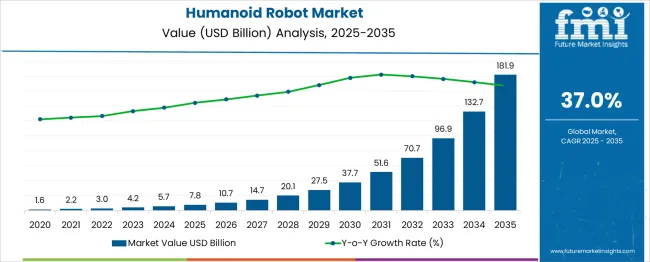
The Humanoid Robot Market is estimated to be valued at USD 7.8 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 181.9 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 37.0% over the forecast period.
Legacy players, primarily from industrial robotics, are expected to maintain their dominance, accounting for nearly 68% of the global market in 2025, driven by their established manufacturing capabilities and global distribution networks. However, this stronghold is projected to decline steadily as AI-native companies, software-driven robotics startups, and big tech firms aggressively enter the space, leveraging advanced cognitive computing, real-time decision-making, and scalable cloud robotics platforms. By 2030, the market is expected to witness a structural break in shareholding, with traditional players potentially losing 15–20% of their share to more agile entrants. These new players, offering cost-effective and highly adaptive humanoid systems, are particularly favored in sectors like elder care, customer service, and logistics. By 2035, disruptors are forecast to hold up to 42–45% of the global humanoid robot market, signifying a clear market share shift driven by innovation, speed to market, and user-centric design.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Humanoid Robot Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 7.8 billion |
| Humanoid Robot Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 181.9 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 37.0% |
The Humanoid Robot Market is projected to undergo multiple strategic breakpoints during its growth trajectory from USD 7.8 billion in 2025 to USD 181.9 billion by 2035, reflecting a staggering CAGR of 37.0%. The first critical breakpoint is anticipated between 2027 and 2028, when the market crosses the USD 10 billion threshold. This inflection point will likely be driven by the integration of generative AI, enhanced mobility, and language capabilities, enabling broader adoption in sectors like hospitality, healthcare, and education.
A second major breakpoint is expected around 2030, when the market surpasses USD 27 billion, coinciding with scalable commercialization of humanoids for public interaction, logistics, and service automation. At this stage, humanoids will transition from pilot projects to widespread deployment in smart cities and urban infrastructure, leading to a sharp acceleration in demand. The final breakpoint is forecast between 2032 and 2033, when the market exceeds USD 70 billion, marking the mass-market adoption phase. This period will be characterized by full autonomy, emotional intelligence, and seamless human-machine collaboration. As costs decline and performance improves, humanoid robots will become a viable solution across industries, cementing their role in daily life and reshaping workforce dynamics.
The humanoid robot market is witnessing significant momentum as industries seek advanced automation for labor-intensive, repetitive, or high-interaction tasks. Technological improvements in AI, machine vision, and motion planning have made humanoid robots more capable of performing human-like functions in real-world settings.
Organizations in healthcare, education, security, and retail are exploring humanoid platforms to enhance service delivery, reduce costs, and improve customer engagement. As social robots gain cultural acceptance and manufacturing costs decrease, demand is expected to expand across emerging markets and institutional settings.
Increasing private and public investments, along with collaborations among robotics developers and universities, are accelerating commercialization of versatile, bipedal robotic systems.
The humanoid robot market is segmented by product, application, and geographic regions. The humanoid robot market is divided into Bipedal service and Wheel Drive. The humanoid robot market is classified into Healthcare, Military & defense, Construction, Underwater Systems, Hospitality, Education & Scientific Research, Residential, Retail, and Others. Regionally, the humanoid robot industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
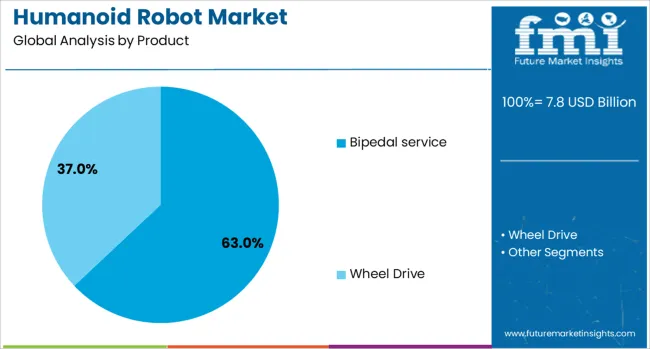
Bipedal service robots are projected to dominate the humanoid robot market with a 63.00% share in 2025. Their structural similarity to humans enables seamless interaction in environments designed for human movement, such as homes, hospitals, and offices.
This segment's dominance is fueled by advancements in dynamic balancing, dexterous limb movement, and real-time gesture recognition, making these robots ideal for front-facing applications like concierge services, elder care, and guided assistance. Bipedal platforms also provide a strategic advantage for companies targeting high-value service markets where mobility, social interaction, and emotional engagement are key.
As tech developers optimize power consumption, sensor integration, and multi-language capabilities, bipedal humanoids are expected to see increased deployment in personalized robotics solutions.
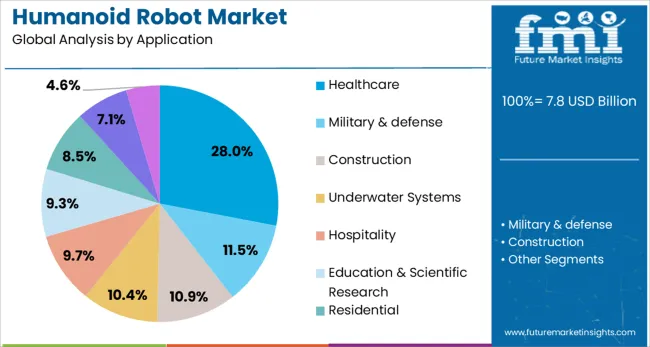
Healthcare is projected to account for 28.00% of the humanoid robot market by 2025, positioning it as the leading application segment. This segment is gaining traction as medical institutions adopt robots for eldercare support, surgical assistance, rehabilitation monitoring, and patient interaction.
Humanoid robots in healthcare settings help address workforce shortages, improve operational efficiency, and reduce caregiver burnout by handling repetitive, non-invasive tasks. Their ability to provide companionship and engage with patients in a human-like manner has shown positive results in mental health therapy, especially for elderly and autistic individuals.
With rising demand for personalized care and the integration of AI-based diagnostics, humanoid robots are being positioned as strategic enablers of smart, responsive healthcare delivery.
The humanoid robot market is steadily expanding as industries explore automation solutions that mimic human interaction. These robots are gaining interest across healthcare, education, customer service, and entertainment for their ability to engage naturally with people. Their design enables operation in human-centered environments with minimal adaptation. Demand grows where repetitive tasks or continuous assistance is required. Companies explore robotics for reception, caregiving, and remote interaction roles. With increased emphasis on emotional responsiveness and social integration, humanoid platforms are diversifying in both function and form.
Humanoid robots are increasingly being deployed in sectors where natural interaction and physical presence matter. In healthcare, they assist patients with rehabilitation routines, provide companionship, and support routine monitoring. In educational institutions, they serve as learning facilitators or assistants, offering a unique way to engage students. Retail and hospitality companies use them for greeting visitors, answering basic queries, and enhancing customer experiences. Their ability to navigate human environments, mimic gestures, and offer verbal communication allows them to fill service gaps where staff shortages or repetitive task demand exists. Many institutions see them not just as tools but as companions or extensions of the human workforce. Their physical design and interactive features help reduce the barrier between machines and people, making them well-suited for roles requiring presence and continuity. As expectations grow for personalized assistance and engagement, humanoid robots are seen as valuable solutions in both private and public-facing roles.
Despite growing curiosity and pilot implementations, humanoid robots remain financially out of reach for many institutions due to their high upfront costs and maintenance requirements. Development involves complex components such as multi-joint actuators, responsive sensors, and specialized software to enable movement, vision, and interaction. These robots often require regular updates and servicing, especially in applications involving physical contact or prolonged operation. Small businesses, schools, and care facilities may hesitate to invest in systems that require dedicated space, power, and trained operators. Moreover, malfunctions or downtimes in sensitive use cases can disrupt operations and lead to user dissatisfaction. Repairing or replacing components can be time-consuming due to the specialized nature of the hardware. Additionally, without a clear cost-benefit outcome, many decision-makers delay adoption or opt for simpler robotic systems. The combination of development complexity and cost hinders broader commercialization and places pressure on manufacturers to balance functionality with affordability.
In many environments, there is rising interest in touchless interaction and consistent, non-judgmental support systems. Humanoid robots can fulfill these expectations by offering conversation, movement assistance, and engagement without physical contact. In post-recovery healthcare, robots help reduce workload on nursing staff by providing reminders, conducting simple mobility checks, or offering emotional support. In customer-facing roles, they can answer frequently asked questions, guide users through digital interfaces, and provide feedback collection. Public institutions are exploring them for interactive kiosks, reception areas, and information points to ease congestion. This shift opens opportunities for vendors to introduce scalable humanoid solutions that support multilingual communication, adaptive responses, and gesture recognition. As more industries look to enhance user experience and reduce face-to-face dependency, humanoid robots with adaptable capabilities are positioned well to meet evolving needs. Developers offering tailored solutions for niche sectors—such as elder care or tourism—can establish long-term value propositions in emerging use cases.
While humanoid robots attract attention for their design and novelty, their real-world effectiveness remains limited in many practical environments. Factors such as inconsistent lighting, background noise, and unpredictable human behavior can hinder recognition and response accuracy. Many robots struggle with dynamic navigation in crowded spaces or performing fine motor tasks that are simple for humans. Language processing may falter with slang, accents, or rapid speech, reducing effectiveness in diverse social settings. Additionally, prolonged interactions may expose gaps in understanding or inappropriate responses, affecting user trust. In sectors requiring emotional intelligence, contextual awareness, or rapid adaptability, current humanoid platforms can fall short. These limitations restrict their roles to predefined routines or scripted environments. Without significant progress in perception and decision-making, broader integration remains difficult. Many users ultimately treat these systems as temporary attractions rather than core service tools. Addressing these gaps in autonomy and comprehension is essential to unlock sustained adoption.
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 50.0% |
| India | 46.3% |
| Germany | 42.6% |
| France | 38.9% |
| UK | 35.2% |
| USA | 31.5% |
| Brazil | 27.8% |
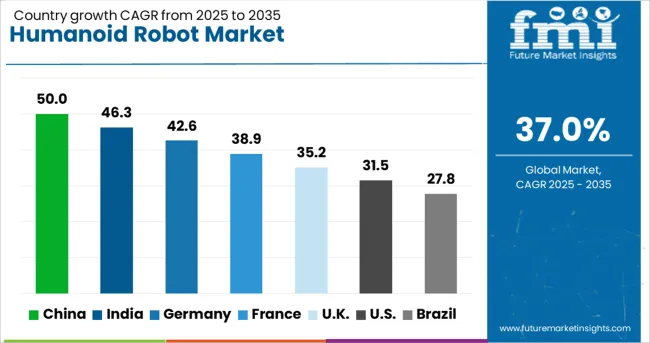
The global humanoid robot market is accelerating rapidly at a CAGR of 37.0%, driven by advancements in AI, robotics engineering, and applications across healthcare, education, and customer service. China leads with a remarkable 50.0% growth rate, supported by heavy investments in robotics R&D and integration in smart city initiatives. India follows at 46.3%, fueled by increasing demand in tech-driven sectors and academic research. Germany reports 42.6% growth, reflecting precision engineering and adoption in industrial automation and eldercare. The United Kingdom shows strong momentum at 35.2%, focusing on humanoid robotics for education, retail, and research. The United States, growing at 31.5%, remains a key innovator, with emphasis on AI-driven functionality and ethical regulation. Market trends are influenced by hardware-software integration, human-machine interaction capabilities, and evolving safety standards. This report includes insights on 40+ countries; the top countries are shown here for reference.
The humanoid robot market in China has expanded rapidly with a 50.0% CAGR, positioning the country as a leader in the global robotics landscape. Factories are deploying humanoid robots for repetitive, high-precision tasks, reducing reliance on human labor. In commercial settings, shopping malls, banks, and public transport hubs are using robots for customer assistance, drawing widespread interest. Educational institutions are integrating humanoid platforms for programming, language learning, and demonstration purposes. Several domestic manufacturers have introduced full-scale production models with speech recognition, facial tracking, and emotional response systems tailored to local languages. With increasing support from pilot zones and tech parks, investment has surged across both public and private sectors.
India has recorded a 46.3% CAGR in the humanoid robot market, with notable uptake in service, education, and healthcare applications. Hospitals are exploring humanoids for patient check-in, medication delivery, and basic diagnostics support. Startups in Bengaluru, Hyderabad, and Pune are leading developments, focusing on affordability and local language communication. Educational institutions, especially STEM-focused schools, are increasingly using humanoids to teach AI and robotics fundamentals. In commercial venues, robots are gaining traction as greeters and customer service aides in airports, exhibitions, and hotels. Collaborations between academic institutions and private developers are encouraging the design of human-interactive robotic models suitable for Indian environments.
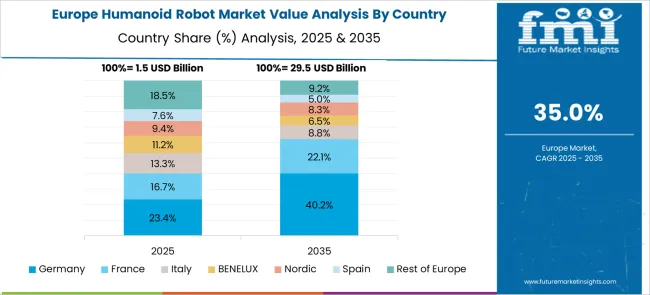
Germany’s humanoid robot market is expanding at a 42.6% CAGR, supported by demand in industrial automation, public services, and aging care. Robotics labs in Berlin, Munich, and Stuttgart are developing humanoid systems for human-machine collaboration, targeting tasks in logistics, assembly, and warehouse navigation. Healthcare institutions are using these systems for elder care support, including companionship, fall detection, and routine check-ins. Libraries, municipal offices, and cultural institutions are also experimenting with humanoids for basic information services and guided tours. German engineering firms focus on safety, reliability, and multi-language communication features to meet domestic and export demands.
The United Kingdom has experienced a 35.2% CAGR in the humanoid robot market, with increasing integration in public service, education, and entertainment. Schools and colleges are using robots for lessons in logic, communication, and basic programming. Museums and event venues deploy humanoids for welcome services, helping visitors navigate exhibitions and facilities. In elderly care homes, early trials are underway to provide cognitive stimulation and assistance with simple tasks. British developers are working closely with European tech firms to adapt humanoid robots for UK-specific social and linguistic settings. There is also a push to introduce robots in small business environments for reception and queuing systems.
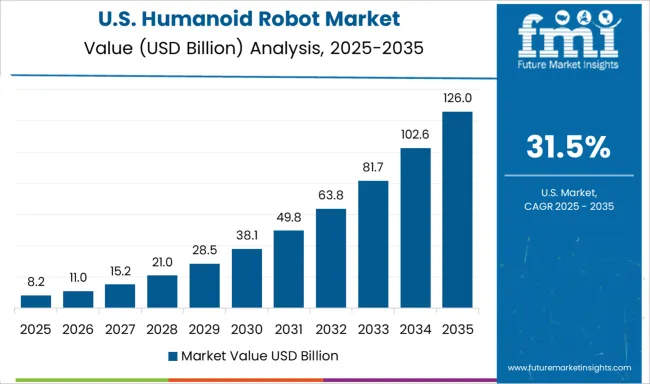
The humanoid robot market in the United States is growing at a 31.5% CAGR, with increasing usage in corporate training, public-facing services, and experimental research. Robotics firms based in California, Massachusetts, and Texas are building humanoid platforms with voice interaction, gesture control, and emotion simulation. Corporate environments are using humanoids for onboarding, safety training, and employee engagement. Airports and malls have piloted service robots to guide travelers and provide information. Universities are heavily involved in pushing the limits of human-robot interaction, testing models for collaboration and social behavior understanding. Funding from both private investors and federal research grants is encouraging widespread experimentation.
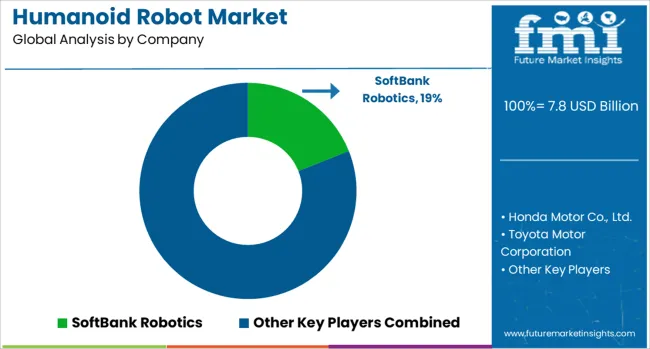
The Humanoid Robot Market is witnessing growing interest across sectors such as customer service, education, healthcare, and research. Humanoid robots, designed to resemble and mimic human actions, are gaining traction for tasks that require social interaction, communication, and mobility. Their ability to engage naturally with people is driving their deployment in reception desks, eldercare, therapy sessions, and even entertainment. With increasing demand for robotic companions and assistants, companies are refining both the mechanical design and emotional intelligence of these robots. SoftBank Robotics, a pioneer in this space, developed "Pepper," one of the most recognizable humanoid robots capable of understanding emotions and engaging in conversation.
Honda Motor Co., Ltd., with its long-standing innovation in robotics, introduced ASIMO, which set benchmarks in mobility and balance. Toyota Motor Corporation has developed humanoid robots aimed at assisting the elderly and individuals with limited mobility, highlighting the company’s focus on social benefit. ROBOTIS and KAWADA ROBOTICS CORPORATION contribute through modular robotics and bipedal robots used extensively in academic and industrial R&D environments. Meanwhile, UBTECH Robotics and HANSON ROBOTICS bring commercial appeal with robots like "Alpha" and "Sophia," respectively, which showcase advanced facial expressions, AI dialogue, and humanlike features. These companies are not only pushing the boundaries of humanoid engineering but also influencing how societies perceive and interact with intelligent machines. As usability improves, the industry is gradually shifting from showcase prototypes to real-world integration, particularly in aging societies and service-focused environments.
Boston Dynamics, in an official March 18, 2025, press release, expanded its collaboration with NVIDIA to integrate Jetson Thor and the Isaac GR00T AI framework into the Atlas humanoid. This strategic move advances Atlas’s autonomous physical intelligence through reinforced learning, vision capabilities, and safety-conscious edge AI architecture.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 7.8 Billion |
| Product | Bipedal service and Wheel Drive |
| Application | Healthcare, Military & defense, Construction, Underwater Systems, Hospitality, Education & Scientific Research, Residential, Retail, and Others |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | SoftBank Robotics, Honda Motor Co., Ltd., Toyota Motor Corporation, ROBOTIS, KAWADA ROBOTICS CORPORATION, UBTECH Robotics Corp. Ltd., and HANSON ROBOTICS LTD. |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales vary by deployment and technology, with industrial and caregiving humanoids dominating, while research and retail assistants grow fastest. North America leads value, while Asia‑Pacific posts highest volume growth. Pricing fluctuates with hardware, AI complexity, and component costs. Growth accelerates via AI/ML integration, edge autonomy, and state-backed robotics initiatives under labor‑shortage mandates |
The global humanoid robot market is estimated to be valued at USD 7.8 billion in 2025.
The market size for the humanoid robot market is projected to reach USD 181.9 billion by 2035.
The humanoid robot market is expected to grow at a 37.0% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in humanoid robot market are bipedal service and wheel drive.
In terms of application, healthcare segment to command 28.0% share in the humanoid robot market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Robot Controller, Integrator and Software Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robotic Warfare Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robotic Lawn Mower Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robotics Welding Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robotic Rehab Tools Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robotics-Assisted Telesurgery Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robotic Packaging Machines Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robot Assisted Surgical Microscope Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robotic Assisted Endovascular Systems Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robotic Lung Biopsy Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robotics as a Service (RaaS) Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robotic X-ray Scanner Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robotic Catheterization Systems Market Growth – Innovations, Trends & Forecast 2025-2035
Robot Sensor Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robotaxi Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robotic Aseptic Syringe Filler Capper Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robot Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robotic Vision Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robotics Actuators Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robotic Biopsy Devices Market Insights - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA