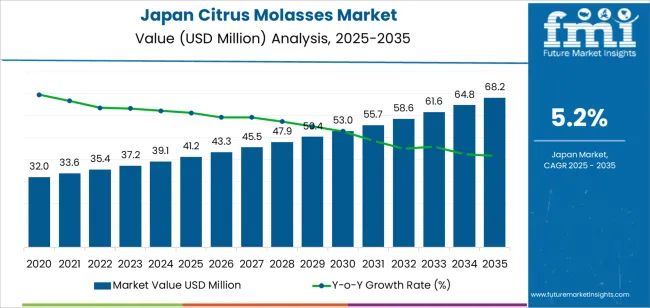
Demand for citrus molasses in Japan is valued at USD 41.2 million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 68.2 million by 2035, registering a CAGR of 5.2 percent. Demand is supported by the steady use of citrus molasses in livestock feed, fermentation processes, and select food and beverage applications. Its sugar content, acidity, and nutrient profile make it suitable for energy-rich feed formulations and as a fermentation substrate in industrial processing. Consistent utilization across livestock and bioprocessing facilities continues to sustain domestic demand.
Conventional citrus molasses represents the leading segment due to broad availability, stable composition, and suitability for large-volume applications. Conventional products align with cost-sensitive feed operations and are commonly used in blending, pelleting, and liquid feed formulations. Improvements in citrus processing efficiency and supply consistency support predictable downstream use across Japan’s feed manufacturing sector.
Demand is strongest in Kyushu and Okinawa, Kanto, and Kinki, where livestock activity, feed production, and food processing capacity are concentrated. Key suppliers include Lemon Concentrate S.L., Louis Dreyfus Company B.V., Citrusuco S.A., Citromax Group, and Sucocitrico Cutrale Ltd. Their focus areas include quality control, standardized processing, and supply reliability for feed and industrial users.
Peak-to-trough analysis shows a moderate cyclical pattern influenced by citrus-processing output, feed-industry demand, and agricultural variability. Between 2025 and 2028, the segment is likely to reach an early peak supported by stable processing volumes in domestic citrus regions and consistent use of citrus molasses as a carbohydrate source in livestock feed and fermentation applications. Reliable sourcing and predictable integration into feed formulations will reinforce this initial upward phase.
A mild trough is expected between 2029 and 2031 due to fluctuations in citrus harvest yields, weather-related production shifts, and adjustments in feed-mix costs. These factors may temporarily moderate procurement without creating sharp declines, as end-use demand remains steady across feed and industrial users. After 2031, the segment is expected to regain upward momentum as processing output stabilizes and formulation improvements increase utilization efficiency. Expanded use in specialized feed blends will contribute to the recovery. The peak-to-trough pattern reflects a stable ingredient segment shaped by agricultural cycles, steady industrial use, and incremental product reformulation within Japan’s feed and fermentation industries.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Japan Citrus Molasses Sales Value (2025) | USD 41.2 million |
| Japan Citrus Molasses Forecast Value (2035) | USD 68.2 million |
| Japan Citrus Molasses Forecast CAGR (2025-2035) | 5.2% |
The demand for citrus molasses in Japan is increasing as feed and agricultural industries seek by-product solutions that align with the country’s focus on food safety, traceability and premium animal production. Citrus processing generates molasses that offers a cost-effective energy source and flavour enhancement for livestock feed, which appeals to operators of high-value beef, dairy and aquaculture systems in Japan. The local citrus industry also emphasises circular economy practices, and utilisation of citrus processing residuals supports ecofriendly goals in regions such as Kyushu, Shikoku and Hokkaido.
Demand is supported by Japanese producers’ interest in ingredient provenance and documentation to meet stringent domestic safety and export standards. Growth is constrained by relatively limited domestic citrus-molasses supply, high logistics cost for piggy-backing into distant livestock regions, and competition from conventional feed ingredients that are well established in Japanese feed formulations. Seasonal variations in citrus processing and regulatory requirements for feed-ingredient approval may also slow wider adoption.
Demand for citrus molasses in Japan is shaped by supply availability, application-specific requirements, and the use of citrus-processing by-products in feed and industrial sectors. Distribution across nature, sales channels, and application categories reflects the importance of consistent quality, energy contribution in feed formulations, and suitability for fermentation-based processes.

Conventional citrus molasses holds 83.4% of the Japanese industry and represents the leading segment. Its dominance reflects steady domestic supply from citrus processing, cost efficiency, and compatibility with high-volume feed and industrial operations. Conventional variants offer predictable nutrient and sugar content, supporting consistent feed formulation and fermentation uses. Organic citrus molasses holds 16.6%, serving niche buyers focused on certified feed inputs and specialty formulations. Its limited share results from higher production costs, certification requirements, and narrow application suitability. Nature-based preferences align with operational scale, procurement priorities, and Japan’s moderate organic livestock-feed adoption rate.
Key drivers and attributes:
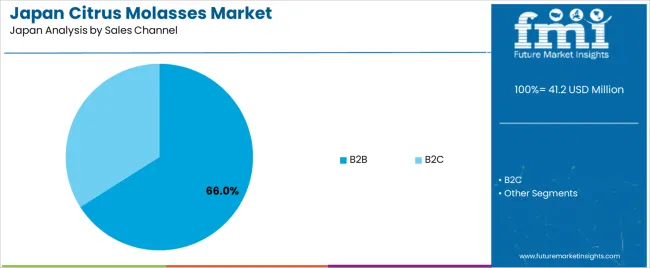
The B2B channel holds an estimated 66.0% share of demand in Japan. Feed manufacturers, industrial processors, and pulp producers source citrus molasses directly to ensure consistency, manage logistics, and secure volume-based contracts. Direct procurement reduces material-handling costs and supports predictable input supply for continuous operations. The B2C channel accounts for 34.0%, serving small-scale farmers, regional distributors, and buyers purchasing limited quantities through retail or online platforms. B2C volumes remain modest due to the product’s industrial nature and limited consumer-facing applications.
Key drivers and attributes:
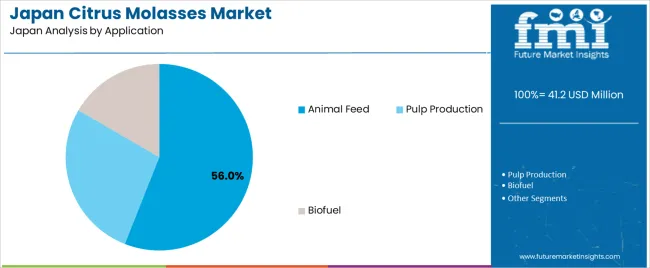
Animal feed holds an estimated 56.0% share of Japanese demand, making it the leading application. Citrus molasses is used to improve feed palatability, provide energy density, and act as a binder in mixed and pelleted feed. Pulp production accounts for 29.0%, using molasses as a fermentation substrate in fiber-derived products and industrial formulations. Biofuel represents 15.0%, where citrus molasses serves as a fermentation feedstock for ethanol and biogas generation. Application distribution reflects scale, process requirements, and economic viability across feed, industrial, and energy sectors.
Key drivers and attributes:
In Japan, demand for citrus molasses is supported by dairy and beef farmers seeking energy-rich, palatable feed ingredients that complement traditional rations. Citrus processing operations in regions such as Shikoku and Kyushu generate by-products that can be processed into molasses, enabling local supply closer to feed mills. The push for higher quality beef such as Wagyu and Japanese Black encourages use of specialty feed additives, which creates a niche for citrus molasses formulations with traceability. Japanese agricultural policy and corporate ecofriendly goals encourage use of circular-economy feed ingredients that convert citrus waste into value, which strengthens demand for citrus-derived molasses.
Citrus molasses production in Japan is subject to seasonal harvest cycles and fluctuating volumes of citrus peel and pulp, which can limit continuous availability and complicate inventory planning. The viscous, liquid nature of many citrus molasses products results in higher logistics, pumping and storage cost in domestic feed distribution networks, which may reduce adoption outside regional supply zones. Established feed ingredients such as beet molasses, cane molasses and standard energy supplements maintain entrenched use in many livestock operations, which limits the incremental growth of citrus-specific molasses blends.
Manufacturers and agricultural cooperatives in Japan are increasingly marketing citrus molasses grades that are certified for feed safety and origin verification, aimed at high-end beef finishing systems and organic livestock operations. Feed formulators are exploring citrus molasses integration in transition cow diets and high-intake dairy rations to improve palatability and consistency of energy supply. Partnerships between citrus processors and feed companies are being established to secure by-product streams and develop dedicated molasses production for livestock feed, which supports broader usage of citrus-derived molasses in Japanese agricultural supply chains.
Demand for citrus molasses in Japan is increasing through 2035, supported by broader use in livestock feed formulations, fermentation operations, and specialty applications within regional agriculture and food-processing environments. Citrus molasses supplies fermentable sugars and enhances palatability in ruminant diets, while fermentation facilities use it for yeast propagation and process stabilization. Availability depends on domestic citrus-processing volumes and import channels that supply concentrated by-product streams. Regional consumption varies according to livestock density, feed-mill distribution, and agricultural production patterns. Kyushu & Okinawa leads with a 6.5% CAGR, followed by Kanto (6.0%), Kinki (5.2%), Chubu (4.6%), Tohoku (4.0%), and the Rest of Japan (3.8%).
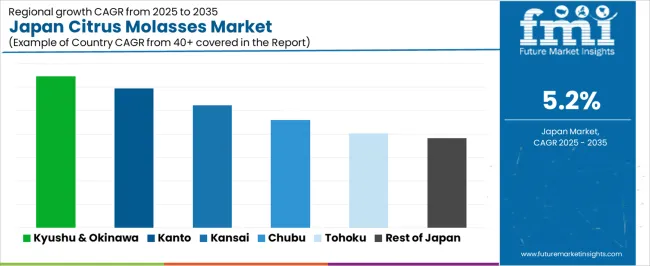
| Region | CAGR (2025-2035) |
|---|---|
| Kyushu & Okinawa | 6.5% |
| Kanto | 6.0% |
| Kinki | 5.2% |
| Chubu | 4.6% |
| Tohoku | 4.0% |
| Rest of Japan | 3.8% |
Kyushu & Okinawa grows at 6.5% CAGR, supported by high livestock density, strong ruminant-feed production, and the presence of citrus-processing facilities in select prefectures. Feed mills in Fukuoka, Miyazaki, and Kagoshima incorporate citrus molasses to improve palatability, enhance energy content, and stabilize blended feed formulations. Beef and dairy operations rely on citrus molasses as a cost-effective carbohydrate source during seasonal feed adjustments.
Fermentation facilities use citrus molasses in yeast production and biochemical processes requiring consistent sugar availability. Regional distribution networks ensure steady delivery to feed manufacturers, while Okinawa’s small-scale livestock operations adopt citrus molasses for ration uniformity. Stable agricultural activity and dependable feed-mill operations reinforce consistent regional demand.
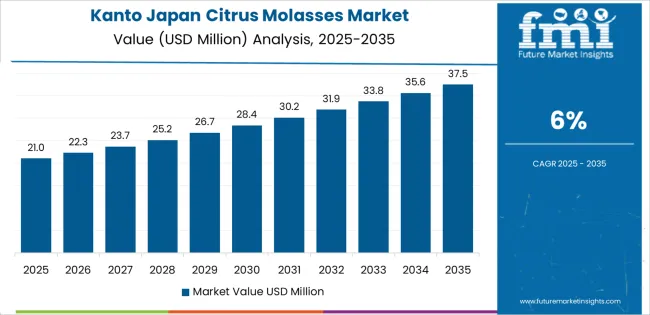
Kanto grows at 6.0% CAGR, supported by its large feed-distribution network, concentrated dairy and cattle operations outside metropolitan cores, and consistent demand from fermentation facilities. Prefectures such as Ibaraki, Chiba, and Tochigi maintain active feed mills that incorporate citrus molasses in mixed rations to improve texture and stabilize carbohydrate content. Urban proximity enables efficient supply-chain movement from processing hubs to feed manufacturers. Fermentation plants use citrus molasses as a substrate for microbial processes, including yeast and organic-acid production. Although Kanto is not a major citrus-processing region, steady demand is sustained by strong livestock activity in surrounding rural areas and reliable transport links supporting consistent supply inflow.
Kinki grows at 5.2% CAGR, supported by moderate livestock production, established feed mills, and a steady industry for fermentation inputs. Prefectures including Nara, Wakayama, and Hyogo maintain consistent demand for citrus molasses in cattle and mixed-feed formulations that require enhanced palatability and controlled energy profiles. Fermentation facilities in the region use citrus molasses for microbial culture development, contributing to reliable baseline consumption. Wakayama’s citrus-growing areas generate seasonal by-product streams that support partial local supply. Distribution networks extend to small livestock operations and commercial feed producers. Although the region has lower livestock density compared with Kyushu, recurring feed-mill operations and seasonal citrus availability maintain stable demand.
Chubu grows at 4.6% CAGR, supported by moderate livestock activity, stable feed-mill operations, and periodic demand from fermentation facilities in Aichi, Shizuoka, and surrounding prefectures. Citrus molasses is used to elevate energy density and improve mixing uniformity in cattle and dairy feed. Shizuoka’s citrus sector generates a limited supply of by-product streams, contributing to regional availability. Industrial fermentation plants adopt citrus molasses for yeast cultivation and organic-matter processing. Demand is steady but moderate due to balanced livestock numbers and limited citrus-processing capacity. Reliable logistics networks support consistent inflow from other regions to maintain supply continuity.
Tohoku grows at 4.0% CAGR, supported by dairy and cattle operations across Miyagi, Iwate, and Aomori that use citrus molasses to improve ration palatability and energy balance. The region relies heavily on transported supply due to limited local citrus-processing activity, yet feed mills maintain consistent usage for blended ruminant diets. Industrial facilities engaged in fermentation processes contribute modest demand. Cooler climates support ongoing feed supplementation practices across much of the year, reinforcing steady consumption of citrus molasses as a carbohydrate source. Although growth is gradual due to a smaller agricultural base, stable livestock activity ensures predictable adoption.
The Rest of Japan grows at 3.8% CAGR, supported by scattered cattle operations, small-scale feed mills, and modest industrial fermentation needs across rural prefectures. Citrus molasses is primarily used as an energy supplement and palatability enhancer in mixed rations for ruminants, with seasonal peaks tied to feed adjustments in colder regions. Limited citrus-processing capacity restricts local supply, so most volumes are transported from major citrus-producing regions. Small food-processing and fermentation facilities incorporate citrus molasses for microbial applications requiring stable sugar content. Growth remains modest due to lower agricultural density, but recurring feed-mill usage maintains a consistent baseline.

Demand for citrus molasses in Japan is shaped by a concentrated group of international processors supplying material for feed formulation, fermentation substrates, and citrus-based industrial applications. Lemon Concentrate S.L. holds the leading position with an estimated 26.0% share, supported by consistent sourcing, controlled acidity levels, and stable soluble-solids content that align with Japanese import requirements. Its role is reinforced by reliable logistics and uniform batch characteristics.
Louis Dreyfus Company B.V. and Citrusuco S.A. follow as major suppliers, offering molasses derived from large-scale citrus processing operations. Their strengths include dependable by-product volumes, predictable sugar composition, and established export frameworks serving Japanese distributors. Citromax Group maintains a strong position through vertically integrated lemon cultivation and processing in the Americas, providing molasses suited to specialized fermentation and blended feed applications.
Sucocitrico Cutrale Ltd. contributes additional supply depth through extensive Brazilian citrus operations, emphasizing consistency in chemical parameters and stable shipment capacity throughout the year. Competition across this segment centers on soluble-sugar accuracy, acidity control, batch uniformity, traceable sourcing, and delivery reliability. Demand remains steady due to ongoing use of citrus molasses in feed mixes, growth in fermentation-based production, and continued reliance on imported citrus by-products with predictable quality profiles suited to Japanese processing requirements.
| Items | Values |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD million |
| Nature | Conventional, Organic |
| Sales Channel | B2B, B2C |
| Application | Animal Feed, Pulp Production, Biofuel |
| Regions Covered | Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, Kinki, Chubu, Tohoku, Rest of Japan |
| Key Companies Profiled | Lemon Concentrate S.L., Louis Dreyfus Company B.V., Citrusuco S.A., Citromax Group, Sucocitrico Cutrale Ltd. |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by nature, sales channel, and application categories; regional adoption trends across Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, Kinki, Chubu, Tohoku, and Rest of Japan; competitive landscape of citrus processors and molasses suppliers; developments in organic citrus by-products and eco-friendly feed inputs; integration with livestock nutrition, pulp processing, and biofuel initiatives in Japan. |
The global demand for citrus molasses in Japan is estimated to be valued at USD 41.2 million in 2025.
The demand for citrus molasses in Japan is projected to reach USD 68.2 million by 2035.
The demand for citrus molasses in japan is expected to grow at a 5.2% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types are conventional and organic.
In terms of sales channel, B2B segment is expected to command 66.0% share in Japan in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Demand Signal Repository Solutions Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand Side Management Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand Response Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
North America Shipping Supplies Market Trends – Innovations & Growth 2024-2034
Demand of Kozani Saffron in Greece Analysis - Size, Share & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Demand of No-acid Whey Strained Dairy Processing Concepts in European Union Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand for Bronte Pistachio in Italy Analysis - Size, Share & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Demand and Trend Analysis of Gaming Monitor in Western Europe Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Trend Analysis of Gaming Monitor in Korea Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Trend Analysis of Gaming Monitor in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glycine Soja (Soybean) Seed Extract Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Trend Analysis of Yeast in Japan - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand of Pistachio-based desserts & ingredients in France Analysis - Size, Share & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Western Europe Men’s Skincare Market Analysis – Forecast 2023-2033
Demand and Trends Analysis of Stevia in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Women’s Intimate Care Market Trends – Growth & Forecast 2024-2034
Demand and Trend Analysis of Fabric Stain Remover in Korea Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Sales Analysis of Paper Cup in Korea Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Sales Analysis of Paper Cup in Western Europe Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand of MFGM-enriched Powders & RTDs in European Union Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA