The Robot Market is estimated to be valued at USD 55.6 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 258.3 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16.6% over the forecast period. This substantial increase reflects the market’s rapid expansion and broadening adoption across industries. From 2020 to 2025, the market experienced steady YoY growth, with annual increases between 15% and 19%, laying a strong foundation for future gains. The growth pace accelerates notably from 2026 onward, with the market reaching USD 119.9 billion by 2030, driven by increased automation, labor optimization, and enhanced production efficiencies. In the decade following 2025, each year adds significantly larger revenue gains, with the period from 2031 to 2035 witnessing annual increases of over USD 30 billion, culminating in a projected value of USD 258.3 billion by 2035. Despite the strong upward curve, the year-on-year growth remains relatively consistent, indicating low volatility and a stable upward trend. This momentum underscores the rising demand for robotics in manufacturing, logistics, defense, healthcare, and service sectors, reinforcing the market’s long-term potential and investment attractiveness.
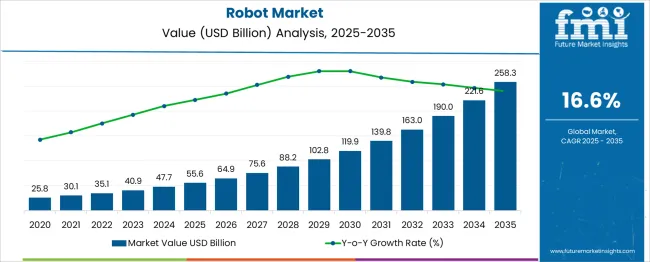
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Robot Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 55.6 billion |
| Robot Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 258.3 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 16.6% |
The robot market operates as a dynamic and fast-growing segment within the broader Industrial Automation and Smart Machinery Market, which encompasses advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine vision, control systems, and connected equipment. The parent market has witnessed strong global demand, largely driven by the increasing push for operational efficiency, labor cost reduction, and improved precision across industries including automotive, electronics, logistics, and healthcare.
Robotics plays a pivotal role within this ecosystem, offering automated solutions that enhance productivity while minimizing human error. In terms of market share, robotic systems account for a significant portion estimated at around 25%–30% of the global industrial automation market. This share is expected to increase steadily as more sectors adopt collaborative robots (cobots), service robots, and autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) to meet evolving operational needs.
The integration of robotics with real-time data platforms and remote monitoring solutions is also strengthening its strategic position within the parent market. The increasing focus on safety, precision, and speed in manufacturing and non-industrial applications is reinforcing the relevance of robotics within the broader automation domain. As the parent market continues to evolve toward more connected and intelligent systems, the robot market is poised to capture a growing share of future capital investments.
The robot market is undergoing structural expansion driven by increasing automation across manufacturing, logistics, and service sectors. Advancements in AI integration, sensor technologies, and real-time control systems have shifted robotics from isolated industrial use to broader cross-sector deployment.
Public and private investment in intelligent automation, coupled with global labor shortages and rising safety standards, has accelerated adoption across both developed and emerging economies. National strategies promoting Industry 4.0, smart factories, and autonomous systems are enabling multi-functional robot development suited for diverse operations.
Forward-looking momentum is further supported by improvements in robotics-as-a-service (RaaS) models, cloud computing capabilities, and software-defined control platforms. As hardware capabilities converge with scalable digital infrastructure, the market is expected to mature through modular deployment, AI-embedded robotics, and increasing human-robot collaboration across decentralized networks.
The robot market is segmented by type, component, deployment type, mobility type, application type, end use, industry and geographic regions. The robot market is divided by type into Industrial Robots and Service Robots. In terms of the components of the robot market, it is classified into Hardware and Software. Based on the deployment type, the robot market is segmented into Cloud-based Robotics and On-premises Robotics. The robot market is segmented by mobility type into Mobile Robots, Fixed Robots, and Humanoid Robots. The robot market is segmented by application type into Assembly & Production. By end-use industry, the robot market is segmented into Manufacturing & Industrial, Healthcare, Defense, Agriculture, and Others. Regionally, the robot industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
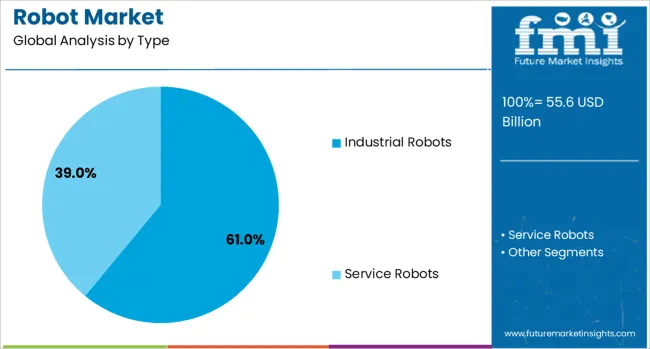
Industrial robots are anticipated to account for 61.0% of the robot market revenue in 2025, making them the leading robot type. This leadership is being driven by rising automation in automotive, electronics, and metalworking industries where high-volume, precision-based tasks dominate operations.
Demand has been fueled by ongoing efforts to reduce operational errors, lower labor dependency, and increase production throughput. Enhanced repeatability and payload capabilities have allowed industrial robots to be deployed across both discrete and process manufacturing environments.
Additionally, growth in smart factory initiatives and cost reductions in robot arms and sensors have reinforced their adoption in both large-scale and mid-sized enterprises. Industrial robots are also benefitting from increased compatibility with AI-powered vision systems, paving the way for semi-autonomous operations and adaptive performance in high-speed production lines
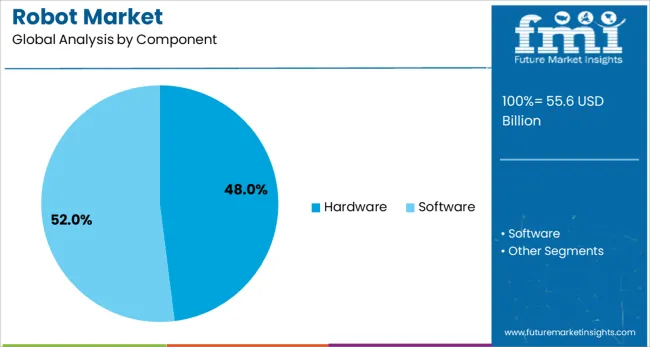
Hardware is projected to contribute 48.0% of the total robot market revenue in 2025, positioning it as the dominant component category. This strength is being sustained by demand for core robotic elements such as actuators, motors, sensors, controllers, and mechanical frames, all essential for functionality and structural performance.
Investment in next-generation actuators and lightweight materials has enhanced mobility and energy efficiency, particularly in autonomous and mobile robotic platforms. The emergence of edge AI and embedded computing has intensified the requirement for modular, high-performance components that can support real-time decision-making.
Hardware innovation is also being driven by the need to ensure long lifecycle durability in extreme or repetitive environments, particularly in heavy industries. As software-defined architecture grows in parallel, foundational hardware continues to hold a critical role in ensuring speed, safety, and mechanical accuracy
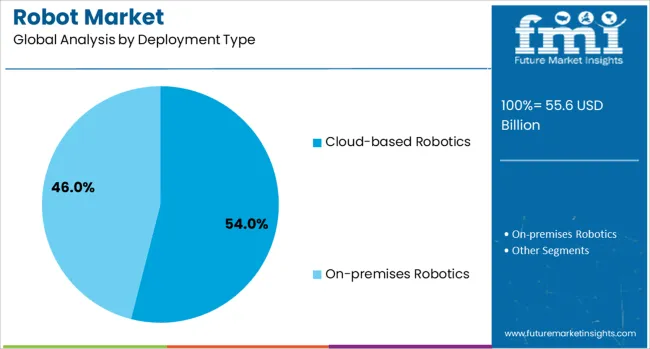
Cloud-based robotics is expected to lead the deployment type category with 54.0% of the market share in 2025. This segment’s growth is being powered by the rise of distributed robotic systems and demand for scalable, remote-operable solutions. Cloud integration allows centralized control, continuous software updates, and shared learning across robotic fleets, making it particularly valuable for logistics, warehousing, healthcare, and security applications.
Reduced reliance on on-premise infrastructure has lowered barriers for small and medium-sized enterprises to adopt robotics. The convergence of robotics and IoT has further enhanced remote diagnostics, fleet management, and predictive maintenance capabilities.
Additionally, cloud-native platforms enable machine learning model deployment and data-driven optimization, aligning well with dynamic workflows and multi-site operations. As edge-cloud architecture becomes more robust, cloud-based robotics is positioned to enable flexible, intelligent, and adaptive automation systems across geographies
The robot market is expanding rapidly across manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and domestic environments. Adoption is driven by the need to improve precision, speed, and reliability in repetitive or hazardous tasks. As labor shortages increase and industries seek consistent output, robots offer operational stability. Key developments focus on mobility, coordination, and flexible task adaptation.
Manufacturers and service providers differentiate by offering scalable systems, simplified programming, and integration support. Meanwhile, concerns about cost, complexity, and workforce adaptation continue to shape deployment rates across regions.
While robotic systems offer productivity benefits, integration into existing workflows often presents operational and cost barriers. Businesses must adapt production layouts, update control systems, and retrain staff to support robotic functions. In smaller firms or legacy environments, system compatibility, space constraints, and return on investment questions can delay projects. Moreover, multi-robot coordination across production lines or warehouses requires detailed mapping, structured data environments, and clear communication protocols. Errors in integration may lead to downtime or inconsistent output. Vendors who provide installation support, post-deployment calibration, and real-time monitoring platforms ease transition barriers for clients. Pilot programs and modular setups are increasingly favored as risk-mitigation tools. Integration challenges are more acute in industries where variability and customization dominate. Companies investing in robotics must carefully balance cost, infrastructure adaptation, and employee upskilling. Until plug-and-play solutions become more common, integration will remain a determining factor in the pace of market expansion.
Modern buyers seek robots that go beyond rigid automation, aiming for flexible systems that can handle multiple tasks and adapt to variable conditions. Collaborative robots, which can work alongside humans safely, are being adopted in environments where full automation is not feasible. These systems assist with lifting, sorting, assembly, and inspection without isolating workspaces. In healthcare, robots that support patient mobility or assist in surgical precision are increasingly in demand. The need for multi-purpose functionality leads to preference for reprogrammable units and adaptable hardware. Simpler interface design and gesture or voice-based controls enhance usability for non-specialist operators. Applications in agriculture, food processing, and small-scale logistics are also seeing uptake as robots become more task-diverse. Vendors that focus on modular builds, upgradable components, and user-friendly command systems appeal to a broader buyer base. This preference for versatility continues to shape product development and customer expectations across industries.
Despite evident advantages, high initial costs and concerns about labor displacement continue to hinder adoption in several sectors. Small and medium-sized enterprises often lack the budget or financial risk appetite to implement robotic systems, particularly when task volume is inconsistent. Additionally, employee apprehension regarding job security can reduce organizational willingness to pursue automation. Resistance may also stem from training fatigue or fear of complex machinery. Companies must invest in communication strategies that clarify how robotic systems enhance rather than replace human roles. Incentive programs, training modules, and phased rollout plans can ease the transition. Service-based robot leasing models are helping reduce upfront costs, but concerns about maintenance and technical support persist. Until perception challenges and affordability issues are addressed through education, financing, and value demonstration, adoption may remain limited in cost-sensitive regions or industries with strong manual labor traditions.
The robot market is heavily reliant on precise components such as actuators, sensors, drives, and control units. Interruptions in sourcing, whether due to geopolitical issues, factory closures, or material shortages, directly affect manufacturing timelines. Custom parts, especially for advanced robotic functions, are not easily substitutable, increasing lead times and reducing deployment reliability. Transport delays and limited local assembly capacity in some regions further constrain availability. In addition, sudden demand surges from industrial sectors or public procurement can strain existing inventories. Manufacturers who invest in supplier diversification, localized production, and scalable design structures mitigate this risk more effectively. Buyers now prioritize vendors who can guarantee delivery timelines and provide clear contingency planning. As long as component access remains uneven, production bottlenecks will affect global robot availability and pricing stability. Reliable sourcing and inventory strategies are becoming critical for maintaining momentum in both established and emerging robotic markets.
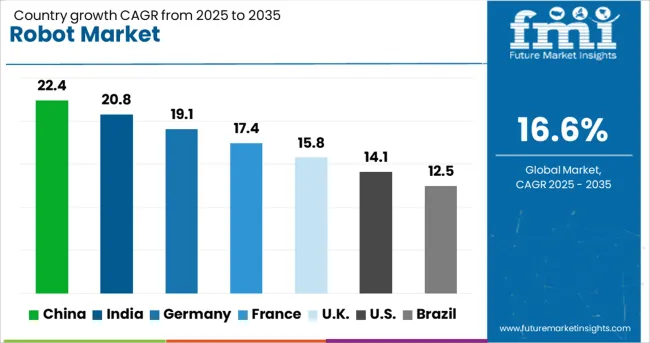
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 22.4% |
| India | 20.8% |
| Germany | 19.1% |
| France | 17.4% |
| UK | 15.8% |
| USA | 14.1% |
| Brazil | 12.5% |
The global robot market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 16.6% through 2035, driven by rapid automation, AI integration, and labor optimization across industries. Among BRICS nations, China leads with a substantial 22.4% growth rate, supported by aggressive industrial automation, government funding, and a thriving robotics manufacturing ecosystem. India follows at 20.8%, fueled by smart manufacturing initiatives, start-up activity, and adoption in sectors like logistics, automotive, and healthcare. Within the OECD region, Germany reports strong 19.1% growth, driven by advancements in precision robotics and leadership in industrial engineering. The United Kingdom records 15.8% growth, supported by robotics in warehousing, defense, and public sector automation. The United States, a mature but rapidly evolving market growing at 14.1%, emphasizes AI integration, service robotics, and regulatory development. These countries represent key hubs shaping the global robotics landscape through innovation, policy, and market demand. This report includes insights on 40+ countries; the top five markets are shown here for reference.
China leads the global robot market with an impressive CAGR of 22.4%, driven by aggressive automation in manufacturing, logistics, and electronics sectors. As the world's top industrial robot consumer, China is deploying robots in automotive plants, electronics assembly lines, and e-commerce warehouses. Regions like Guangdong and Jiangsu are witnessing the highest robot density, supported by local government incentives for smart factories. Domestic companies are also innovating in AI-driven service robots used in healthcare, hospitality, and retail. In parallel, export volumes of Chinese-built robots are rising, especially to Southeast Asia and Europe. The Made in China 2025 policy continues to fuel R&D in collaborative and humanoid robot technologies.
India is experiencing a robust 20.8% CAGR in the robot market, fueled by its rapid industrialization, warehousing expansion, and digital transformation in sectors like healthcare and education. Robotics adoption is surging in automotive manufacturing hubs such as Pune and Chennai, while warehouse automation is accelerating in cities like Bengaluru and Hyderabad. Indian startups are developing cost-effective robots for logistics, surveillance, and even agriculture. Meanwhile, hospitals and public service centers are piloting humanoid robots for patient care and customer service. Government programs under Make in India and Production-Linked Incentives (PLI) are encouraging domestic robot production to reduce import dependency and promote innovation.
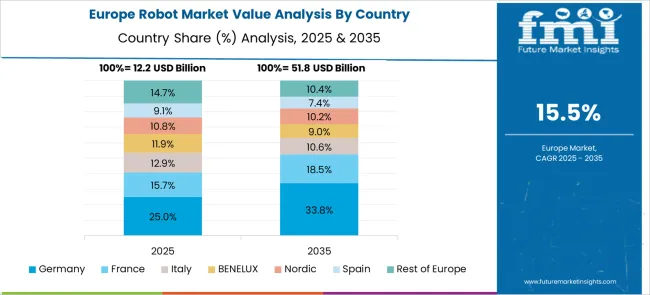
Germany holds a strong position in the global robot market with a CAGR of 19.1%, thanks to its leadership in precision engineering and Industry 4.0 practices. German manufacturers are integrating advanced robots in automotive lines, electronics assembly, and packaging operations. The country is also a major exporter of high-performance robotic arms and automation components. With a growing aging population, demand is increasing for robots in elder care and rehabilitation. Universities and research institutions collaborate closely with industry to develop next-gen robots powered by AI and edge computing. Sustainable robot production and modular designs are gaining momentum to reduce lifecycle costs.
The United Kingdom robot market is growing at a CAGR of 15.8%, spurred by demand in logistics, healthcare, and infrastructure automation. Retail and e-commerce companies are deploying warehouse robots to streamline order fulfillment, particularly in response to labor shortages. Hospitals and clinics are adopting disinfection robots, surgical assistants, and automated delivery units to improve service quality. The UK's focus on robotics in national R&D strategy has led to increased collaboration between universities and startups to develop homegrown solutions. In civil engineering, robots are being used for tunnel inspection, bridge maintenance, and hazardous environment assessment.
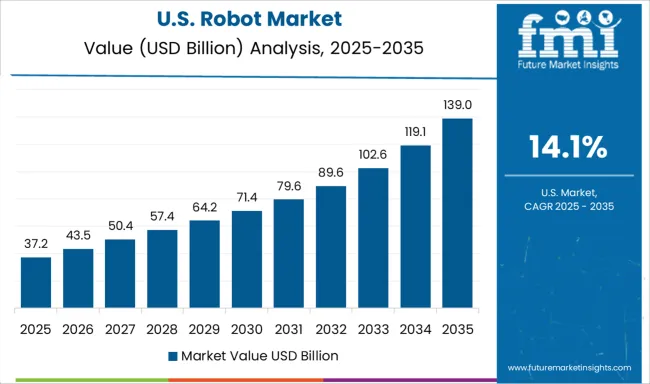
The United States continues to play a pivotal role in the global robot market with a CAGR of 14.1%, led by innovations in AI, aerospace, and medical robotics. Industrial automation is expanding across automotive plants, electronics facilities, and food processing units, especially in states like Michigan, Texas, and California. USA-based firms are pioneers in surgical robotics, defense bots, and warehouse automation systems. Tech giants and startups alike are experimenting with humanoid and home assistant robots. Government agencies and universities are investing heavily in robotics education and safety standards. The integration of 5G and cloud computing is enhancing real-time robot control and fleet management.
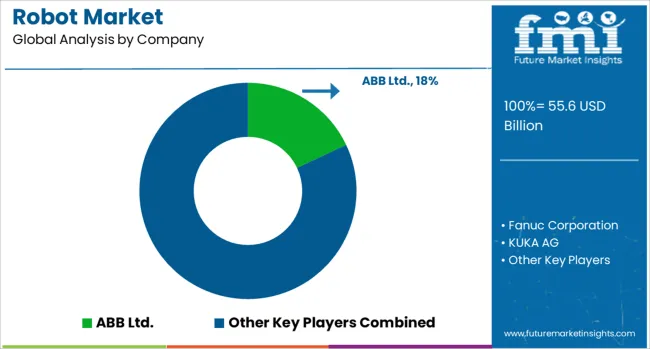
The global robot market is driven by the increasing deployment of robotic systems across manufacturing, logistics, defense, healthcare, and service sectors. Leading suppliers offer a mix of industrial robots, collaborative robots (cobots), mobile units, and humanoid systems tailored for automation, precision handling, and repetitive task management.
Market dynamics are shaped by demand for reliability, payload flexibility, and real-time control systems. ABB Ltd., Fanuc Corporation, and KUKA AG dominate the industrial robotics segment, offering comprehensive automation solutions for assembly, welding, painting, and material handling. These companies are known for robust hardware combined with advanced motion control and programming interfaces, making them preferred partners in automotive, electronics, and heavy machinery sectors. Their global presence and extensive service networks reinforce their competitiveness in both developed and emerging manufacturing economies.
Universal Robots leads in collaborative robot development, providing lightweight, easy-to-integrate cobots that operate safely alongside humans in space-constrained environments. These are widely used in packaging, inspection, and light-duty assembly lines.
Boston Dynamics, on the other hand, brings innovation to the mobile and service robotics sector with its quadruped and humanoid platforms, designed for dynamic environments such as warehouses, surveillance, and emergency response. As robotic applications broaden, suppliers that deliver agile form factors, customizable control systems, and cross-industry versatility are expected to see expanded adoption and stronger market positioning.
NEURA Robotics officially announced in a press release dated January 15, 2025, that it secured €120 million in Series B funding led by Lingotto Investment Management, with participation from BlueCrest Capital, Volvo Cars Tech Fund, InterAlpen Partners, and others. NEURA’s press release on June 24, 2025, confirms the world premiere of the 3rd‑generation 4NE1 humanoid, launch of the MiPA household/service robot, and unveiling of the Neuraverse ecosystem at Automatica 2025
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 55.6 Billion |
| Type | Industrial Robots and Service Robots |
| Component | Hardware and Software |
| Deployment Type | Cloud-based Robotics and On-premises Robotics |
| Mobility Type | Mobile Robots, Fixed Robots, and Humanoid Robots |
| Application Type | Assembly & Production |
| End Use Industry | Manufacturing & Industrial, Healthcare, Defense, Agriculture, and Others |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | ABB Ltd., Fanuc Corporation, KUKA AG, Universal Robots, and Boston Dynamics |
The global robot market is estimated to be valued at USD 55.6 billion in 2025.
The market size for the robot market is projected to reach USD 258.3 billion by 2035.
The robot market is expected to grow at a 16.6% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in robot market are industrial robots, _articulated robots, _scara robots, _cartesian robots, _delta robots, _collaborative robots (cobots), _parallel robots, service robots, _personal service robots and _professional service robots.
In terms of component, hardware segment to command 48.0% share in the robot market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Robot Controller, Integrator and Software Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robotic Warfare Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robotic Lawn Mower Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robotics Welding Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robotic Rehab Tools Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robotics-Assisted Telesurgery Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robotic Packaging Machines Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robot Assisted Surgical Microscope Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robotic Assisted Endovascular Systems Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robotic Lung Biopsy Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robotics as a Service (RaaS) Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robotic X-ray Scanner Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robotic Catheterization Systems Market Growth – Innovations, Trends & Forecast 2025-2035
Robot Sensor Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robotaxi Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robotic Aseptic Syringe Filler Capper Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robotic Vision Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robotics Actuators Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Robotic Biopsy Devices Market Insights - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Robotic Palletizers & De-Palletizers Market Growth - Forecast 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA