The demand for carrier infrastructure in telecom applications in Japan is projected to grow from USD 14.3 billion in 2025 to USD 31.3 billion by 2035, reflecting a CAGR of 8.2%. This growth is primarily driven by the need for advanced telecom networks to accommodate rising data traffic, 5G deployments, and the expansion of IoT services. The increasing demand for high-speed connectivity, fueled by the rollout of next-generation wireless technologies, will be a major factor propelling this industry. As telecom networks evolve to handle higher volumes of data, infrastructure upgrades that enhance capacity, speed, and reliability will become critical.
The demand for carrier infrastructure will be further supported by the rising adoption of 5G technology, which requires substantial investment in base stations, fiber optics, and related technologies. These investments are expected to expand the telecom network's reach and enable faster data transmission, supporting various sectors such as manufacturing, healthcare, and transportation that rely on high-speed connectivity for their digital transformation.

Telecom providers will need to modernize their infrastructure to handle the increased number of connected devices. This will drive ongoing investments in scalable, future-proof infrastructure solutions. The industry is also expected to benefit from growing demand for enhanced network reliability, security, and energy-efficient infrastructure, as telecom operators strive to meet evolving consumer and business needs. As a result, carrier infrastructure investments will play a central role in supporting Japan's digital transformation throughout the forecast period.
From 2025 to 2030, the industry for carrier infrastructure in telecom applications in Japan will grow from USD 14.3 billion to USD 22.9 billion, adding USD 8.6 billion in value. This period will see robust growth, driven by accelerated investments in 5G networks, fiber optics, and the expansion of data centers. Telecom providers will focus on upgrading existing infrastructure to meet the increasing demand for higher data capacity, speed, and reliability. This phase will also witness a surge in telecom service adoption as consumer and business demand for seamless connectivity rises.
From 2030 to 2035, the industry will grow from USD 22.9 billion to USD 31.3 billion, contributing USD 8.4 billion in value. Growth will continue, though at a more moderate pace, as the industry matures. The demand for infrastructure will still be strong, particularly for emerging technologies like 5G and 6G. Telecom operators will focus on optimizing existing infrastructure and ensuring energy efficiency to reduce operational costs. As IoT adoption expands, additional infrastructure investments will be necessary to support the growing number of connected devices. Despite a slower growth rate, the demand for more efficient, scalable, and sustainable telecom infrastructure will remain a key driver through the forecast period.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Demand for Carrier Infrastructure in Telecom Applications in Japan Value (2025) | USD 14.3 billion |
| Demand for Carrier Infrastructure in Telecom Applications in Japan Forecast Value (2035) | USD 31.3 billion |
| Demand for Carrier Infrastructure in Telecom Applications in Japan Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 8.2% |
Investment in telecom infrastructure is increasing in Japan as major carriers expand their 5G and prepare for 6G networks. With operators building more base stations and upgrading backend systems, the requirement for network equipment and infrastructure is rising. Japan’s mobile carriers are planning to deploy extensive base stations to support enhanced connectivity.
Use cases such as the Internet of Things (IoT), machine-to-machine (M2M) communications, and connected vehicles are driving the need for robust infrastructure capable of handling high device density and ultra-low latency. As network traffic grows and carriers face increasing demands from both enterprises and consumers, infrastructure spending continues to rise.
Technological shifts such as Open RAN, virtualization of radio access networks, and higher-capacity fibre backhaul systems are altering the infrastructure landscape. Japan’s networks are adopting flexible, software-defined architecture to reduce deployment costs and enable rapid scaling. As carriers and infrastructure vendors collaborate on new models to support heterogeneous network types and dynamic traffic loads, investment in carrier infrastructure is set to continue growing through 2035.
Demand for carrier infrastructure in telecom applications in Japan is segmented by technology, end user, and component. By technology, demand is divided into 2G, 5G, 3G, and 4G/LTE, with 2G holding the largest share. In terms of end user, the industry is categorized into telecom operators and government & public sector, with telecom operators leading the demand. The industry is also segmented by component, including hardware and services, with hardware being the dominant component. Regionally, demand is divided into Kanto, Kinki, Chubu, Kyushu & Okinawa, Tohoku, and the Rest of Japan.
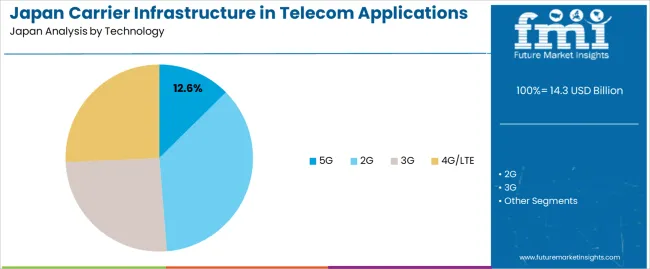
2G accounts for 36% of the demand for carrier infrastructure in telecom applications in Japan. Despite the growth of newer technologies like 4G and 5G, 2G continues to have a significant presence in Japan due to its widespread use in legacy systems, especially for basic voice and messaging services. Many telecom operators continue to support 2G networks, particularly in rural and less densely populated areas where newer technologies may not yet be as widely adopted.
The demand for 2G infrastructure is driven by its cost-effectiveness and reliability, which make it a practical choice for certain telecom applications, including IoT (Internet of Things) devices and low-data applications. 2G networks are still a critical part of Japan's telecom infrastructure, particularly in regions that have not fully transitioned to newer technologies. As the transition to 5G continues, 2G will remain essential for supporting existing services and devices that rely on this older network.
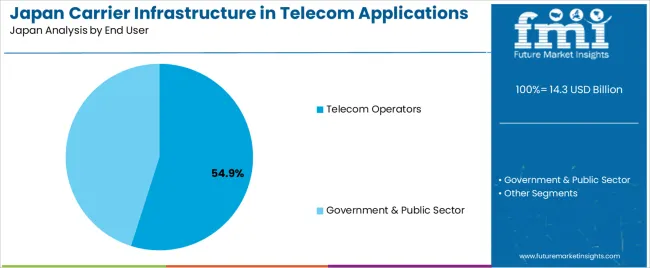
Telecom operators account for 54.9% of the demand for carrier infrastructure in telecom applications in Japan. These operators are the primary customers for carrier infrastructure, as they are responsible for building, maintaining, and expanding telecom networks to provide services to consumers and businesses. Telecom operators are at the forefront of adopting new technologies such as 4G, 5G, and even IoT systems, which require significant investments in network infrastructure.
The demand from telecom operators is driven by their need for robust, scalable, and efficient networks to meet the growing demand for mobile data, internet services, and emerging technologies. As operators in Japan continue to invest in next-generation networks, particularly 5G, they will require advanced carrier infrastructure to support higher data speeds, lower latency, and improved connectivity. Telecom operators are also focused on ensuring that their infrastructure can accommodate the increasing use of mobile devices and data-intensive applications, further driving the need for ongoing investment in carrier infrastructure.
Operators are upgrading networks to support 5G and preparing for 6G, which require new base stations, fiber‑optic backhaul, and edge‑data‑centre infrastructure. The rising traffic from video streaming, IoT devices, and enterprise digitalisation is pushing carriers to expand capacity and modernise core networks. At the same time, regulatory and national security concerns are motivating carriers to adopt open, disaggregated architectures and domestic supply chains. Restraints include the high capital investment required for infrastructure upgrades, a relatively saturated consumer industry meaning slower growth in mobile subscriptions, and supply‑chain and component‑cost pressures (e.g., for semiconductor and optics) that can delay deployments.
In Japan, demand is growing because operators such as KDDI Corporation, NTT DoCoMo and SoftBank Corp. are investing in next‑generation network capacity, driven by higher data use, enterprise IoT, smart‑manufacturing and smart‑city initiatives. The country’s push for digital transformation and national infrastructure resilience means carriers must upgrade their infrastructure fiber, 5G/6G radio access, core routers, network cloud platforms to stay competitive and secure. Carriers are also moving toward open‑network architectures to reduce vendor lock‑in, lower costs and accelerate service rollout. As a result, equipment and software that support fibre, wireless, core network upgrades and network‑automation are seeing increasing demand.
Technological innovations are key to the growth of carrier infrastructure demand in Japan. Innovations include open‑RAN and disaggregated network architectures (for example carriers partnering with vendors for open, software‑based core and router deployments) which lower cost and improve flexibility. Fibre‑optic and packet‑transport technology improvements support higher capacity and lower latency for 5G/edge networks. Network operators are also leveraging cloud‑native network functions, AI for network optimisation, and edge‑computing for latency‑sensitive applications. These innovations enable carriers to handle growing data volumes and support new applications (e.g., enterprise, AR/VR, autonomous systems), driving infrastructure upgrades.
The capital‑expenditure burden is significant upgrading radio, fibre, core network and edge infrastructure demands heavy investments, and carriers must balance cost and return. Second, the consumer industry is mature and mobile‑subscriber growth is limited, putting pressure on carrier ROI for new infrastructure. Global supply‑chain risks such as component shortages, rising prices for semiconductors and optics and geopolitical pressures affect cost and lead times. Complexity of upgrading while maintaining existing networks (ensuring backwards compatibility, orchestrating multi‑vendor environments) can slow deployment. Regulatory and security requirements (especially for infrastructure that may impact national resilience) add further layers of compliance and cost.

| Region | CAGR (%) |
|---|---|
| Kyushu & Okinawa | 10.2% |
| Kanto | 9.4% |
| Kinki | 8.3% |
| Chubu | 7.3% |
| Tohoku | 6.4% |
| Rest of Japan | 6.0% |
The demand for carrier infrastructure in telecom applications in Japan is growing across all regions, with Kyushu & Okinawa leading at a 10.2% CAGR. This growth is driven by the increasing need for high-speed internet, mobile connectivity, and 5G rollout in various regions. Kanto follows closely with a 9.4% CAGR, supported by its dense population and technological advancements. Kinki shows an 8.3% CAGR, influenced by urban development and telecom investments. Chubu experiences a 7.3% CAGR, driven by growing demand for telecom infrastructure in industrial sectors. Tohoku and the Rest of Japan show moderate growth at 6.4% and 6.0%, respectively, as regional telecom providers continue to expand network coverage.
Kyushu & Okinawa is experiencing the highest demand for carrier infrastructure in telecom applications in Japan, with a 10.2% CAGR. The region is undergoing significant investments in telecom infrastructure, particularly as the need for high-speed internet and 5G connectivity rises. Cities like Fukuoka are becoming key hubs for tech and telecom companies looking to expand their networks. The region’s geographic location and growing tourism industry make it a priority for robust telecom infrastructure to support both residents and visitors.
The expansion of 5G networks, along with the need for more reliable mobile and broadband services, is driving the demand for carrier infrastructure in Kyushu & Okinawa. The local government’s push to modernize telecommunications and the growing demand for IoT and connected services are also contributing to the region’s rapid adoption of telecom technologies. As these trends continue, Kyushu & Okinawa is expected to maintain strong growth in the telecom infrastructure sector.
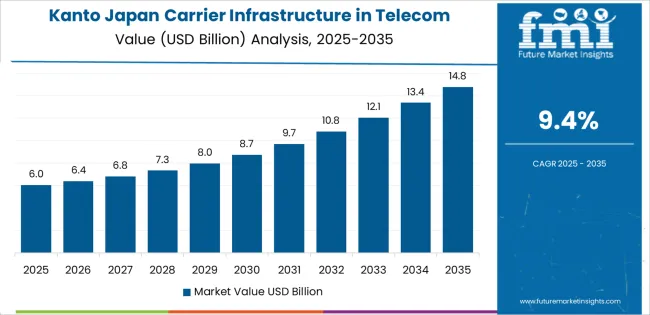
Kanto is seeing robust growth in demand for carrier infrastructure in telecom applications, with a 9.4% CAGR. The region, which includes Tokyo and its surrounding areas, is a major center for technological innovation and urban development. The high population density and rapid adoption of digital technologies are key drivers of this demand. With the increasing use of mobile devices, smart technologies, and cloud-based services, telecom infrastructure is critical to supporting the region’s digital transformation.
The Kanto region is at the forefront of Japan’s 5G rollout, and the demand for carrier infrastructure continues to rise as mobile and broadband providers work to expand their networks to meet the growing need for faster, more reliable services. The region’s focus on smart cities, IoT applications, and other advanced technologies is further propelling demand for telecom infrastructure. As the digital landscape in Kanto continues to evolve, the need for modern, high-performance telecom networks will drive continued growth in the sector.
Kinki is experiencing steady demand for carrier infrastructure in telecom applications, with an 8.3% CAGR. The region, which includes major cities like Osaka, Kyoto, and Kobe, is a key economic hub for both business and technology in Japan. As the region continues to urbanize and develop its tech ecosystem, the demand for high-quality telecom infrastructure, including fiber-optic networks and 5G connectivity, is rising.
Kinki’s strong industrial and commercial sectors, particularly in retail, manufacturing, and services, are increasingly reliant on robust telecom infrastructure to support digital operations and smart technologies. The growing adoption of IoT, mobile applications, and cloud services further drives the need for advanced telecom networks. As the region continues to focus on technological advancements and improving its telecommunications systems, demand for carrier infrastructure in Kinki is expected to remain steady, ensuring continued growth in the coming years.
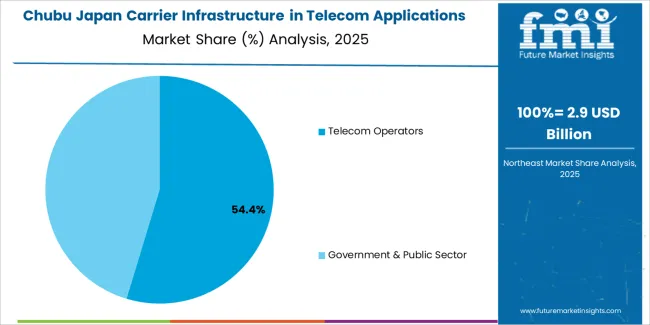
Chubu is seeing moderate growth in demand for carrier infrastructure in telecom applications, with a 7.3% CAGR. The region, known for its industrial base and cities like Nagoya, is increasingly adopting advanced telecom infrastructure to support its diverse sectors, including automotive, manufacturing, and technology. As industries in Chubu continue to digitalize and expand, the need for reliable mobile connectivity and high-speed internet is growing.
The rollout of 5G networks in Chubu is another factor contributing to the demand for telecom infrastructure. As more businesses and consumers rely on faster, more efficient digital services, the region’s telecom providers are investing in modern networks to meet these needs. The expansion of smart manufacturing, IoT applications, and digital services in the region ensures that the demand for carrier infrastructure will continue to grow in the coming years.
Tohoku is experiencing moderate demand growth for carrier infrastructure in telecom applications, with a 6.4% CAGR. The region is seeing increasing investments in telecommunications as the need for reliable mobile and broadband services rises. While Tohoku’s population density is lower than in other regions, there is growing demand for connectivity, particularly as the region works to modernize its infrastructure.
Tohoku’s rural areas, which are often underserved by high-speed internet and mobile services, are becoming a key focus for telecom providers. The expansion of 5G networks and the growing adoption of connected technologies like IoT are contributing to the region’s demand for upgraded telecom infrastructure. As more businesses and consumers in Tohoku seek access to faster, more efficient services, the region will continue to experience steady growth in telecom infrastructure.
The Rest of Japan is seeing moderate growth in demand for carrier infrastructure in telecom applications, with a 6.0% CAGR. This includes rural and smaller urban areas where the demand for modern telecom services, including high-speed internet and 5G connectivity, is rising. Telecom providers are increasingly focusing on expanding their networks to underserved areas to meet growing consumer expectations for better digital experiences.
As the Japanese government continues to invest in digital infrastructure and connectivity, there is a steady increase in the adoption of advanced telecom solutions in these regions. The expansion of IoT, smart homes, and mobile services is further driving demand for telecom infrastructure in the Rest of Japan. As the need for high-performance networks grows, the Rest of Japan will continue to see growth in the sector, albeit at a slower pace compared to more urbanized areas like Kanto and Kyushu & Okinawa.

| Items | Values |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Unit | USD billion |
| Technology | 2G, 5G, 3G, 4G/LTE |
| End User | Telecom Operators, Government & Public Sector |
| Component | Hardware, Services |
| Regions Covered | Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, Kinki, Chubu, Tohoku, Rest of Japan |
| Key Players Profiled | Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., Ericsson AB, Nokia Corporation, ZTE Corporation, Cisco Systems, Inc., Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by technology type, end user, component, and regional trends with a focus on 5G rollout, telecom operator infrastructure investments, and government contracts. |
The demand for carrier infrastructure in telecom applications in Japan is estimated to be valued at USD 14.3 billion in 2025.
The market size for the carrier infrastructure in telecom applications in Japan is projected to reach USD 31.3 billion by 2035.
The demand for carrier infrastructure in telecom applications in Japan is expected to grow at a 8.2% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in carrier infrastructure in telecom applications in Japan are 5g, 2g, 3g and 4g/lte.
In terms of end user, telecom operators segment is expected to command 54.9% share in the carrier infrastructure in telecom applications in Japan in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Demand Signal Repository Solutions Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand Side Management Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand Response Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
North America Shipping Supplies Market Trends – Innovations & Growth 2024-2034
Demand of Kozani Saffron in Greece Analysis - Size, Share & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Demand of No-acid Whey Strained Dairy Processing Concepts in European Union Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand for Bronte Pistachio in Italy Analysis - Size, Share & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Demand and Trend Analysis of Gaming Monitor in Western Europe Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Trend Analysis of Gaming Monitor in Korea Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Trend Analysis of Gaming Monitor in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glycine Soja (Soybean) Seed Extract Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Trend Analysis of Yeast in Japan - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand of Pistachio-based desserts & ingredients in France Analysis - Size, Share & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Western Europe Men’s Skincare Market Analysis – Forecast 2023-2033
Demand and Trends Analysis of Stevia in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Women’s Intimate Care Market Trends – Growth & Forecast 2024-2034
Demand and Trend Analysis of Fabric Stain Remover in Korea Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Sales Analysis of Paper Cup in Korea Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Sales Analysis of Paper Cup in Western Europe Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand of MFGM-enriched Powders & RTDs in European Union Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA