The eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA) treatment market focuses on the drugs that are currently in clinical development for treatment of eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA), a rare disease characterized by small-to-medium blood vessel vasculitis, systemic eosinophilia, and eosinophil-induced damage and inflammation of various organ systems.
Respective therapeutic strategies include corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and biologic agents to IL-5 pathways. This market growth is largely driven by an increasing awareness regarding rare autoimmune diseases, a rising availability of biologic therapies, and rapid advancements in precision medicine. Additionally, the market is driven by active clinical trials assessing novel biologics.
In 2025, the estimated value of the global EGPA treatment market was USD 192.3 million in 2025 and is expected to have a value of USD 307.3 million in 2035, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.8% in the period.
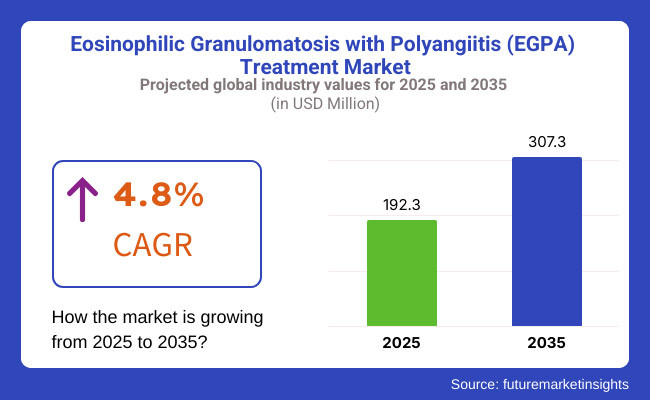
The anticipated CAGR highlights the expanding pipeline of monoclonal antibodies (e.g., mepolizumab, Benralizumab), increasing adoption of biologics in rheumatology and pulmonology, and improved diagnostic tools for early detection of EGPA. Additionally, increased patient access to specialty care and reimbursement support for biologic treatments is expected to drive market adoption.
With the highest number of rare vasculitis disorders, sophisticated diagnostic technologies, and considerable investment in biologic drug research, North America holds the largest share of the EGPA treatment market. FDA-approved therapies for EGPA (e.g., mepolizumab) are available in the USA and Canada, and uptake of targeted immunotherapies in rheumatology and pulmonology clinics is growing. In addition, expanding insurance coverage on biologics as well as specialty drugs are promoting patient access to newer therapy.
Europe, Germany and France, along with the disposal of the United Kingdom, are the leading country in Europe with regards to the scientific research of vasculitis and autoimmune diseases. Increasing access to treatment has been achieved with the approval of IL-5 pathway, monoclonal antibodies by European Medicines Agency (EMA). Additionally, the growth of the market is attributed to raising awareness about rare diseases and reimbursement policies due to increased patient advocacy.
Driving the EGPA treatment market in the Asia-Pacific region would be, expanding access to health care, rising prevalence of autoimmune diseases, and widening use of biologic drugs in China, Japan, India and South Korea. Growing active pharmaceutical ingredients subscriptions and clinical trial of rare diseases in the region have augmented the adoption of market. The development of government programs to enable therapies for rare diseases and specialty drug approvals will also drive market expansion.
Challenges
Delayed Diagnosis and High Cost of Targeted Therapies
Since EGPA has symptoms, which overlap those of asthma and other eosinophilic diseases, the EGPA treatment market faces challenge of delayed or missed diagnosis. Primary care physicians and rheumatologists, however, know less about it, resulting in underdiagnoses and delaying initiation of appropriate treatment.
In addition, high List Price of targeted biologic agents such as IL-5 inhibitors (mepolizumab, Benralizumab) and reliance on corticosteroids remain potent deterrents to global uptake especially in developing healthcare markets.
Opportunity
Advancements in Biologic Therapies and Personalized Treatment Approaches
With evolving studies on eosinophilic-mediated inflammation and autoimmune vasculitis, targeted biologics and novel immunotherapies are emerging as alternatives to high-dose corticosteroids. In this context, the advancement of the dual targeted monoclonal antibodies anti-IL-5 and anti-IL-4/IL-13 offers the prospect of improving disease control while reducing dependency on steroids.
AI based biomarkers discovery, gene based therapies and real world evidence insights will also help in further refining the precision medicine paradigm for EGPA patients. This increases patient access to advanced treatments through the increasing integration of EGPA into global rare disease databases and improved reimbursement systems.
Between 2020 and 2024, the market saw a significant increase in the number of biologic therapies approved; mepolizumab (Nucala) was granted FDA and EMA approval for EGPA. That said, high prices, regulatory delays for new biologics, and continued use of corticosteroids and immunosuppressants (methotrexate, azathioprine, and cyclophosphamide) limited treatment advances.
From 2025 to 2035 the market will transition to AI-enabled personalized medicine, next-gen biologics, and novel immunomodulatory agents. Novel therapies include gene therapy development, small-molecule inhibitors of eosinophilic pathways and AI-based drug discovery to increase treatment efficacy, decrease side effects, and improve long-term patient outcomes.
EGPA management options will also expand with the emergence of digital health solutions for the real-time monitoring of the disease and optimizing patient-specific treatment.
Market Shifts: A Comparative Analysis 2020 to 2024 vs. 2025 to 2035
| Market Shift | 2020 to 2024 Trends |
|---|---|
| Regulatory Landscape | Compliance with FDA, EMA, and orphan disease regulations for biologics |
| Technology Innovations | Adoption of IL-5 inhibitors (mepolizumab, Benralizumab) and corticosteroid-sparing treatments |
| Market Adoption | Growth in biologic therapies for steroid-dependent EGPA patients |
| Affordability & Accessibility | High cost of biologic drugs limiting widespread adoption |
| Market Competition | Dominated by biopharma companies (GSK, AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Teva, Roche, Regeneron) |
| Consumer Trends | Demand for long-term EGPA management with reduced steroid dependency |
| Market Shift | 2025 to 2035 Projections |
|---|---|
| Regulatory Landscape | Stricter oversight on gene-based therapies, AI-driven diagnostics, and precision medicine in EGPA |
| Technology Innovations | Advancements in gene therapy, small-molecule eosinophil inhibitors, and AI-driven biomarker research |
| Market Adoption | Expansion into personalized medicine, AI-assisted drug matching, and novel cytokine-targeting therapies |
| Affordability & Accessibility | Increased availability of biosimilar, cost-effective targeted therapies, and expanded reimbursement policies |
| Market Competition | Rise of biotech firms focusing on next-gen immunotherapies and AI-driven drug development |
| Consumer Trends | Growth in home-based biologic injections, digital patient monitoring, and individualized treatment plans |
The USA eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA) Treatment market is gradually increasing with increased awareness about rare autoimmune disorders and improved diagnostic centers. Several new biologic molecules, including interleukin-5 (IL-5) inhibitors and immunosuppressants, which are approved for asthma treatment are contributing to the growth of the asthma drugs market.
The availability of leading pharma companies for performing clinical trials for innovative EGPA treatments and FDA approvals of targeted therapies further drives the market growth. Moreover, personalized medicine and biomarker-driven treatment strategies when adopted are improving patient’s outcome multidisciplinary teams through personalized medicine and biomarker-driven therapy.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| USA | 5.1% |
The UK eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis EGPA treatment market is anticipated to grow in the coming years, driven by a demand for eosinophilic disorder therapies and the availability of targeted biologic drugs. The National Health Service (NHS) is incentivising diagnostics by early diagnosis and treatment of orphan diseases. Enhancing patient’s access to innovative treatment.
Strong research partnerships between biotech companies and universities are driving growth in innovative therapeutics as well. Additionally, the UK favorable regulatory position, which facilitates the penetration of orphan drugs, also drives market growth.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| UK | 4.6% |
The EU eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA) treatment market is poised to experience positive growth across the globe owing to increasing demand for biologic and immunosuppressive therapy. In Europe the EMA has also helped speed the approval of target therapy and its uptake by EU nations.
They have also established a presence in the key markets of Germany, France, and Italy, as also integrated research in rare diseases and immunology into their portfolio. The expansion of the market is further fuelled by increased collaborations among healthcare providers and pharma firms on improving the standards of treatment.
The growing emphasis on precision medicine in the EU and on equitable access to new-generation biologics for rare conditions is also having an effect on the landscape for treatments of EGPA.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| EU | 4.5% |
Japan eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA) treatment market will witness a considerable growth in the coming years, owing to increase in healthcare expenditure and innovative therapies brought by precision medicine. Innovative biologic therapy research for autoimmune diseases, such as EGPA, is fueling the country's pharmaceutical industry.
The Japanese government's emphasis on earlier diagnosis and treatment of orphan diseases along with increasing availability of innovative monoclonal antibody drugs are driving market growth. In addition, advances in genetic testing and biomarker studies will enhance therapeutic options for EGPA individuals.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| Japan | 4.8% |
The South Korea EGPA treatment market is growing, due to increasing awareness of rare autoimmune diseases and increased availability of biologic drugs. The country's thriving biotech industry is investing heavily in drugs that work through immunology.
Market expansion is driven by government initiatives to promote rare disease diagnosis and improve biologic access. Furthermore, South Korea's strengths in AI high-throughput diagnostics and precision medicine will further improve EGPA treatment capabilities.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| South Korea | 4.7% |
Corticosteroids are the backbone of EGPA therapy, suppressing inflammation with minimal activation of eosinophils and preventing organ damage. Prednisone, methylprednisolone, and dexamethasone are commonly prescribed for controlling acute disease flares and for inducing remission.
The major utility of steroids in the management of EGPA is their rapid anti-inflammatory effect to ease respiratory complaints, avert vascular injuries, and enhance the patients' quality of living. Doctors typically administer high-dose steroids at the beginning of treatment and taper the dosage down to avoid long-term side effects
But chronic steroid use brings its own difficulties, such as osteoporosis, diabetes, hypertension and infection risk. In order to overcome these challenges, researchers have developed steroid-sparing approaches, to use low-dose corticosteroids in combination with immunosuppressants or biologic therapies to establish disease control while minimizing long-term steroid dependence.
Immunosuppressants are cornerstone therapy for steroid-refractory EGPA cases and for long-term maintenance of disease. Methotrexate, azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil and cyclophosphamide are given by doctors to modulate the immune system and prevent disease relapses and eosinophilic infiltration of vital organs.
One of the great drivers of the immunosuppressant use has been the steroid-sparing therapies. Since many patients will develop steroid-induced complications, immunosuppressants are a good option for long-term disease control. The drugs can sustain remission, dampen inflammation and decrease eosinophil-induced tissue toxicity.
In addition, immunosuppressants, as part of combination regimens along with biologics or corticosteroids, enhance the overall treatment effectiveness and mitigate the risk of adverse effects. Immunotherapy is becoming an important focus in EGPA treatment and vasculitis, along with the development of targeted immunosuppressive therapies capable of selectively modulating immune responses with limited systemic side effects.
Most treatments for EGPA, such as steroids, immunosuppressants and certain biologic therapies, are taken orally. Patients prefer oral medications for practical, cost-effective, and long-term disease management use.
Most commonly, patients are treated with oral medications including prednisone, methotrexate, and mycophenolate mofetil to achieve adequate symptom control and prevent relapse once a patient has been diagnosed with EGPA. Oral formulations offer:
Simple to self-administer limiting dependence on health care systems. Broad range of processing, and manufacturing potential. And improved patient adherence relative to intravenous therapies.
Although very effective, oral steroids and immunosuppressants have potentially serious systemic side effects such as gastrointestinal distress, immune suppression and metabolic derangements. Intensive efforts from the healthcare sector are targeting these issues by optimizing dosing strategies and combination therapies to reduce side effects while maintaining therapeutic efficacy.
In cases of severe or refractory EGPA, immediate control of symptoms and high drug bioavailability is needed and such manifestations require treatment of intravenous (IV) administration. IV therapy is most commonly used for:
Extravasation of high-dose corticosteroid therapy (e.g., methylprednisolone pulse therapy) in life-threatening exacerbations of EGPA. And cyclophosphamide infusions for vasculitis-related organ damage. And IV biologic therapy (e.g., mepolizumab, rituximab) to kill eosinophils
IV therapy may help in EGPA by rapidly suppressing eosinophilic inflammation and preventing long-term complications. However, limits include hospital administration, costs and risks of infusion-related reactions. History of fighting these dangers: Manufacturers invented subcutaneous formulations and prolonged-release amazing IV workouts made medication invisible and have a restart treatment for customers.
Eosinophilic granulomatosis is a group of diseases associated with vascular system and EGPA is rare systemic vasculitis with eosinophilic granulomatosis affecting small and medium size blood vessels. EGPA is a rare systemic autoimmune disease characterized by eosinophilic inflammation and vasculitis involving the lungs, sinuses, and skin predominantly, although there can be nervous system and cardiac involvement as well.
The demand for the market is propelled by the rise in approvals of monoclonal antibody (mAb) treatments, increasing research for these types of immunomodulatory therapies and the growing personalized medicine approaches.
Market Share Analysis by Key Players
| Company/Organization Name | Estimated Market Share (%) |
|---|---|
| GlaxoSmithKline plc | 20-24% |
| AstraZeneca plc | 16-20% |
| Teva Pharmaceuticals | 12-16% |
| Sanofi S.A. | 10-14% |
| Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | 8-12% |
| Others | 22-28% |
| Company/Organization Name | Key Offerings/Activities |
|---|---|
| GlaxoSmithKline plc | Offers Nucala (Mepolizumab), an FDA-approved IL-5 inhibitor for treating EGPA and eosinophilic inflammation. |
| AstraZeneca plc | Provides Fasenra (Benralizumab), a monoclonal antibody targeting IL-5 receptor alpha, reducing eosinophil levels. |
| Teva Pharmaceuticals | Develops Cinqair (Reslizumab), an anti-IL-5 biologic therapy for severe eosinophilic conditions, including EGPA. |
| Sanofi S.A. | Produces Dupixent (Dupilumab), an IL-4/IL-13 inhibitor that may have potential in treating EGPA-associated inflammation. |
| Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Engaged in R&D for next-generation biologics and immunotherapy approaches for EGPA and related eosinophilic disorders. |
Key Market Insights
GlaxoSmithKline plc (20-24%)
GSK dominates the EGPA treatment market with Nucala (Mepolizumab), the first FDA-approved biologic therapy specifically for EGPA. This IL-5 inhibitor reduces eosinophilic inflammation, improving disease control and lowering the need for corticosteroids.
AstraZeneca plc (16-20%)
AstraZeneca’s Fasenra (Benralizumab), a monoclonal antibody that depletes eosinophils, is a promising therapy being explored for EGPA treatment beyond its existing severe asthma indication.
Teva Pharmaceuticals (12-16%)
Teva’s Cinqair (Reslizumab) is a targeted IL-5 therapy designed for severe eosinophilic asthma, with potential off-label applications for EGPA.
Sanofi S.A. (10-14%)
Sanofi’s Dupixent (Dupilumab), an IL-4/IL-13 pathway inhibitor, is being investigated for treating eosinophilic inflammation beyond atopic diseases, with potential applications in EGPA.
Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (8-12%)
Regeneron, in collaboration with Sanofi, is researching next-generation biologics targeting inflammatory pathways involved in EGPA.
Other Key Players (22-28% Combined)
Several emerging and regional players are exploring novel treatment options for EGPA, including
The overall market size for eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis treatment market was USD 192.3 million in 2025.
The eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis treatment market is expected to reach USD 307.3 million in 2035.
Rising cases of EGPA, increasing research in biologic therapies, and growing healthcare investments in rare disease treatments will drive market growth.
The top 5 countries which drives the development of eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis treatment market are USA, European Union, Japan, South Korea and UK.
Intravenous therapy command significant share over the assessment period.
Table 1: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Region, 2018 to 2033
Table 2: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 3: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Table 4: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channels, 2018 to 2033
Table 5: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 6: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 7: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Table 8: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channels, 2018 to 2033
Table 9: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 10: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 11: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Table 12: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channels, 2018 to 2033
Table 13: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 14: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 15: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Table 16: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channels, 2018 to 2033
Table 17: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 18: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 19: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Table 20: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channels, 2018 to 2033
Table 21: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 22: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 23: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Table 24: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channels, 2018 to 2033
Table 25: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 26: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 27: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Table 28: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channels, 2018 to 2033
Table 29: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 30: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 31: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Table 32: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channels, 2018 to 2033
Figure 1: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 2: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 3: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channels, 2023 to 2033
Figure 4: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 5: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Region, 2018 to 2033
Figure 6: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 7: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 8: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 9: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 10: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 11: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Figure 12: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 13: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 14: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channels, 2018 to 2033
Figure 15: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channels, 2023 to 2033
Figure 16: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channels, 2023 to 2033
Figure 17: Global Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 18: Global Market Attractiveness by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 19: Global Market Attractiveness by Distribution Channels, 2023 to 2033
Figure 20: Global Market Attractiveness by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 21: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 22: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 23: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channels, 2023 to 2033
Figure 24: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 25: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 26: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 27: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 28: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 29: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 30: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 31: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Figure 32: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 33: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 34: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channels, 2018 to 2033
Figure 35: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channels, 2023 to 2033
Figure 36: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channels, 2023 to 2033
Figure 37: North America Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 38: North America Market Attractiveness by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 39: North America Market Attractiveness by Distribution Channels, 2023 to 2033
Figure 40: North America Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 41: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 42: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 43: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channels, 2023 to 2033
Figure 44: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 45: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 46: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 47: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 48: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 49: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 50: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 51: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Figure 52: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 53: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 54: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channels, 2018 to 2033
Figure 55: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channels, 2023 to 2033
Figure 56: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channels, 2023 to 2033
Figure 57: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 58: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 59: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Distribution Channels, 2023 to 2033
Figure 60: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 61: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 62: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 63: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channels, 2023 to 2033
Figure 64: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 65: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 66: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 67: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 68: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 69: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 70: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 71: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Figure 72: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 73: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 74: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channels, 2018 to 2033
Figure 75: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channels, 2023 to 2033
Figure 76: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channels, 2023 to 2033
Figure 77: Europe Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 78: Europe Market Attractiveness by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 79: Europe Market Attractiveness by Distribution Channels, 2023 to 2033
Figure 80: Europe Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 81: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 82: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 83: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channels, 2023 to 2033
Figure 84: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 85: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 86: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 87: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 88: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 89: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 90: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 91: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Figure 92: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 93: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 94: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channels, 2018 to 2033
Figure 95: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channels, 2023 to 2033
Figure 96: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channels, 2023 to 2033
Figure 97: South Asia Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 98: South Asia Market Attractiveness by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 99: South Asia Market Attractiveness by Distribution Channels, 2023 to 2033
Figure 100: South Asia Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 101: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 102: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 103: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channels, 2023 to 2033
Figure 104: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 105: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 106: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 107: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 108: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 109: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 110: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 111: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Figure 112: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 113: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 114: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channels, 2018 to 2033
Figure 115: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channels, 2023 to 2033
Figure 116: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channels, 2023 to 2033
Figure 117: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 118: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 119: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Distribution Channels, 2023 to 2033
Figure 120: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 121: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 122: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 123: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channels, 2023 to 2033
Figure 124: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 125: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 126: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 127: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 128: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 129: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 130: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 131: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Figure 132: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 133: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 134: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channels, 2018 to 2033
Figure 135: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channels, 2023 to 2033
Figure 136: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channels, 2023 to 2033
Figure 137: Oceania Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 138: Oceania Market Attractiveness by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 139: Oceania Market Attractiveness by Distribution Channels, 2023 to 2033
Figure 140: Oceania Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 141: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 142: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 143: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channels, 2023 to 2033
Figure 144: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 145: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 146: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 147: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 148: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 149: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 150: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 151: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Figure 152: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 153: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 154: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channels, 2018 to 2033
Figure 155: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channels, 2023 to 2033
Figure 156: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channels, 2023 to 2033
Figure 157: MEA Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 158: MEA Market Attractiveness by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 159: MEA Market Attractiveness by Distribution Channels, 2023 to 2033
Figure 160: MEA Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Eosinophilic Esophagitis Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Treatment-Resistant Hypertension Management Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Treatment-Resistant Depression Treatment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Treatment Pumps Market Insights Growth & Demand Forecast 2025 to 2035
Pretreatment Coatings Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Air Treatment Ozone Generator Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
CNS Treatment and Therapy Market Insights - Trends & Growth Forecast 2025 to 2035
Seed Treatment Materials Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Acne Treatment Solutions Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Scar Treatment Market Overview - Growth & Demand Forecast 2025 to 2035
Soil Treatment Chemicals Market
Algae Treatment Chemical Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Water Treatment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Water Treatment Ozone Generator Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Water Treatment Equipment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Burns Treatment Market Overview – Growth, Demand & Forecast 2025 to 2035
CRBSI Treatment Market Insights - Growth, Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Water Treatment Polymers Market Growth & Demand 2025 to 2035
Water Treatment System Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Water Treatment Chemical Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2024-2034

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA