The Gluten Feed Market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.3 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 2.2 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.5% over the forecast period.
The gluten feed market is expected to show moderate but steady growth over the next five years. The projected values for this period are USD 1.2 billion in 2025, USD 1.3 billion in 2026, USD 1.3 billion in 2027, USD 1.4 billion in 2028, USD 1.5 billion in 2029, and USD 1.6 billion by 2030. This indicates an absolute dollar increase of USD 0.4 billion during the forecast window, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 5.9% from 2025 to 2030.
The growth outlook is driven by the rising utilization of gluten feed as a cost-effective and nutrient-rich component in livestock feed formulations, particularly for ruminants. Its high energy and digestibility make it a popular choice for cattle feed, supporting better weight gain and overall animal health. The demand for affordable protein alternatives in the animal feed industry is contributing to this steady upward trend.
Despite this positive outlook, the market remains relatively mature in developed regions, and its expansion depends heavily on corn processing by-products. Future growth opportunities lie in enhancing distribution networks, improving feed blending technologies, and ensuring consistent supply. Companies focusing on regional penetration and competitive pricing strategies will be well-positioned to benefit from this moderate but reliable growth phase.
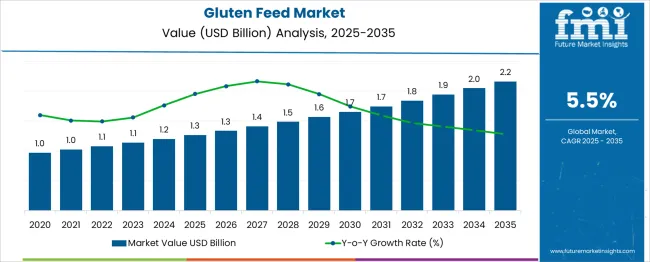
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Gluten Feed Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 1.3 billion |
| Gluten Feed Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 2.2 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 5.5% |
The gluten feed segment holds around 0.7% share within the overall animal feed market, which includes compound feed, forages, and nutritional additives for poultry, swine, ruminants, and aquaculture species. This segment has gained relevance as a cost-efficient protein source derived primarily from corn wet-milling and wheat processing. Its ability to provide energy and digestible fiber at a competitive price point makes it an attractive option for livestock producers seeking economical formulations.
Adoption has grown in beef and dairy cattle diets due to its role in improving feed conversion efficiency and reducing dependency on traditional grains. In regions with limited access to premium protein sources, the availability of gluten feed as a byproduct has supported its inclusion in feed rations, particularly near ethanol and starch production plants. Demand has also been reinforced by rising meat and dairy consumption globally, which drives the need for sustainable and cost-effective feed solutions.
However, despite these advantages, gluten feed remains a niche compared to dominant feed ingredients like soybean meal and corn. The market outlook indicates steady growth, supported by logistical efficiencies, increasing awareness among livestock producers, and strategic partnerships between feed manufacturers and bioethanol processors. Continued product standardization and regional distribution expansion will likely enhance its penetration in developing markets over the coming years.
Increasing feed cost optimization across the animal husbandry sector, especially in developing economies, has driven preference for alternative feed solutions that support both performance and profitability.
Derived from the wet milling of corn, gluten feed offers digestible fiber, protein, and essential nutrients, making it suitable for multiple livestock categories. The market outlook is further supported by the rising availability of corn processing byproducts, the expansion of ethanol production, and efforts to reduce feed imports through locally sourced feed solutions.
Environmental sustainability and circular economy objectives are also enhancing the acceptance of gluten feed as it promotes resource efficiency by utilizing agricultural byproducts. The future of this market is expected to benefit from advancements in feed formulation technologies, increased integration of feed analytics, and the expansion of intensive poultry and cattle farming practices across Asia Pacific, Latin America, and parts of Eastern Europe.
The gluten feed market is segmented by source, form, livestock, and geographic regions. The gluten feed market is divided by source into Corn-based gluten feed, Wheat-based gluten feed, Barley-based gluten feed, and Others. The gluten feed market is classified into Dry and Wet Forms. The gluten feed market is segmented into Poultry, Ruminants, Swine, Aquaculture, and Others. Regionally, the gluten feed industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
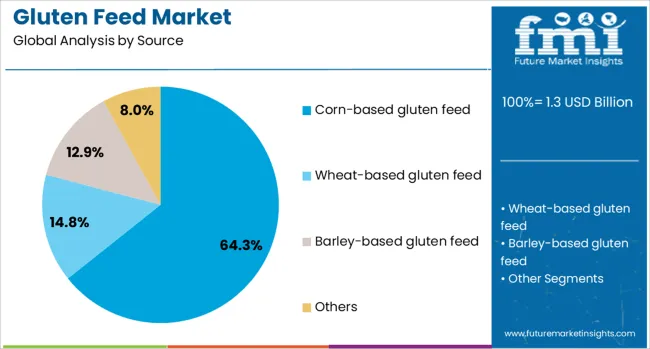
Corn based gluten feed is expected to account for 64.3% of the overall revenue share in the gluten feed market in 2025, making it the dominant source segment. The stronghold of this subsegment is being supported by abundant global availability of corn and the well-established wet milling infrastructure used to extract multiple corn derivatives.
Corn-based feed has gained favor due to its balanced nutrient profile, which includes highly digestible fiber and moderate levels of protein, making it particularly effective for ruminants and monogastric animals. The co-production of corn gluten feed alongside ethanol and corn oil has improved cost efficiencies, allowing producers to meet large-scale demand without significant price volatility.
Regulatory acceptance and favorable feed safety standards have also strengthened its use in commercial operations. The consistency in nutritional quality and ease of formulation with other feed ingredients have further enhanced the dependability of corn based gluten feed, establishing it as the preferred choice for large feed manufacturers and integrators globally.
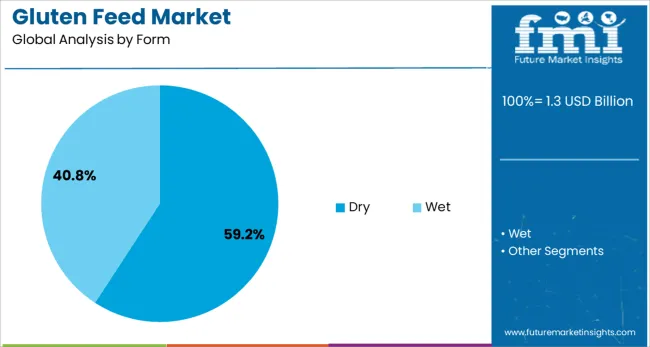
Dry form gluten feed is projected to hold 59.2% of the gluten feed market share in 2025, highlighting its leading role in the form segment. The dominance of this subsegment is being attributed to logistical advantages, longer shelf life, and ease of bulk transportation without spoilage. Unlike wet forms, dry gluten feed allows for easier storage and reduced microbial contamination risk, which is critical for maintaining feed hygiene across the supply chain.
Its adaptability in diverse climatic conditions and compatibility with automated feed distribution systems have encouraged widespread use, especially in commercial feed mills and integrated livestock farms. The lower moisture content ensures better stability and energy concentration per unit, making it cost-effective for high-volume feeding programs.
In regions where feed importation or inter-regional transfer is common, dry gluten feed has proven to be more economically viable and operationally efficient. These benefits have collectively reinforced its stronghold in the global gluten feed market.
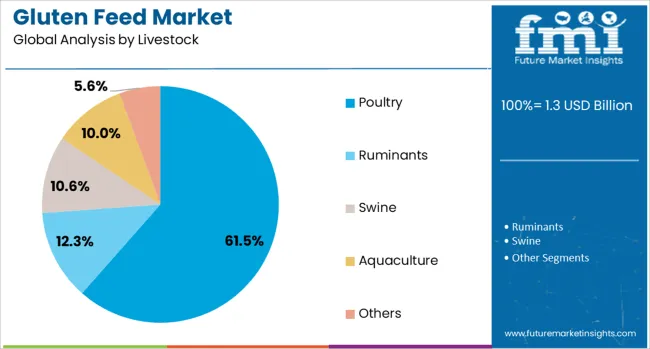
Poultry is projected to account for 61.5% of the total revenue share in the gluten feed market by 2025, representing the most significant livestock category. The segment’s prominence is being driven by rapid growth in global poultry meat and egg production, which has increased demand for consistent and affordable protein-rich feed inputs. Gluten feed has been increasingly incorporated into poultry diets due to its digestibility, energy density, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional soybean or fish meal.
Integration of corn based gluten feed in broiler and layer feed formulations has supported enhanced growth rates and feed conversion ratios. As the poultry industry scales up across emerging markets, particularly in Asia and Latin America, feed manufacturers have focused on formulating balanced rations that include gluten feed to manage feed costs.
The segment has also benefited from favorable policies promoting domestic feed production and the expansion of vertically integrated poultry operations. As biosecurity and cost-efficiency remain critical for poultry producers, gluten feed continues to be a strategically positioned feed ingredient.
Gluten feed adoption has grown due to its cost efficiency, nutritional value, and role in improving livestock performance. Expanding distribution networks and localized sourcing have strengthened supply reliability and enhanced its presence in emerging feed markets.
The preference for gluten feed has been influenced by its proven ability to deliver high-energy nutrition for cattle, poultry, and swine. Feed formulations have incorporated gluten-based components to enhance digestion efficiency and maintain consistent growth performance. Cost competitiveness against conventional protein sources has contributed to higher inclusion rates in compound feeds. Corn-based gluten feed has seen greater demand as feed mills optimize nutrient balance for ruminants and non-ruminants. Increased availability of distillers’ byproducts has further complemented its integration in mixed rations. Market sentiment indicates that pricing stability and nutritional consistency have positioned gluten feed as a practical alternative for commercial livestock producers seeking performance-based feed solutions
Distribution strategies for gluten feed have been reinforced through partnerships between milling facilities and feed manufacturers, ensuring a consistent supply to key livestock-producing regions. Transportation and storage practices have been adjusted to reduce spoilage risks and maintain product quality across long-distance shipments. Regional consumption patterns have shown stronger uptake in areas where maize processing facilities operate at scale, creating localized supply advantages. Competitive pricing in export destinations has strengthened its role in animal diets within emerging economies. Industry responses to changing trade flows and grain price volatility have highlighted the need for flexible sourcing models, making integrated supply chains a critical factor in market resilience.
The use of gluten feed is being reinforced as livestock producers seek to reduce feed costs without compromising nutritional quality. Its inclusion in rations offers a balance of energy, protein, and fiber that complements traditional grains. Feed manufacturers are integrating gluten feed into blended formulations to optimize feed conversion efficiency, particularly in dairy and beef cattle operations. This practice has been further supported by the volatility in corn and soybean meal prices, which encourages reliance on alternative protein sources. Regional proximity to ethanol and starch processing units also plays a critical role, ensuring lower transportation costs and consistent supply availability. These advantages have positioned gluten feed as a strategic component in cost-sensitive production systems worldwide.
Gluten feed adoption has moved beyond traditional markets into developing regions, driven by expanding livestock populations and the need for accessible feed resources. Producers in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are increasingly favoring gluten feed due to limited domestic availability of premium ingredients and rising demand for animal protein. Strategic partnerships between ethanol producers and feed companies have created integrated supply chains, improving availability and reducing procurement risks. Digital platforms and regional distribution hubs are making it easier for small and mid-scale farms to source gluten feed. These initiatives, combined with efforts to standardize quality and enhance shelf life, are anticipated to strengthen market penetration and encourage broader utilization in diversified animal diets.
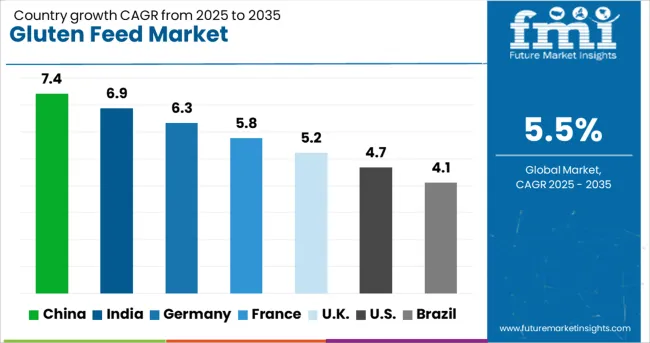
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 7.4% |
| India | 6.9% |
| Germany | 6.3% |
| France | 5.8% |
| UK | 5.2% |
| USA | 4.7% |
| Brazil | 4.1% |
The gluten feed industry, projected to grow at a global CAGR of 5.5% from 2025 to 2035, shows a strong performance across major livestock-producing nations. A 7.4% CAGR is being observed in China, a BRICS member, supported by higher maize processing and commercial feed integration. India, another BRICS nation, is reporting a 6.9% CAGR due to increased compound feed adoption in the poultry and dairy sectors. Germany, part of the OECD, is witnessing a 6.3% CAGR as demand for specialized animal nutrition intensifies within high-value livestock segments.
The United Kingdom, also an OECD member, records a 5.2% CAGR, steady uptake in ruminant feed formulations. The United States, another OECD economy, shows a 4.7% CAGR attributed to mature feed markets and competition from alternative protein sources. BRICS regions continue to offer aggressive expansion opportunities, while OECD markets maintain moderate yet consistent adoption trends. The report presents a comprehensive assessment across 40+ countries, with the top five highlighted for reference.
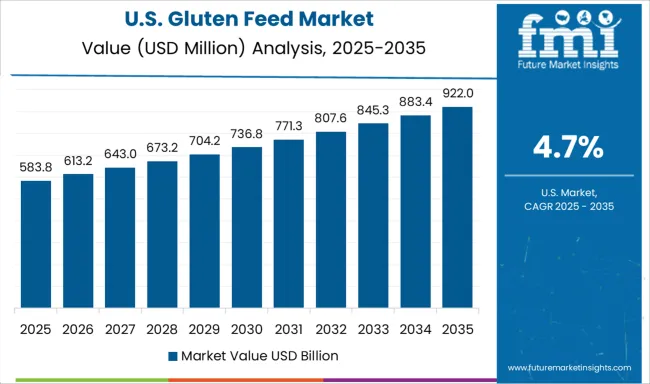
The CAGR for the United States gluten feed market advanced from about 3.9% during 2020–2024 to 4.7% for 2025–2035, signaling steady yet modest expansion. This increase can be attributed to cost optimization strategies in feed formulations and the integration of alternative energy sources to maintain livestock performance. Commercial feed manufacturers in the USA placed greater emphasis on gluten feed inclusion to stabilize protein ratios without raising input costs. Adoption has been particularly consistent in cattle and dairy segments as price fluctuations in soybean meal reinforced the need for substitutes. Regional trade networks and logistics infrastructure supported uninterrupted supply despite raw material constraints.
The CAGR in the United Kingdom rose from nearly 4.4% in 2020–2024 to 5.2% between 2025–2035, with stronger adoption across ruminant feed categories. Growth acceleration occurred due to pricing advantages over traditional protein-rich feeds and integration with silage-based diets in dairy systems. Compliance with EU feed safety directives promoted confidence among compound feed producers, encouraging larger-scale usage. Industry stakeholders focused on contract-based sourcing models to hedge against maize price volatility. Regional distributors emphasized bulk delivery systems to maintain consistency in moisture-sensitive gluten feed products.
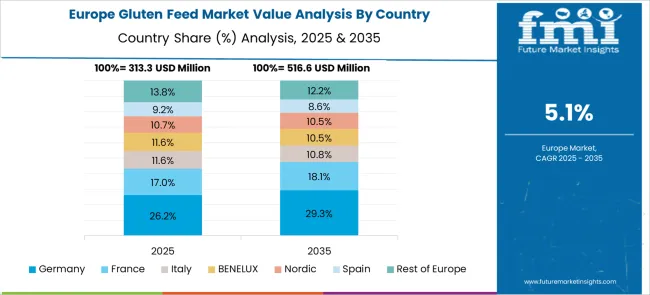
Germany witnessed a CAGR shift from around 5.5% during 2020–2024 to 6.3% for the 2025–2035 timeframe, supported by advanced livestock nutrition frameworks. German feed manufacturers utilized gluten feed for balancing high-starch diets in precision feeding programs. Local mills benefited from proximity to ethanol production plants, reducing input costs and transportation risks. Contract manufacturing agreements with regional feed groups strengthened gluten feed penetration into high-value dairy and swine sectors. As sustainability-linked certifications in protein sourcing gained traction, gluten feed was positioned as a cost-efficient, compliant solution.
China reported a notable CAGR increase from about 6.3% during 2020–2024 to 7.4% for 2025–2035, supported by large-scale industrial feed manufacturing and favorable maize availability. Integration of gluten feed into swine and poultry rations gained momentum due to competitive pricing and nutritional efficiency. Domestic ethanol production provided a steady supply, minimizing reliance on imports. Provincial feed producers scaled adoption as part of protein diversification strategies to counter soybean meal price volatility. Strong feed mill consolidation trends enhanced procurement and distribution efficiencies, allowing uniform quality control.
India experienced a sharp CAGR improvement from 5.8% in 2020–2024 to 6.9% during 2025–2035, fueled by intensified livestock population growth and rising demand for cost-effective feed solutions. Gluten feed gained traction in the dairy and poultry sectors as producers sought alternatives to conventional high-cost protein sources. Domestic ethanol production clusters emerged as critical suppliers, reducing logistical complexity and ensuring steady material flow. Animal nutrition guidelines under FSSAI facilitated market acceptance by promoting energy-rich feed formulations. Rising contract farming models in Tier-2 and Tier-3 regions pushed compound feed adoption, reinforcing gluten feed inclusion.
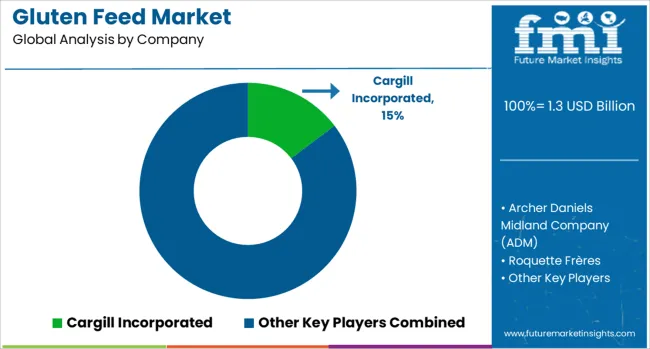
The gluten feed market is characterized by strategic initiatives focused on supply chain efficiency, product innovation, and regional market penetration. Cargill Incorporated and Archer Daniels Midland Company (ADM) maintain a leadership position through vertically integrated operations, ensuring consistent sourcing of corn-based byproducts and robust distribution to global feed manufacturers.
These companies prioritize formulation improvements that enhance energy density and fiber content, supporting nutritional requirements for ruminants and poultry. Roquette Frères and Bunge Ltd. have reinforced their market standing by investing in advanced wet-milling technologies and regional logistics hubs, enabling reliable access to cost-efficient feed solutions in high-demand regions.
Ingredion Incorporated and Tate & Lyle Plc strengthen their competitive profile by offering diversified gluten feed variants, targeting specialized livestock diets that prioritize digestibility and energy optimization. Grain Processing Corporation (GPC) and Tereos Syral capitalize on synergies with ethanol production, ensuring a steady supply of co-products and mitigating raw material price fluctuations. Emerging players such as Gulshan Polyols and AGRANA Beteiligungs-AG are leveraging localized production and flexible pricing models to attract small and mid-tier feed manufacturers, particularly in Asia-Pacific and Latin America.
These strategies, coupled with the rising global demand for animal protein and the economic need for alternative feed ingredients, position the market for steady expansion while reinforcing gluten feed’s role as an essential component in sustainable, cost-effective livestock nutrition.
In February 2024, Ingredion Incorporated launched NOVATION Indulge 2940, a clean-label native starch boasting improved gelling and mouthfeel for health-oriented foods.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 1.3 Billion |
| Source | Corn-based gluten feed, Wheat-based gluten feed, Barley-based gluten feed, and Others |
| Form | Dry and Wet |
| Livestock | Poultry, Ruminants, Swine, Aquaculture, and Others |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Cargill Incorporated, Archer Daniels Midland Company (ADM), Roquette Frères, Bunge Ltd., Ingredion Incorporated, Tate & Lyle Plc, Grain Processing Corporation (GPC), Tereos Syral, Gulshan Polyols, and AGRANA Beteiligungs-AG |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by livestock category, share of corn-based and wheat-based variants, regional consumption trends, price volatility impact, competitive landscape, raw material sourcing risks, regulatory compliance, distribution models, and emerging demand in poultry and dairy feed segments. |
The global gluten feed market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.3 billion in 2025.
The market size for the gluten feed market is projected to reach USD 2.2 billion by 2035.
The gluten feed market is expected to grow at a 5.5% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in gluten feed market are corn-based gluten feed, wheat-based gluten feed, barley-based gluten feed and others.
In terms of form, dry segment to command 59.2% share in the gluten feed market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Gluten Index Device Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Gluten-free Food Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feed Mixer for Livestock Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feed Preparation Machine Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feed Additive Nosiheptide Premix Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feeder Container Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feed Machine Market Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feed Pigment Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feed Mixer Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Gluten Free Flours Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feed Grade Spray-dried Animal Plasma (SDAP) Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Gluten-free Bakery Premix Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feed Electrolytes Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feed Micronutrients Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feed Acidifier Market Analysis Size Share and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feed Flavors Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feed Enzymes Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feed Mycotoxin Binders Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feed Phytogenics Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Feed Carbohydrase Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA