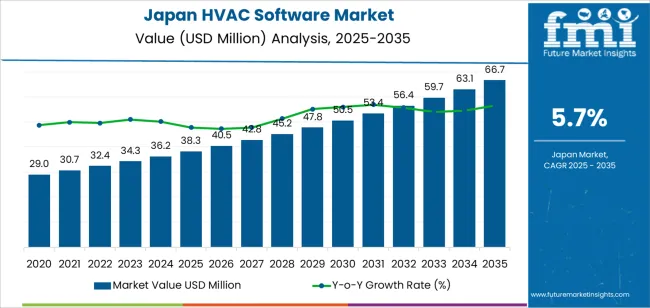
The demand for HVAC software in Japan is valued at USD 38.3 million in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 66.7 million by 2035, with a CAGR of 5.7%. Demand is shaped by continued digital adoption across building management, commercial facilities, and industrial sites seeking to improve operational efficiency and system oversight. HVAC software platforms support functions such as equipment monitoring, fault detection, energy-use analysis, and maintenance scheduling. Their role in improving runtime performance and reducing energy consumption supports stable uptake across new construction and retrofit projects.
Large enterprises represent the leading user segment. Their extensive facility portfolios, higher operational loads, and established energy-management programs create sustained demand for software solutions capable of integrating multiple HVAC assets. These organisations rely on data-driven tools to manage complex system architectures, automate workflows, and support compliance with building-performance standards.
Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, and Kinki remain the strongest regional industries. These areas include dense commercial districts, manufacturing bases, and public-infrastructure installations that depend on efficient climate-control systems. Their concentration of multi-site enterprises and modern building projects contributes to consistent investment in digital HVAC management tools. Honeywell International Inc., Johnson Controls International plc, Siemens AG, Carrier Global Corporation, Trane Technologies plc, and Lennox International Inc. are the principal suppliers. Their portfolios include building-management software, connected HVAC platforms, and analytics tools used for system optimisation, preventive maintenance, and long-term equipment planning.
The growth rate volatility index shows a stable pattern with limited fluctuation, driven by the steady nature of HVAC service cycles and the predictable adoption of digital tools across installation, maintenance, and building-performance monitoring. From 2025 to 2029, volatility remains low as contractors, facility managers, and commercial-building operators introduce scheduling, diagnostics, and load-calculation software at a controlled pace. Demand is guided by routine compliance checks, energy-efficiency programmes, and gradual system upgrades rather than large demand surges.
Between 2030 and 2035, volatility continues to remain contained as adoption matures and digital workflows become embedded across HVAC service operations. Annual growth is shaped by incremental releases in cloud-based maintenance platforms, improved fault-detection algorithms, and better integration with building-management systems. The absence of sharp spikes reflects the sector’s reliance on existing building stock, long HVAC equipment lifecycles, and predictable service patterns. The resulting volatility profile indicates a stable, mid-range expansion path, with growth supported by ongoing digitalisation of HVAC planning, monitoring, and maintenance across Japan’s commercial and residential environments.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Japan HVAC Software Sales Value (2025) | USD 38.3 million |
| Japan HVAC Software Forecast Value (2035) | USD 66.7 million |
| Japan HVAC Software Forecast CAGR (2025-2035) | 5.7% |
Demand for HVAC software in Japan is increasing because building operators, facility managers and contractors seek platforms that support digitisation, system optimisation and energy efficiency in HVAC systems. Smart building initiatives, tight energy-efficiency regulations and retrofit activity in older commercial, industrial and residential buildings drive uptake of software tools for automation, monitoring, fault detection and performance analytics. Software that integrates with building management systems, IoT sensors and cloud-based dashboards appeals to Japanese users aiming to reduce operating cost, manage refrigerant transitions well and maintain indoor environmental quality.
The movement toward zero-energy buildings (ZEB) and incentive programmes for greenery certification also bolster investment in HVAC control and analytics software. Constraints include the cost of deploying software licences, training staff and integrating with legacy HVAC systems that dominate Japan’s existing building stock. Some smaller facilities may delay software adoption until savings become clearly measurable or until system replacements justify automation enhancements.
Demand for HVAC software in Japan reflects the need for system monitoring, scheduling, energy optimisation, and equipment lifecycle coordination across commercial, industrial, and institutional settings. Adoption patterns depend on organisational scale, facility-complexity levels, integration needs, and maintenance workflows. Deployment preferences reflect cloud-based accessibility, update frequency, data centralisation, and the practicality of web-based platforms in controlled building environments.
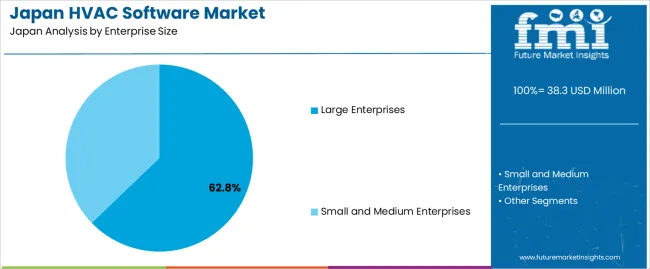
Large enterprises hold 62.8% of national demand and represent the leading user group for HVAC software. Their extensive facility networks, high-density equipment installations, and reliance on coordinated energy-management programs support strong adoption of digital tools for monitoring and optimisation. Large organisations benefit from advanced scheduling, predictive maintenance, and integration with building-management systems. Small and medium enterprises represent 37.2%, adopting HVAC software to streamline operations, reduce manual oversight, and manage equipment with greater efficiency despite limited technical personnel. Enterprise-size distribution reflects differences in building complexity, data-management capacity, and the extent of centralised control across Japanese commercial and industrial facilities.
Key drivers and attributes:
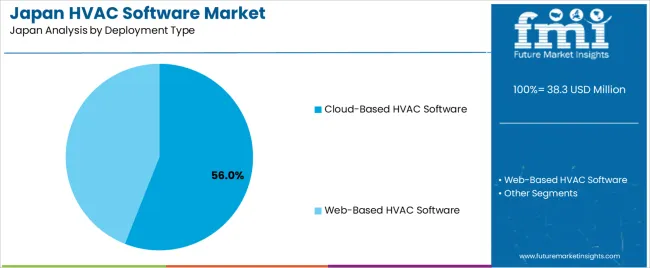
Cloud-based HVAC software holds 56.0% of national demand and represents the dominant deployment type. Cloud platforms support remote accessibility, continuous updates, multi-site monitoring, and centralised data analysis, making them suitable for enterprises managing distributed facilities. Web-based software represents 44.0%, supporting locally hosted or browser-accessed systems that integrate with on-premise equipment and maintain predictable operating conditions. Deployment-type distribution reflects organisational preferences for data management, cybersecurity policies, operational continuity, and the need for real-time performance visibility across HVAC systems. Japanese users prioritise deployment methods that align with building-automation requirements and internal IT frameworks.
Key drivers and attributes:
Growing digital building-management demands, stricter energy efficiency targets, and integration of IoT in HVAC systems are driving software demand.
In Japan, building owners and facility managers increasingly adopt HVAC software solutions to monitor, control and optimise heating, ventilation and air-conditioning systems. Government mandates for energy efficiency, building certification programmes and decarbonisation goals accelerate use of software that provides data analytics, fault-detection and operational optimisation. A rise in smart buildings, retrofits of ageing infrastructure and the need to handle distributed HVAC systems in high-density urban centres further support uptake. Software platforms that interface with sensors, building-automation systems and HVAC control units enable real-time performance tracking and improve maintenance scheduling.
Legacy system prevalence, limited software skills among installers and variable return-on-investment restrain broader implementation.
Many Japanese buildings continue to rely on older HVAC control systems without connectivity or analytics capability, which slows migration to sophisticated software platforms. HVAC contractors and facility teams may lack software skills or resources to fully employ advanced analytics and IoT tools, impeding rollout. Some buyers hesitate due to uncertainty about cost savings or performance gains from HVAC software relative to traditional maintenance or manual control, which reduces aggressive investment.
Shift toward cloud-based HVAC management platforms, increased adoption in retrofit and service-contract models, and expansion of software features for predictive maintenance define key trends.
Software vendors are delivering HVAC management suites hosted in the cloud, which offer remote access, scalability and lower upfront infrastructure cost this appeals to building-owners and facility-services firms. The retrofit industry is expanding as thermal-system upgrades in commercial and residential stock create opportunities for software add-ons rather than full system replacements. Features such as predictive maintenance, anomaly detection, performance benchmarking and integration with energy-management systems are gaining prominence in Japan. These developments support continued growth of HVAC-software demand across real estate, commercial and industrial sectors.
Demand for HVAC software in Japan is rising through 2035 as building operators, facility managers, HVAC contractors, and equipment manufacturers expand the use of digital tools for system monitoring, load calculation, maintenance scheduling, and energy-efficiency optimization. Software platforms support predictive maintenance, automated diagnostics, air-quality monitoring, and integration with building-management systems. Adoption is influenced by energy-efficiency regulations, aging building stock, skilled-technician shortages, and increased interest in remote system oversight. Commercial buildings, industrial facilities, hospitals, schools, and retail sites rely on HVAC software to improve operational stability and reduce energy consumption. Kyushu & Okinawa lead with 7.1%, followed by Kanto (6.6%), Kinki (5.8%), Chubu (5.1%), Tohoku (4.4%), and the Rest of Japan (4.2%).
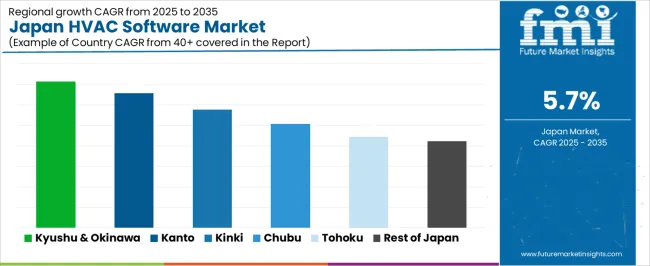
| Region | CAGR (2025-2035) |
|---|---|
| Kyushu & Okinawa | 7.1% |
| Kanto | 6.6% |
| Kinki | 5.8% |
| Chubu | 5.1% |
| Tohoku | 4.4% |
| Rest of Japan | 4.2% |
Kyushu & Okinawa grow at 7.1% CAGR, supported by rising commercial-building modernization, strong deployment of energy-efficiency programs, and increasing use of digital building-management tools across hotels, retail facilities, and public institutions. High temperatures and humidity across the region lead operators to adopt HVAC software for continuous system monitoring, cooling-load forecasting, and automated control adjustments. Tourism-driven facilities implement software for managing energy use during variable occupancy patterns. Industrial sites use digital HVAC tools for temperature regulation in production areas and storage spaces. Municipal buildings rely on HVAC software to manage maintenance cycles and air-quality standards.
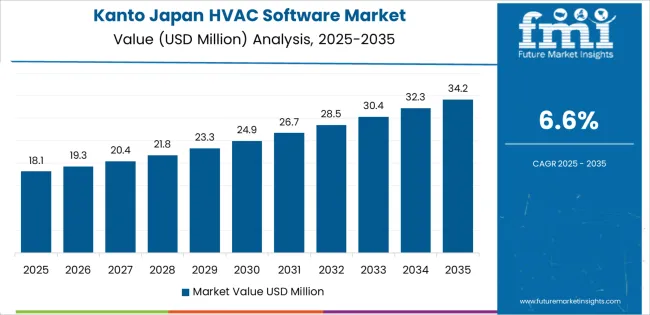
Kanto grows at 6.6% CAGR, driven by dense urban commercial infrastructure, high office-building concentration, and large-scale use of building-automation systems across Tokyo, Kanagawa, and Saitama. Facility operators adopt HVAC software for centralized monitoring, airflow optimization, and remote management of multi-building portfolios. Data centers rely on cooling-management tools to maintain thermal stability and reduce electricity use. Hospitals and research facilities use software to track air-quality indicators and maintain regulated environments. Retail chains integrate HVAC platforms into store-management systems for consistent temperature control. Strong digital-transformation programs across corporate and public sectors reinforce steady adoption.
Kinki grows at 5.8% CAGR, supported by varied commercial infrastructure, regional manufacturing activity, and expanding digital-management requirements across Osaka, Kyoto, and Hyogo. Large shopping centers, hotels, and mixed-use complexes adopt HVAC platforms for energy-consumption tracking and occupancy-responsive cooling. Manufacturers use software-enabled ventilation and temperature-control tools to support production processes requiring stable conditions. Universities and cultural institutions adopt air-quality monitoring and automated-maintenance features to maintain regulated indoor environments. Although adoption speed varies across building types, steady modernization of facility operations drives consistent demand.
Chubu grows at 5.1% CAGR, shaped by industrial activity, logistics-facility expansion, and commercial-building upgrades across Aichi, Shizuoka, and Gifu. Automotive and machinery plants use HVAC software to regulate temperatures in precision-manufacturing areas. Warehouses and logistics hubs adopt digital platforms to manage ventilation and maintain stable conditions during seasonal temperature shifts. Office buildings and retail facilities integrate HVAC software for centralized monitoring and energy-performance tracking. Although adoption levels differ between industrial and commercial segments, strong regional manufacturing activity ensures stable demand.
Tohoku grows at 4.4% CAGR, supported by steady adoption of building-automation tools, public-facility modernization, and increased interest in energy-efficient systems across Miyagi, Fukushima, and Akita. Hospitals and public buildings implement HVAC software to maintain air-quality standards and manage equipment-maintenance schedules. Industrial facilities use digital HVAC tools for climate control in processing and storage spaces. Educational institutions adopt monitoring platforms to improve ventilation in learning environments. Although budgets are smaller than metropolitan regions, essential infrastructure upgrades maintain consistent demand.
The Rest of Japan grows at 4.2% CAGR, supported by gradual modernization of commercial buildings, moderate industrial adoption, and increased interest in energy-saving solutions across regional cities and towns. Retail stores and hotels use HVAC software to manage temperature settings and reduce energy expenditures. Smaller manufacturing facilities adopt basic monitoring tools to stabilize indoor conditions. Municipal buildings implement maintenance-scheduling features to support limited staff resources. While adoption is incremental, the combination of energy-efficiency initiatives and aging building stock sustains ongoing software demand.
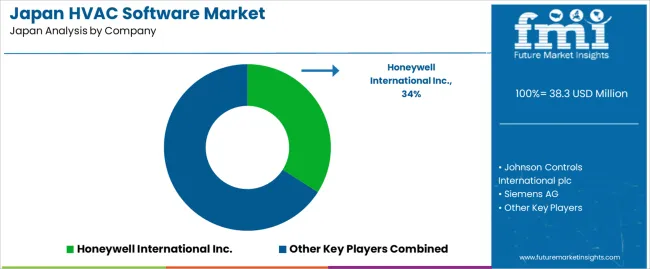
Demand for HVAC software in Japan is shaped by a concentrated group of building-technology and automation suppliers supporting commercial buildings, industrial facilities, and advanced residential systems. Honeywell International Inc. holds the leading position with an estimated 34.0% share, supported by controlled building-management platforms, stable HVAC-control algorithms, and long-standing use across office complexes, hospitals, and manufacturing sites. Its position is reinforced by predictable integration with sensors, actuators, and energy-monitoring systems.
Johnson Controls International plc and Siemens AG follow as major participants, offering HVAC-control suites embedded within broader building-automation frameworks. Their strengths include consistent system interoperability, reliable HVAC scheduling tools, and strong adoption among Japanese facility operators seeking stable performance in large, multi-zone environments. Carrier Global Corporation maintains a notable presence through software paired with its HVAC hardware lines, emphasizing dependable equipment monitoring and controlled efficiency management.
Trane Technologies plc contributes capability with analytics-driven HVAC-performance tools used to support predictive maintenance and load optimisation in commercial buildings. Lennox International Inc. supports additional demand through control platforms suited to smaller facilities and residential applications, providing consistent temperature management and stable connectivity with modern HVAC units.
Competition across this segment centres on control accuracy, system interoperability, energy-efficiency optimisation, reliability of sensor integration, and long-term software stability. Demand continues to grow as Japanese building owners prioritise energy savings, equipment lifecycle management, and reliable automation frameworks that support efficient HVAC operation across commercial and residential settings.
| Items | Values |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD million |
| Enterprise Size | Large Enterprises, Small and Medium Enterprises |
| Deployment Type | Cloud-Based HVAC Software, Web-Based HVAC Software |
| Regions Covered | Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, Kinki, Chubu, Tohoku, Rest of Japan |
| Key Companies Profiled | Honeywell International Inc., Johnson Controls International plc, Siemens AG, Carrier Global Corporation, Trane Technologies plc, Lennox International Inc. |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by enterprise size and deployment type; regional adoption trends across Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, Kinki, Chubu, Tohoku, and Rest of Japan; competitive landscape of HVAC software providers; integration with building automation systems, energy efficiency management, predictive maintenance tools, and IoT-enabled HVAC monitoring across Japanese commercial and industrial facilities. |
The demand for hvac software in Japan is estimated to be valued at USD 38.3 million in 2025.
The market size for the hvac software in Japan is projected to reach USD 66.7 million by 2035.
The demand for hvac software in Japan is expected to grow at a 5.7% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in hvac software in Japan are large enterprises and small and medium enterprises.
In terms of deployment type, cloud-based hvac software segment is expected to command 56.0% share in the hvac software in Japan in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Demand Signal Repository Solutions Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand Side Management Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand Response Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
North America Shipping Supplies Market Trends – Innovations & Growth 2024-2034
Demand of Kozani Saffron in Greece Analysis - Size, Share & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Demand of No-acid Whey Strained Dairy Processing Concepts in European Union Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand for Bronte Pistachio in Italy Analysis - Size, Share & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Demand and Trend Analysis of Gaming Monitor in Western Europe Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Trend Analysis of Gaming Monitor in Korea Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Trend Analysis of Gaming Monitor in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glycine Soja (Soybean) Seed Extract Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Trend Analysis of Yeast in Japan - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand of Pistachio-based desserts & ingredients in France Analysis - Size, Share & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Western Europe Men’s Skincare Market Analysis – Forecast 2023-2033
Demand and Trends Analysis of Stevia in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Women’s Intimate Care Market Trends – Growth & Forecast 2024-2034
Demand and Trend Analysis of Fabric Stain Remover in Korea Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Sales Analysis of Paper Cup in Korea Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Sales Analysis of Paper Cup in Western Europe Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand of MFGM-enriched Powders & RTDs in European Union Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA