The demand for small satellites in Japan is projected to reach USD 761.2 million by 2035, reflecting an absolute increase of USD 454.8 million over the forecast period. The demand, valued at USD 306.4 million in 2025, is expected to grow at a CAGR of 9.5%. This growth is primarily driven by the increasing demand for satellite-based services in telecommunications, earth observation, and global internet connectivity, along with the expanding use of small satellites for scientific research, environmental monitoring, and defense applications.
Small satellites are becoming increasingly popular due to their lower cost, quicker deployment times, and ability to deliver specialized services, such as high-resolution imaging, global internet connectivity, and real-time data analysis. The demand for small satellites is also driven by the rise in commercial space missions and the growing number of private companies launching their own satellite constellations, which are expected to revolutionize communications and data collection across a variety of industries.
Advancements in satellite miniaturization and the increasing capabilities of small satellites, including advanced propulsion systems, payloads, and on-board processing, further contribute to their expanding role in space operations. Japan’s strategic interest in space technology and its leadership in satellite manufacturing are expected to provide a favorable environment for the growth of this industry.
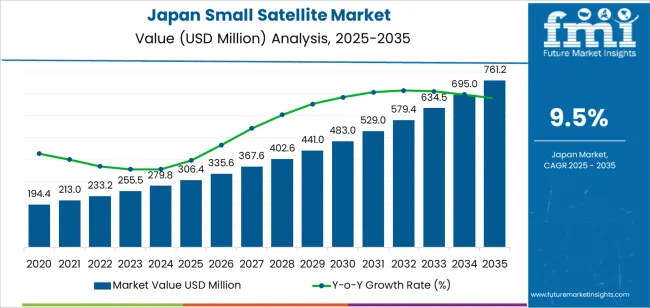
The first inflection point occurs between 2025 and 2030, where the demand increases from USD 306.4 million to USD 335.6 million, adding USD 29.2 million. During this period, the growth is moderate, driven by the expansion of satellite communications, remote sensing, and earth observation applications. Japan’s continued investment in satellite technology and infrastructure, along with rising demand for satellite-based services across sectors like telecommunications, defense, and environmental monitoring, will drive demand for small satellites. While the growth during this period is steady, it is constrained by the need for initial infrastructure developments and regulatory approvals for satellite constellations and space-based services.
The second inflection point occurs between 2030 and 2035, when the demand surges from USD 335.6 million to USD 761.2 million, adding USD 425.6 million. This represents a sharp acceleration in the growth of the small satellite sector. The major drivers during this period will be the deployment of large-scale satellite constellations for global internet coverage, increased commercial space missions, and the expanding use of small satellites for a wide range of applications such as scientific research, weather monitoring, and defense. Technological advancements in satellite miniaturization, payload capability, and on-orbit propulsion systems will further drive the widespread adoption of small satellites, marking a significant shift from steady growth to rapid expansion.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Japan Small Satellite Sales Value (2025) | USD 306.4 million |
| Japan Small Satellite Forecast Value (2035) | USD 761.2 million |
| Japan Small Satellite Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 9.5% |
Japan is experiencing growing demand for small satellites as both government agencies and commercial enterprises seek highly capable yet cost‑effective platforms. Small satellites offer flexible deployment, shorter build cycles, and lower launch costs compared to traditional large satellites. They are increasingly used in applications such as Earth observation, disaster monitoring, communications, and technology demonstration, making them valuable to Japan’s space ambitions.
The Japanese government’s space policy, private sector investment, and a focus on innovation across aerospace sectors are key drivers of demand. Japan’s need for rapid response capabilities in monitoring natural disasters like earthquakes and typhoons supports the use of constellations of small satellites for high‑frequency imagery and real‑time data. Commercial satellite operators and research institutions are also pushing for new, compact satellite platforms that can be tailored for specific missions.
Advancements in satellite manufacturing, miniaturised electronics, ride‑share launch options, and growing global demand for satellite services are making small satellites more accessible and attractive. Japan’s established electronics and manufacturing base, along with its growing ecosystem of space startups, further accelerate adoption. As new mission requirements emerge, including space situational awareness and broadband communications, the demand for small satellites in Japan is poised to continue rising steadily through 2035.
Demand is segmented by satellite type, orbit type, and application. By satellite type, demand is divided into minisatellite, picosatellites, microsatellite, CubeSats, and femtosatellites. In terms of orbit type, the industry is categorized into Low Earth Orbit (LEO), Medium Earth Orbit (MEO), and Geosynchronous Orbit (GEO). The industry is also segmented by application, including military intelligence, communication and navigation, earth observation, remote sensing, and scientific research & exploration. Regionally, demand is divided into Kanto, Kinki, Chubu, Kyushu & Okinawa, Tohoku, and the Rest of Japan.
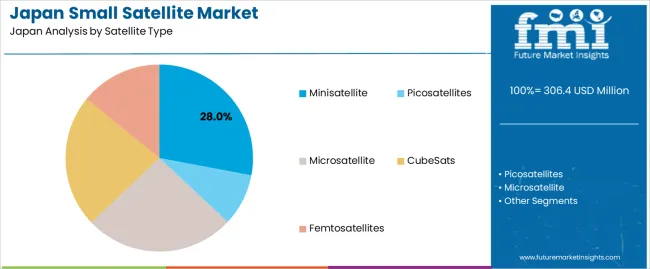
Minisatellites account for 28% of the demand for small satellites in Japan. They are favored for their versatility, balanced size, and enhanced payload capacity compared to smaller satellites. Minisatellites are used in a wide range of applications, including communication, earth observation, and scientific research. Their larger size allows them to carry more advanced instruments, making them suitable for complex missions that require high-resolution imaging, data collection, and communication systems.
The growing demand for satellite-based services in Japan, particularly in military intelligence and telecommunications, drives the need for minisatellites. These satellites offer a cost-effective solution for government agencies and private enterprises looking to expand their satellite capabilities. As the demand for high-quality data transmission and global communications increases, minisatellites continue to be the preferred choice for many missions. With their ability to provide substantial payload capacity and the growing trend of space exploration and defense applications, minisatellites are expected to maintain their leadership in the small satellite industry.
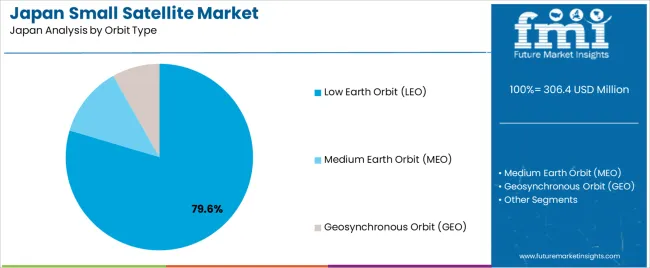
Low Earth Orbit (LEO) accounts for 79.6% of the demand for small satellites in Japan. LEO is the most commonly used orbit for small satellites due to its proximity to Earth, which allows for faster data transmission and lower latency compared to higher orbits. This makes LEO ideal for applications like communication, earth observation, and remote sensing, where real-time data collection and minimal delay are crucial.
Satellites in LEO are also easier and more cost-effective to launch, which contributes to their dominance in the small satellite industry. The increasing demand for global connectivity, including high-speed internet and communication services, along with the growing need for real-time earth monitoring, further drives the demand for LEO satellites. As more countries, including Japan, expand their satellite constellations for various applications, LEO remains the preferred orbit for small satellites, ensuring its continued growth in the industry.
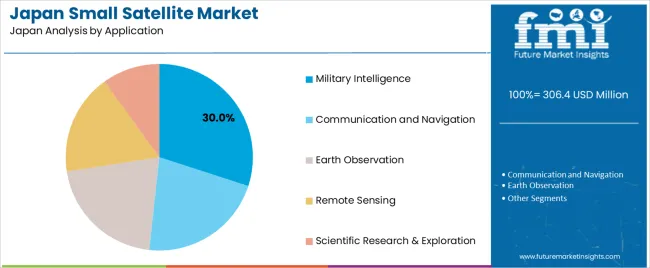
The military intelligence application category accounts for 30% of the demand for small satellites in Japan. These satellites are crucial for national defense and security, providing real-time surveillance, reconnaissance, and communication capabilities. Small satellites in military intelligence are used for monitoring borders, tracking movements, and gathering intelligence, which is vital for military operations and strategic planning.
The increasing need for secure, high-resolution data for defense purposes has driven the demand for small satellites in this sector. Japan’s continued investment in defense technology and space-based surveillance systems fuels this growth. As the demand for more advanced, cost-effective solutions for military intelligence increases, small satellites in LEO are expected to play a larger role in supporting Japan’s defense infrastructure. The ability of small satellites to provide timely and reliable data makes them indispensable in the evolving landscape of national security.
Small satellites support applications such as Earth observation, communications, disaster monitoring, and technology demonstration. Key drivers include national policy backing for space innovation, the need for rapid deployment of satellite constellations for coverage and data services, and growing private‑sector participation in the space ecosystem. Restraints stem from high development and launch costs, regulatory and export‑control complexities, and domestic launch‑vehicle limitations, which may slow the quick scaling of small‑satellite programs.
Demand for small satellites in Japan is growing because the country is positioning itself to expand its space industry and strengthen national security, communications, and environmental‑monitoring capabilities. The increasing frequency and need for remote sensing, especially for natural disaster response in a typhoon‑ and earthquake‑prone region, push the adoption of small satellites with rapid revisit cycles. The expanding commercial space start‑up ecosystem and government support lower entry barriers, enabling companies and research institutions to deploy small satellite missions for technology demonstration and service delivery. These combined factors make small satellites an increasingly important component of Japan’s space strategy.
Technological innovations in Japan are fueling small satellite growth by improving miniaturization, payload modularity, and launch‑flexibility. Manufacturers and research institutions are developing smaller bus platforms, improved electric propulsion systems, advanced imaging and communication payloads, and cost‑effective manufacturing methods that shorten development cycles. Improvements in launch‑vehicle access and rideshare opportunities make deployment more accessible. These innovations reduce mission costs and complexity, enabling more Japanese firms and institutions to undertake small satellite projects, thereby broadening the industry.
Despite strong momentum, Japan’s small satellite segment faces several constraints. The high total cost of development, launch, and operation remains a barrier—while small satellites are cheaper than large GEO platforms, they still require substantial investment for meaningful missions. Regulatory and export‑control frameworks can also slow commercial deployment and international collaboration. Domestic launch‑infrastructure limitations, including fewer dedicated small‑satellite launch vehicles, increase time‑to‑orbit and dependency on overseas launches. Finally, many planned constellations and service models are still unproven, which creates industry‑perception risk and may delay broader commercial adoption in Japan.
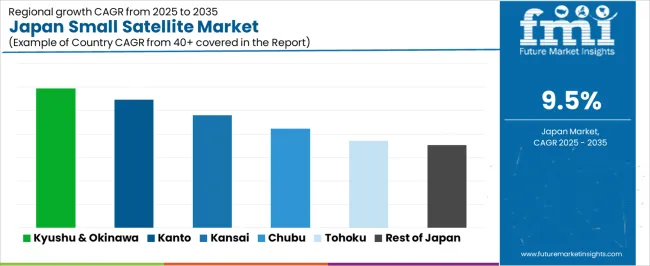
| Region | CAGR (%) |
|---|---|
| Kyushu & Okinawa | 11.9% |
| Kanto | 11.0% |
| Kinki | 9.6% |
| Chubu | 8.5% |
| Tohoku | 7.4% |
| Rest of Japan | 7.0% |
The demand for small satellites in Japan is growing across all regions, with Kyushu & Okinawa leading at an 11.9% CAGR. This growth is driven by advancements in telecommunications, space exploration, and satellite technologies. Kanto follows closely with an 11.0% CAGR, fueled by Tokyo’s strong presence in space-related industries and research institutions. Kinki sees a 9.6% CAGR, influenced by its well-established aerospace sector. Chubu, with an 8.5% CAGR, is seeing growing interest due to the region's industrial base. Tohoku and the Rest of Japan show more moderate growth at 7.4% and 7.0%, respectively, supported by ongoing advancements in satellite technology.
Kyushu & Okinawa is experiencing the highest demand growth for small satellites in Japan, with an 11.9% CAGR. The region’s rapid growth in the satellite industry is primarily driven by its key role in space exploration and satellite manufacturing. Cities like Fukuoka are becoming central hubs for space startups and satellite companies, benefiting from both private sector investment and government initiatives to expand Japan's space infrastructure.
The region’s proximity to launch facilities, such as those at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), further strengthens its role in the satellite industry. Kyushu & Okinawa’s growing emphasis on satellite communication systems, particularly for telecommunications and scientific research, has made it a leader in small satellite demand. The region’s expanding focus on technological innovation in space systems ensures that the demand for small satellites will continue to grow rapidly, with both commercial and government sectors investing heavily in satellite technology.
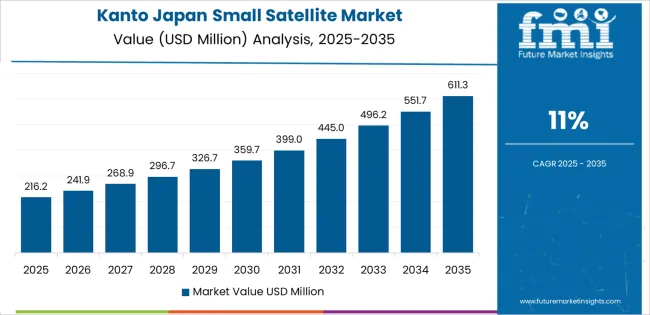
Kanto is experiencing strong growth in demand for small satellites, with an 11.0% CAGR. The region’s dominance in Japan’s space industry is driven by the concentration of high-tech companies, research institutions, and government agencies involved in satellite development. Tokyo, as a major global tech and innovation hub, plays a central role in advancing satellite technologies, making the region a key player in the small satellite industry.
Kanto is also home to JAXA and several aerospace companies, which contribute to the region’s strong research and development sector for small satellite technologies. The rise in commercial space ventures and growing investments in satellite communication systems and Earth observation applications further fuel the demand for small satellites in the region. As Kanto continues to lead Japan in space technology advancements, its demand for small satellites is expected to grow steadily in line with the expansion of Japan’s space infrastructure.
Kinki, with a 9.6% CAGR, is also experiencing significant growth in demand for small satellites. The region is home to Osaka, a city with a strong aerospace manufacturing base, which is playing an increasingly vital role in satellite development. Kinki's aerospace sector, which includes a mix of established companies and innovative startups, is focusing on small satellite technology to meet the rising demand for global communications and Earth observation capabilities.
The region’s demand for small satellites is further driven by collaborations between its academic institutions, government agencies, and private enterprises. As Kinki’s aerospace industry invests in cutting-edge satellite technologies, the region is becoming a key player in Japan’s satellite industry. The increasing use of small satellites in commercial applications, such as telecommunications and weather forecasting, is expected to continue driving demand in Kinki in the coming years, making it a crucial region for satellite manufacturing and innovation.
Chubu is experiencing steady growth in the demand for small satellites, with an 8.5% CAGR. The region’s industrial base, which includes major manufacturers in automotive, electronics, and aerospace, has increasingly shifted towards satellite development to support telecommunications and remote sensing applications. Cities like Nagoya, known for their strong manufacturing sectors, are becoming key contributors to Japan’s satellite production, especially small satellites that can be used for Earth observation, communication, and scientific research.
Chubu’s steady growth in satellite technology adoption is also supported by investments from both government and private sectors. As the region focuses on improving infrastructure for satellite data transmission and developing advanced small satellite systems, the demand for these devices will continue to increase. Chubu’s ongoing efforts to integrate small satellites into its industrial sectors ensure that the region will remain a strong player in Japan’s satellite industry, despite the moderate growth rate compared to other regions.
Tohoku is seeing steady demand for small satellites, with a 7.4% CAGR. The region’s growth is largely driven by its strong focus on research and space exploration, particularly in satellite technology development. Tohoku benefits from collaborations between universities, research institutions, and the private sector, which are helping to advance satellite capabilities. These partnerships are crucial in pushing the boundaries of satellite technology for various applications, including Earth observation and scientific research.
The Japanese government’s continuous investment in space infrastructure development, including in Tohoku, is a key factor contributing to this growth. The region’s push toward space-related research, alongside government-funded initiatives to develop and enhance satellite systems, ensures that demand for small satellites will remain strong. While not as dominant in the satellite industry as other regions like Kanto, Tohoku’s emphasis on scientific innovation and infrastructure development provides a foundation for continued growth in the small satellite industry.
The Rest of Japan is experiencing steady growth in demand for small satellites, with a 7.0% CAGR. While the region is not as central to Japan’s satellite industry as Kanto or Kyushu & Okinawa, it is seeing increased adoption of satellite systems for a variety of applications. Key drivers for growth in this region include the integration of satellite technology in sectors such as communication, agriculture, and disaster monitoring.
As the government continues to back space initiatives across Japan, the Rest of Japan benefits from these national efforts. The region’s adoption of satellite systems for monitoring natural disasters, managing remote communication, and enhancing data collection for scientific purposes is contributing to demand. Though it lags behind other regions in terms of satellite production and research facilities, the Rest of Japan is leveraging satellite technologies to improve infrastructure and meet growing technological needs. With continued government investment and expanding satellite applications, this region is expected to see steady growth in small satellite demand.
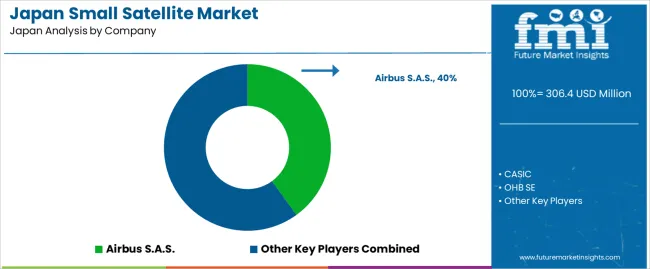
The demand for small satellites in Japan is growing, driven by a wide range of applications including earth observation, telecommunications, and technology development. Japan's commitment to advancing its space capabilities, especially for disaster monitoring, environmental surveillance, and broadband connectivity, is accelerating the need for small, cost‑effective satellite solutions. The country's increasing focus on utilizing low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites for real‑time data collection and communications is further fueling this demand.
Airbus S.A.S. leads the industry in Japan, with an estimated share of 40.0%, reflecting its strong presence and extensive expertise in satellite technology. Other key players in the Japanese industry include CASIC, OHB SE, Lockheed Martin Corporation, and Boeing. These companies contribute by offering various satellite systems, services, and infrastructure that meet Japan’s specific requirements for compact, high‑performance satellites. As satellite technology advances, these players are well‑positioned to cater to the growing demand for small satellite solutions across the country.
Key drivers of the demand include the need for efficient, low‑cost satellite systems capable of providing services like broadband internet, remote sensing, and data transmission. Japan’s expanding reliance on space technology for environmental monitoring, climate change research, and disaster preparedness is also contributing to growth in the sector. While challenges such as regulatory hurdles, spectrum allocation issues, and integration with existing infrastructure remain, Japan’s growing space initiatives and partnerships are likely to sustain strong demand for small satellites in the years ahead.
| Items | Values |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Unit | USD million |
| Product Type | Minisatellite, Picosatellites, Microsatellite, CubeSats, Femtosatellites |
| Orbit Type | Low Earth Orbit (LEO), Medium Earth Orbit (MEO), Geosynchronous Orbit (GEO) |
| Application | Military Intelligence, Communication and Navigation, Earth Observation, Remote Sensing, Scientific Research & Exploration |
| Regions Covered | Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, Kinki, Chubu, Tohoku, Rest of Japan |
| Key Players Profiled | Airbus S.A.S., CASIC, OHB SE, Lockheed Martin Corporation, Boeing |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales are projected across various satellite types, including minisatellites, picosatellites, microsatellites, CubeSats, and femtosatellites. Orbit types such as Low Earth Orbit (LEO), Medium Earth Orbit (MEO), and Geosynchronous Orbit (GEO) contribute to demand. The military, communication, and research applications drive significant sales, particularly in regions like Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, Kinki, Chubu, Tohoku, and the rest of Japan, with military intelligence and scientific research being prominent sectors. |
The global demand for small satellite in japan is estimated to be valued at USD 306.4 million in 2025.
The market size for the demand for small satellite in japan is projected to reach USD 761.2 million by 2035.
The demand for small satellite in japan is expected to grow at a 9.5% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in demand for small satellite in japan are minisatellite, picosatellites, microsatellite, cubesats and femtosatellites.
In terms of orbit type, low earth orbit (leo) segment to command 79.6% share in the demand for small satellite in japan in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Demand Signal Repository Solutions Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand Side Management Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand Response Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
North America Shipping Supplies Market Trends – Innovations & Growth 2024-2034
Demand of Kozani Saffron in Greece Analysis - Size, Share & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Demand of No-acid Whey Strained Dairy Processing Concepts in European Union Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand for Bronte Pistachio in Italy Analysis - Size, Share & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Demand and Trend Analysis of Gaming Monitor in Western Europe Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Trend Analysis of Gaming Monitor in Korea Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Trend Analysis of Gaming Monitor in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glycine Soja (Soybean) Seed Extract Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Trend Analysis of Yeast in Japan - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand of Pistachio-based desserts & ingredients in France Analysis - Size, Share & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Western Europe Men’s Skincare Market Analysis – Forecast 2023-2033
Demand and Trends Analysis of Stevia in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Women’s Intimate Care Market Trends – Growth & Forecast 2024-2034
Demand and Trend Analysis of Fabric Stain Remover in Korea Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Sales Analysis of Paper Cup in Korea Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Sales Analysis of Paper Cup in Western Europe Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand of MFGM-enriched Powders & RTDs in European Union Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA