The Japan advance wound care demand is valued at USD 680.2 million in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 875.0 million by 2035, recording a CAGR of 2.6%. Demand is shaped by continued use of specialised wound-management products across hospitals, long-term care centres, and outpatient clinics. Rising incidence of chronic wounds linked to ageing populations, diabetes, and mobility-related conditions supports steady procurement of advanced dressing systems. These products help maintain moisture balance, reduce infection risk, and support tissue regeneration in complex wound types.
Advanced wound-care dressings represent the leading product category due to their broad clinical acceptance and suitability for pressure ulcers, venous leg ulcers, diabetic foot ulcers, and surgical wounds. Hydrocolloid, foam, alginate, and antimicrobial dressings are widely used because they offer predictable absorption performance and compatibility with standard clinical workflows. Developments in breathable materials and infection-control coatings continue to influence product selection.

Demand is concentrated in Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, and Kinki, where hospitals, wound-care clinics, and home-health providers drive usage. Key suppliers include Smith & Nephew plc, Mölnlycke Health Care AB, 3M Company, ConvaTec Group, and Coloplast A/S, offering structured product portfolios for chronic and acute wound-management needs.
Year-on-year growth analysis indicates a stable, low-volatility pattern shaped by steady clinical demand and Japan’s aging population. Between 2025 and 2028, YoY growth will remain close to the long-term average as hospitals and long-term care facilities maintain consistent use of advanced dressings, antimicrobial solutions, and negative-pressure systems. Routine treatment of chronic wounds, including diabetic and pressure ulcers, will support predictable annual increases.
From 2029 to 2032, YoY growth may show mild variation due to procurement cycles, reimbursement adjustments, and incremental shifts in clinical-pathway adoption. These variations will remain limited because wound-care protocols and product utilization rates are well established across Japanese healthcare settings. Between 2033 and 2035, YoY growth is expected to stabilise as product categories mature and innovation focuses on improved absorbency, less-invasive materials, and sensor-supported monitoring rather than major platform changes. The YoY pattern reflects a mature therapeutic segment characterised by steady clinical need, long treatment durations, and consistent reliance on standardized wound-management systems across Japan’s healthcare institutions.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Japan Advance Wound Care Sales Value (2025) | USD 680.2 million |
| Japan Advance Wound Care Forecast Value (2035) | USD 875.0 million |
| Japan Advance Wound Care Forecast CAGR (2025-2035) | 2.6% |
Demand for advanced wound care in Japan is increasing due to the ageing population, higher incidence of chronic diseases and growing need for effective therapies that accelerate healing. Many older adults are at greater risk of pressure ulcers, diabetic foot ulcers or compromised skin integrity, which create demand for specialised dressings, negative-pressure therapy systems and bioengineered wound care materials. Healthcare providers in Japan seek solutions that reduce hospital stays, prevent complications and improve quality of care.
Technological advances in wound therapies, increased awareness of evidence-based care and greater adoption of advanced wound care devices in outpatient and home settings support this growth. Constraints include the higher cost of advanced wound care products, mixed reimbursement coverage for newer therapies and the challenge of training medical staff in adoption of newer treatment protocols. Some smaller care facilities may delay investment until cost-efficiency and clinical outcomes are clearly established.
Demand for advanced wound-care products in Japan reflects clinical needs across chronic and acute cases, supported by an ageing population and structured treatment protocols. Product adoption varies with wound severity, expected healing duration, and access to specialised care. Indication patterns reflect the prevalence of chronic wounds and the clinical workload across hospitals and outpatient facilities. End-user distribution aligns with treatment complexity, equipment availability, and long-term care requirements.

Advanced wound-care dressings hold 54.0% of demand in Japan, making them the leading product category. These dressings include hydrocolloid, alginate, foam, and antimicrobial formats designed to support moisture control, protect against infection, and encourage stable healing across chronic and acute cases. Their adaptable structure allows use in post-surgical, diabetic, and pressure-related wounds. Negative-pressure wound-therapy systems represent 31.0%, supporting management of deep or complex wounds that require controlled suction and structured exudate removal. Compression-therapy devices hold 15.0%, serving patients affected by venous ulcers or circulatory disorders. Product selection varies with wound depth, exudate levels, patient mobility, and facility capacity.
Key drivers and attributes:
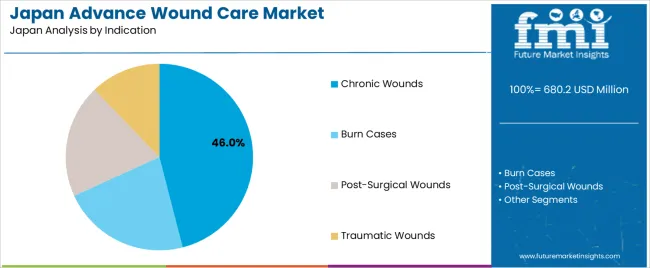
Chronic wounds hold 46.0% of Japanese demand and represent the largest indication group. Diabetic foot ulcers, venous leg ulcers, and pressure injuries require extended treatment cycles supported by advanced dressings and negative-pressure systems. These wounds are common within an ageing population and require structured monitoring across long-term care and outpatient settings. Post-surgical wounds hold 24.0%, driven by routine postoperative management needs in hospitals and ambulatory centres. Traumatic wounds represent 18.0%, including cases resulting from accidents or occupational incidents. Burn cases hold 12.0%, requiring dressings that maintain moisture balance and reduce the risk of infection. Indication patterns reflect demographic profiles, chronic-disease rates, and facility-level treatment capability.
Key drivers and attributes:
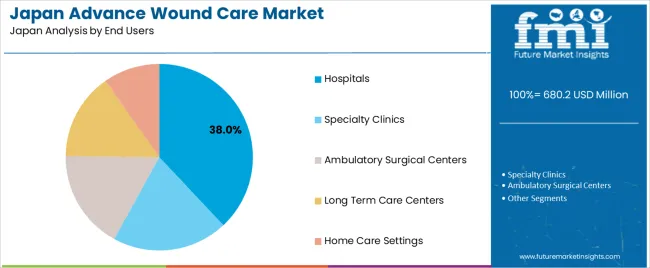
Hospitals hold 38.0% of advanced wound-care demand in Japan, making them the primary end-user group. They manage complex cases, including deep wounds, surgical sites, and chronic conditions requiring device-based therapy. Specialty clinics represent 24.0%, focusing on chronic-wound management and personalised dressing protocols. Ambulatory surgical centres hold 17.0%, supporting postoperative care following outpatient procedures. Long-term care centres account for 12.0%, driven by pressure-injury prevention and elderly patient needs. Home-care settings represent 9.0%, supported by simplified dressing formats and portable negative-pressure devices. End-user distribution reflects treatment complexity, staffing resources, and patient-management pathways in different facilities.
Key drivers and attributes:
Demand for advance wound care in Japan is shaped by increasing focus on improved patient outcomes in hospitals, outpatient clinics, and home-based treatment settings. Chronic wounds, age-related ulcers, and post-operative wounds require reliable solutions that support faster recovery and reduce complications, which draws attention toward modern dressings and therapeutic systems. At the same time, clinical protocols set by care providers encourage greater use of products that support moisture balance, infection control, and ease of application. Budget pressure within healthcare institutions, variations in reimbursement clarity, and the need for trained staff in complex wound procedures influence the pace of adoption. These combined elements define the evolving demand environment for advance wound care in Japan.
What Are the Primary Growth Drivers for Advance Wound Care Demand in Japan?
Several drivers support expansion. First, the rise in chronic wound incidence, particularly diabetic foot ulcers, venous leg ulcers, and pressure injuries, creates steady requirements for advanced dressings, negative pressure therapy, and infection-management solutions. Second, hospitals and long-term care facilities in Japan are strengthening wound-care protocols that emphasize standardized care pathways and evidence-based product usage. Third, clinical teams increasingly prefer solutions that reduce dressing-change frequency and improve patient comfort. Fourth, demand is supported by increased home-care utilization, where caregivers seek products that simplify wound handling without compromising safety. Together, these elements reinforce consistent uptake across healthcare environments.
What Are the Key Restraints Affecting Advance Wound Care Demand in Japan?
Despite promising momentum, restraints remain. The higher price of advanced dressings and therapy systems can limit adoption when cost-containment policies are applied in hospitals and clinics. Reimbursement complexity in certain product categories slows purchasing decisions. Some facilities face shortages of specialized wound-care nurses, which can reduce usage of complex therapies such as negative-pressure wound therapy. Concerns around correct application, maintenance, and patient-handling procedures may discourage smaller clinics from expanding their product mix. In addition, variation in procurement processes across prefectures creates uneven uptake in some settings.
What Are the Key Trends Shaping Advance Wound Care Demand in Japan?
Key trends include greater use of foam-based dressings, hydrocolloids, alginates, and antimicrobial options that support moisture control and reduction of infection risk. Hospitals are integrating digital wound-documentation tools, allowing care teams to monitor progress and justify use of advanced therapies. Suppliers are introducing dressings designed for longer wear time, gentler removal, and improved exudate handling to address patient-comfort concerns. Home-care providers and visiting-nurse services are increasingly adopting compact negative-pressure systems suitable for community settings. Interest in training programs and standardized wound-assessment frameworks is rising, strengthening product confidence in both acute and long-term care environments.
Demand for advance wound care in Japan is rising through 2035 as healthcare providers adopt modern dressings, moisture-management systems, and antimicrobial products for chronic, postoperative, and trauma-related wounds. Hospitals, long-term care facilities, and outpatient clinics rely on specialized wound-care materials that support faster healing and reduce dressing-change frequency. Regional demand differs based on healthcare density, patient demographics, adoption of advanced wound technologies, and procurement structures across clinics and retail networks. An aging population and rising chronic-disease incidence reinforce long-term usage of advanced dressings nationwide. Kyushu & Okinawa leads with a 3.2% CAGR, followed by Kanto (2.9%), Kinki (2.6%), Chubu (2.3%), Tohoku (2.0%), and the Rest of Japan (1.9%).
| Region | CAGR (2025-2035) |
|---|---|
| Kyushu & Okinawa | 3.2% |
| Kanto | 2.9% |
| Kinki | 2.6% |
| Chubu | 2.3% |
| Tohoku | 2.0% |
| Rest of Japan | 1.9% |
Kyushu & Okinawa grows at 3.2% CAGR, supported by consistent usage of advanced dressings across hospitals, surgical centers, and long-term care facilities. Medical teams in Fukuoka, Kumamoto, and Kagoshima manage significant volumes of diabetic ulcers, pressure injuries, and chronic postoperative wounds, driving steady procurement of hydrocolloid, foam, alginate, and antimicrobial products. Community clinics and home-care programs use moisture-management materials for elderly patients requiring ongoing wound monitoring. Regional hospitals rely on negative-pressure wound therapy for complex cases. Okinawa’s distributed healthcare system depends on reliable logistics to maintain uninterrupted supply of essential wound-care materials across remote islands. Stable patient workloads and recurring dressing requirements sustain long-term product consumption.

Kanto grows at 2.9% CAGR, driven by Japan’s highest concentration of hospitals, outpatient centers, and specialized surgical facilities. Tokyo, Kanagawa, and Chiba record strong demand for advanced wound-care dressings used in postoperative recovery, trauma care, and chronic-disease management. High patient volumes generate continuous need for hydrocolloid, silicone-foam, and antimicrobial products. Long-term care facilities rely heavily on pressure-injury prevention materials and moisture-control dressings. Clinical teams adopt negative-pressure devices for complex wounds, reinforcing procurement cycles. Retail pharmacies maintain steady turnover of basic dressings, expanding total consumption. Large wholesalers support uninterrupted supply across metropolitan corridors, ensuring consistent availability for hospitals with intensive wound-care workloads.
Kinki grows at 2.6% CAGR, supported by established healthcare networks across Osaka, Kyoto, and Hyogo that regularly treat chronic wounds, postoperative incisions, and pressure injuries. Hospitals adopt foam, hydrocolloid, and alginate dressings to manage a broad range of wound types, while outpatient clinics use lightweight hydrogel and silicone-based materials for routine care. Long-term care facilities maintain steady demand due to older populations requiring continuous monitoring for skin breakdown and pressure-related injuries. Rehabilitation centers use advanced dressings to support mobility-impaired patients. Regional procurement remains stable because facilities prioritize products that improve healing quality, enhance moisture balance, and reduce dressing-change frequency.
Chubu grows at 2.3% CAGR, supported by balanced healthcare demand across Aichi, Shizuoka, and Mie. Hospitals rely on advanced dressings for postoperative wounds, pressure injuries, and diabetic-ulcer management. Clinics use alginate, hydrogel, and silicone-foam materials for moderate chronic wounds and outpatient treatment cycles. Long-term care facilities maintain recurring orders for moisture-control and antimicrobial dressings to support elderly-care routines. Retail pharmacies show steady turnover of essential dressings used for minor wounds. While overall patient density is moderate, stable medical workloads ensure continuous usage of advanced wound-care materials. Regional distributors provide consistent supply, supporting dependable access for both hospitals and extended-care providers.
Tohoku grows at 2.0% CAGR, supported by predictable clinical usage across hospitals, clinics, and elderly-care facilities in Miyagi, Fukushima, and Iwate. Healthcare providers manage chronic wounds associated with aging populations, diabetes, and long-term immobility, requiring consistent supply of hydrocolloid, alginate, and foam dressings. Outpatient centers treat minor traumatic injuries and postoperative wounds, maintaining steady turnover of advanced materials. Long-term care facilities rely on moisture-balance products to prevent and manage pressure injuries. Although the region has lower population density, essential wound-care needs ensure stable procurement volumes. Regional wholesalers maintain reliable distribution to facilities across rural and semi-urban prefectures.
The Rest of Japan grows at 1.9% CAGR, supported by distributed healthcare systems across rural hospitals, community clinics, and home-care programs. Facilities rely on advanced dressings for chronic wound management, postoperative recovery, and pressure-injury prevention. Elderly-care centers maintain routine use of moisture-management and antimicrobial materials to support vulnerable populations. Retail pharmacies provide steady access to basic dressings for minor injuries and home-care needs. Population density is lower, but essential medical demands create ongoing consumption of wound-care materials. Regional logistics networks ensure that even remote facilities maintain continuous access to required supplies.
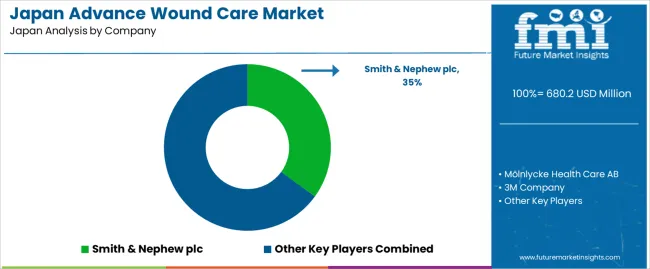
Demand for advanced wound-care products in Japan is shaped by a concentrated group of medical-technology suppliers supporting hospitals, long-term-care facilities, and home-health providers. Smith & Nephew plc holds the leading position with an estimated 35.0% share, supported by its broad range of foam dressings, antimicrobial products, and negative-pressure solutions. Its position is reinforced by consistent clinical performance, established relationships with Japanese hospital networks, and dependable product availability.
Molnlycke Health Care AB and 3M Company follow as major participants, offering dressings designed for exudate management, infection control, and postoperative wound care. Their strengths include predictable healing support, strong clinical evidence, and wide use in both acute and chronic wound settings. ConvaTec Group maintains a notable presence through hydrocolloid dressings and negative-pressure technologies that support reliable moisture balance and wound protection. Coloplast A/S contributes additional capability with dressings and skin-care products suited for long-term-care and home-care environments, emphasizing gentle adhesion, patient comfort, and stable moisture control.
Competition across this segment centers on exudate-handling performance, infection-prevention capability, patient comfort, durability, and consistency across extended wear. Demand remains steady due to Japan’s aging population, higher incidence of chronic wounds, and increased adoption of advanced dressings and pressure-relief technologies that support predictable healing outcomes in clinical and home-based care settings.
| Items | Values |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD million |
| Products | Advance Wound Care Dressings, Negative Pressure Wound Therapy, Compression Therapy Devices |
| Indication | Chronic Wounds, Burn Cases, Post-Surgical Wounds, Traumatic Wounds |
| End Users | Hospitals, Specialty Clinics, Ambulatory Surgical Centers, Long Term Care Centers, Home Care Settings |
| Regions Covered | Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, Kinki, Chubu, Tohoku, Rest of Japan |
| Key Companies Profiled | Smith & Nephew plc, Mölnlycke Health Care AB, 3M Company, ConvaTec Group, Coloplast A/S |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by product type, indication, and end-user categories; regional adoption trends across Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, Kinki, Chubu, Tohoku, and Rest of Japan; competitive landscape of advanced wound care solution providers; developments in negative pressure wound therapy, moist wound healing materials, and compression devices; integration with hospital wound management programs, long-term care facilities, and home-based wound care practices in Japan. |
The global demand for advance wound care in Japan is estimated to be valued at USD 680.2 million in 2025.
The demand for advance wound care in Japan is projected to reach USD 875.0 million by 2035.
The demand for advance wound care in Japan is expected to grow at a 2.6% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types are advance wound care dressings, negative pressure wound therapy and compression therapy devices.
In terms of indication, chronic wounds segment to command 46.0% share in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Demand Signal Repository Solutions Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand Side Management Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand Response Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
North America Shipping Supplies Market Trends – Innovations & Growth 2024-2034
Demand of Kozani Saffron in Greece Analysis - Size, Share & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Demand of No-acid Whey Strained Dairy Processing Concepts in European Union Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand for Bronte Pistachio in Italy Analysis - Size, Share & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Demand and Trend Analysis of Gaming Monitor in Western Europe Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Trend Analysis of Gaming Monitor in Korea Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Trend Analysis of Gaming Monitor in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Glycine Soja (Soybean) Seed Extract Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Trend Analysis of Yeast in Japan - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand of Pistachio-based desserts & ingredients in France Analysis - Size, Share & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Demand and Trends Analysis of Stevia in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Trend Analysis of Fabric Stain Remover in Korea Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Sales Analysis of Paper Cup in Korea Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Sales Analysis of Paper Cup in Western Europe Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand of MFGM-enriched Powders & RTDs in European Union Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Sales Analysis of Paper Cup in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand and Trend Analysis of Avocado Oil in Western europe Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA