provide protein, fibre and minerals without lengthy soaking or cooking, which appeals to working adults, students and elderly households. Growth in home cooking, interest in simple recipes and adoption of Western-style dishes such as chili, salads and stews support regular use of canned legumes. Retailers promote canned chickpeas, kidney beans, lentils and mixed beans as versatile meal components, and this encourages repeat purchases.
Emergency preparedness habits also contribute to steady demand because canned foods are commonly stored for disaster readiness. Expanding availability through supermarkets, online grocery platforms and convenience stores increases accessibility across regions. Constraints include competition from fresh and dried legumes, which some consumers prefer for taste or cost reasons. Concerns about sodium content in certain canned varieties may also limit adoption among health-conscious buyers. Import dependency for specific bean types can lead to pricing variability, which may reduce purchase frequency in cost-sensitive households.
Demand for canned legumes in Japan reflects growing interest in convenient plant-based foods, extended shelf life products, and ready-to-use ingredients suited to Japanese cooking habits. Legume selection varies by texture, flavor adaptability, and suitability for salads, simmered dishes, and blended preparations. Category preferences show how consumers differentiate between conventional and organic options based on price, perceived quality, and dietary preferences. Distribution patterns highlight how Japanese households purchase canned legumes across supermarkets, online platforms, and convenience stores.
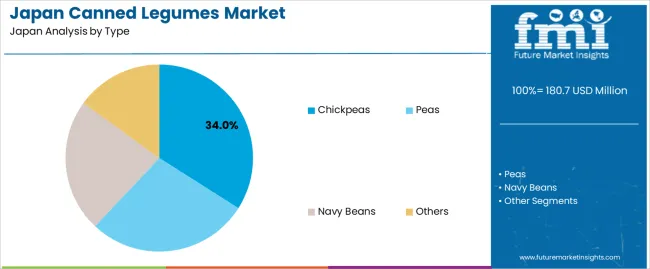
Chickpeas hold 34.0% of national demand and represent the leading canned legume type in Japan. Their neutral flavor and firm texture support use in stews, salads, curries, and blended preparations. Peas account for 28.0%, widely used in soups, mixed dishes, and ready meals that require quick preparation. Navy beans represent 23.0%, serving consumers seeking mild flavors suited to slow-cooked or seasoned dishes. Other legumes hold 15.0%, covering red beans, lentils, and mixed-legume blends used in niche or imported canned products. Legume-type distribution reflects how Japanese consumers incorporate plant-based proteins into varied meals while prioritizing convenience, neutral taste profiles, and cooking versatility.
Key points:
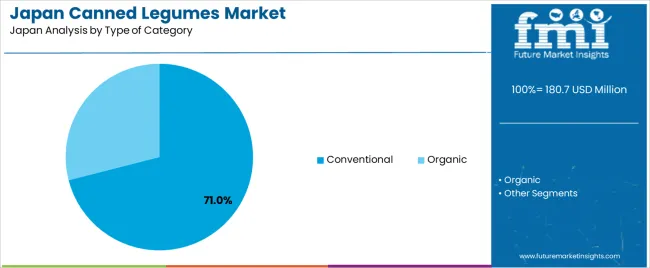
Conventional canned legumes hold 71.0% of national demand and represent the primary category in Japan. Their affordability, wide availability, and established presence in major retail chains support routine household purchases. Organic canned legumes account for 29.0%, appealing to consumers emphasizing pesticide-free ingredients, dietary sensitivity, or premium quality. Category-type distribution reflects how price sensitivity and product familiarity shape consumer decisions, while a smaller but stable group continues to select organic options for perceived health alignment. Retailers maintain broad assortments across both categories to meet diverse consumer expectations, ranging from budget-oriented purchases to premium or specialty-food preferences.
Key points:
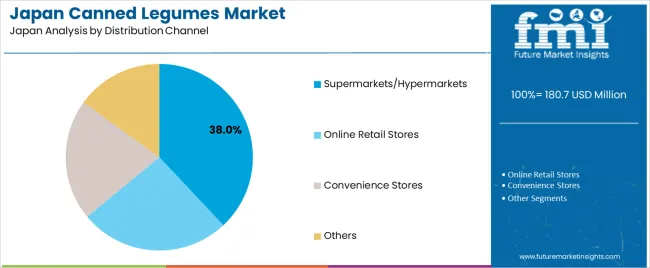
Supermarkets and hypermarkets hold 38.0% of national demand and represent the leading distribution channel for canned legumes in Japan. These outlets offer consistent stock, varied brands, and competitive pricing suited to routine household shopping. Online retail stores account for 26.0%, driven by convenience, bulk purchases, and access to imported varieties. Convenience stores represent 21.0%, supporting impulse purchases and small-portion shopping common in urban areas. Other channels hold 15.0%, including specialty stores and cooperative industries offering premium or region-specific legumes. Distribution patterns reflect Japan’s mixed retail landscape combining large chains, expanding e-commerce habits, and frequent small-format shopping behavior.
Key points:
Growth of health-focused eating habits, increased use of legumes in home cooking and rising demand for ready-to-use ingredients in small households are driving demand.
In Japan, canned legumes gain traction as consumers look for convenient plant-based protein sources that support balanced diets promoted through national health campaigns. Households in urban regions such as Tokyo and Osaka use canned chickpeas, kidney beans and lentils for salads, curry, and nimono dishes that require minimal preparation time. Single-person households and elderly residents value shelf-stable items that fit limited cooking capacity and small kitchen storage. Supermarkets and drugstores have expanded canned-legume assortments in response to growing interest in fiber-rich foods, supporting consistent demand throughout the year.
Preference for fresh or boil-at-home beans, limited category awareness and competition from ready-to-eat convenience-store meals restrain adoption.
Many Japanese consumers still prefer dried beans cooked at home, especially azuki and soy-based varieties used in traditional dishes, reducing frequent reliance on canned formats. Awareness of Western legumes such as chickpeas or cannellini beans remains modest outside major metropolitan regions, limiting penetration in regional industries. Convenience stores offer a wide range of ready-to-eat salads and side dishes that reduce the need for canned ingredients, especially among younger consumers. These cultural and behavioural factors moderate the pace of canned-legume category expansion.
Shift toward low-salt and additive-free variants, increased use in meal kits and rising demand from health-food retailers define key trends.
Manufacturers serving the Japanese industry are expanding low-salt, additive-free canned legumes to appeal to health-conscious consumers who prioritize clean-label products. E-commerce meal-kit services incorporate canned legumes for recipes requiring consistent texture and quick preparation, supporting adoption among busy households. Health-food stores and natural-ingredient retailers in urban centers are introducing imported and domestic varieties to meet growing interest in plant-based diets. These trends demonstrate gradual diversification of canned-legume usage within Japan’s retail, home-cooking and meal-kit channels.
Demand for canned legumes in Japan is increasing as households, retailers, food processors, and institutions adopt shelf-stable plant-protein ingredients for daily cooking, convenience meals, and preparedness storage. Canned legumes such as chickpeas, red beans, soybeans, and mixed pulses support fast meal preparation, bento use, and long-term storage. Regional demand reflects differences in household consumption habits, convenience-store penetration, food-service usage, and emergency-readiness practices. Kyushu & Okinawa leads at 4.0%, followed by Kanto (3.7%), Kansai (3.3%), Chubu (2.9%), Tohoku (2.5%), and Rest of Japan (2.4%).
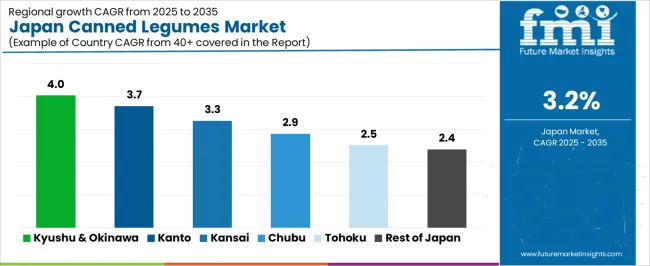
| Region | CAGR (2025-2035) |
|---|---|
| Kyushu & Okinawa | 4.0% |
| Kanto | 3.7% |
| Kansai | 3.3% |
| Chubu | 2.9% |
| Tohoku | 2.5% |
| Rest of Japan | 2.4% |
Kyushu & Okinawa grows at 4.0% CAGR, supported by strong household reliance on convenient meal components, tourism-driven retail activity, and established use of shelf-stable foods in local diets. Households in Fukuoka, Kumamoto, and Kagoshima incorporate canned legumes into soups, stews, and rice dishes, reinforcing steady demand across supermarkets and local stores. Okinawa shows additional consumption due to tourism, where travel-oriented retailers and small shops stock canned legumes for quick meal use in hotels, guesthouses, and service apartments. Regional preparedness culture encourages households to maintain canned food supplies, increasing underlying rotation. Retail networks across Kyushu carry a wide range of canned pulses, including chickpeas and mixed beans used in both Japanese and Western-style home cooking. Institutions such as community centers and care facilities store canned legumes for reliable protein supply.
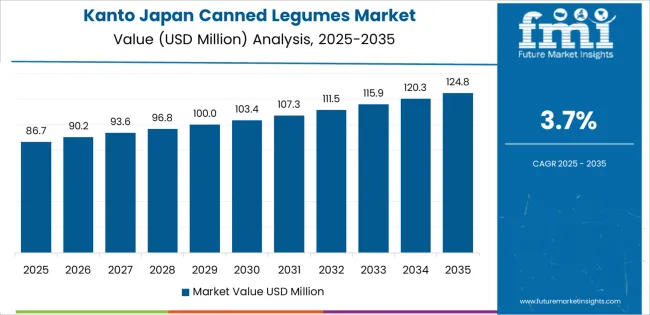
Kanto grows at 3.7% CAGR, driven by dense urban consumption, strong convenience-store presence, and broad adoption of quick-cooking foods in Tokyo, Kanagawa, Chiba, and Saitama. Households purchase canned legumes for salads, curry dishes, and fast home-meal preparation, supporting consistent retail turnover. Office workers and students use canned legumes as ready additions to lunchboxes and microwavable meals. Preparedness programs in Tokyo reinforce household stocking of long-life foods, including canned pulses. Convenience stores maintain high visibility and frequent restocking across urban districts, while supermarkets offer expanded assortments such as low-salt and mixed-bean products. Food-service operators, including small cafés, use canned legumes to streamline menu preparation.
Kansai grows at 3.3% CAGR, supported by supermarket accessibility, household convenience needs, and student-driven consumption across Osaka, Kyoto, and Kobe. Canned legumes are used in curry dishes, salad bowls, and home-cooked recipes requiring minimal preparation. Retailers maintain broad assortments, including chickpeas, kidney beans, and mixed-bean blends suited to diverse cooking styles. Student populations in Kyoto and Osaka incorporate canned legumes into affordable meal planning, adding to baseline demand. Households maintain modest canned-food reserves for emergencies, reinforcing predictable purchasing patterns. Retail networks ensure circulation across both major cities and nearby suburban towns.
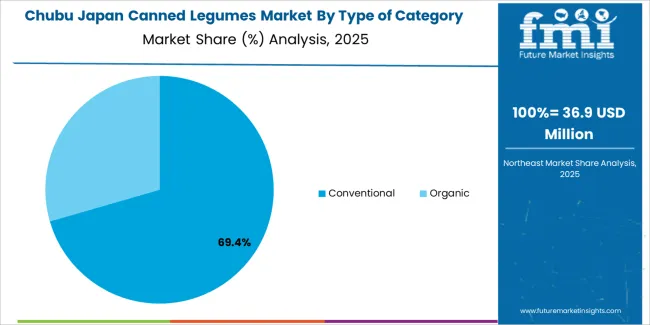
Chubu grows at 2.9% CAGR, shaped by mixed urban-rural consumption patterns, strong supermarket networks, and consistent household interest in shelf-stable foods across Nagoya, Shizuoka, and adjacent prefectures. Households use canned legumes in stews, rice bowls, and simple meal kits, supporting stable sales across supermarkets and drugstores. Regional logistics hubs in Aichi and Shizuoka facilitate efficient stocking, ensuring product availability across both metropolitan and smaller communities. Community facilities, dormitories, and care institutions include canned legumes in their inventories due to long shelf life and flexible menu incorporation. Retailers maintain predictable inventory turnover aligned with routine household consumption.
Tohoku grows at 2.5% CAGR, driven by strong disaster-preparedness culture, seasonal consumption trends, and dependable supermarket distribution across Sendai and surrounding prefectures. Households routinely stock canned legumes for emergency use and for practical winter cooking. Long cold seasons encourage adoption of easy-to-store foods that support warm dishes and minimal-prep meals. Retailers maintain essential assortments with steady turnover, even in smaller towns. Community centers and municipal preparedness programs stock canned legumes as part of long-term emergency reserves. Rural households, often located far from large stores, use canned legumes as dependable pantry items with predictable usage cycles.
Rest of Japan grows at 2.4% CAGR, influenced by smaller population centers, moderate retail turnover, and steady household use of shelf-stable foods. Local supermarkets, cooperatives, and community stores supply essential canned-legume varieties used in home recipes and long-life storage. Households maintain small emergency reserves and purchase canned legumes for convenience cooking. Distribution networks restock stores at regular intervals despite lower population density, ensuring adequate availability across rural and coastal regions. Institutions such as care facilities and small community establishments include canned legumes in menus for ease of storage and predictable meal preparation.
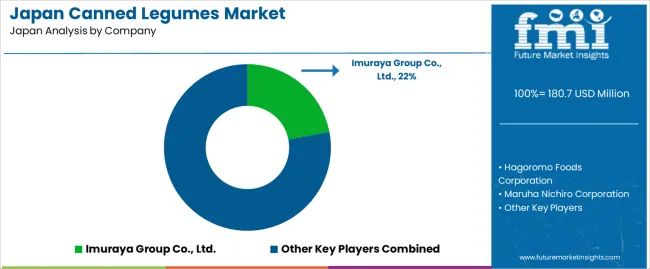
Demand for canned legumes in Japan is shaped by domestic food processors that supply both traditional sweet-bean products and Western-style ready-to-use beans. Imuraya Group Co., Ltd. holds an estimated 22.0% share, supported by controlled preparation of azuki and sweetened beans widely used in confectionery, home cooking, and convenience-store desserts. Its products offer predictable texture, stable sweetness control, and consistent quality, reinforcing strong national demand.
Hagoromo Foods Corporation maintains significant presence with canned chickpeas, kidney beans, and mixed legumes positioned for salads, soups, and pasta dishes. Its offerings provide reliable firmness, uniform sizing, and steady distribution through supermarkets. Maruha Nichiro Corporation contributes additional volume with canned legumes integrated into retort meals and ready-to-eat dishes, offering stable processing and dependable shelf life.
Hotei Foods Corporation plays a key role in regional and convenience-focused canned-bean products, emphasizing flavour consistency and ease of use. Kokubu Group Corp. (K&K) supports the import channel with canned chickpeas, lentils, and kidney beans sourced from overseas suppliers, fulfilling niche demand for Western legumes. Competition in Japan centers on texture reliability, sweetness control, brine stability, packaging durability, and nationwide retail coverage. Demand remains steady as consumers incorporate traditional azuki beans and Western legumes into home cooking, meal preparation, and convenience-oriented food routines.
| Items | Values |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD million |
| Type | Chickpeas, Peas, Navy Beans, Others |
| Type of Category | Conventional, Organic |
| Distribution Channel | Supermarkets/Hypermarkets, Online Retail Stores, Convenience Stores, Others |
| Regions Covered | Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, Kansai, Chubu, Tohoku, Rest of Japan |
| Key Companies Profiled | Imuraya Group Co., Ltd., Hagoromo Foods Corporation, Maruha Nichiro Corporation, Hotei Foods Corporation, Kokubu Group Corp. (K&K brand) |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by legume type, product category, and distribution channel; regional consumption trends across Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, Kansai, Chubu, Tohoku, and Rest of Japan; rising demand for plant-based protein ingredients, ready-to-use legumes, and imported chickpeas; growth in organic canned legumes driven by health-conscious consumers; expansion of private-label offerings in major retail chains; competitive landscape of Japanese canned food manufacturers and distributors. |
The demand for canned legumes in Japan is estimated to be valued at USD 180.7 million in 2025.
The market size for the canned legumes in Japan is projected to reach USD 248.2 million by 2035.
The demand for canned legumes in Japan is expected to grow at a 3.2% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in canned legumes in Japan are chickpeas, peas, navy beans and others.
In terms of type of category, conventional segment is expected to command 71.0% share in the canned legumes in Japan in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Canned Legumes Market Insights – Protein-Packed Convenience Foods 2025 to 2035
Demand for Canned Meat in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand for Canned Pasta in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Faith-based Tourism Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Sports Tourism Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Canned Wet Cat Food Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Respiratory Inhaler Devices Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Halal Tourism Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Canned Food Packaging Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Canned Wine Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Canned Pet Food Market Analysis - Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Automated People Mover Industry Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Automotive Load Floor Industry Analysis Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Canned Food Packaging Industry Analysis in the United Kingdom Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Food Cling Film Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Polypropylene Packaging Films Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Canned Fruits Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Overview of Key Trends Shaping Canned Tuna Business Landscape.
Canned Soup Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Canned Mackerel Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA