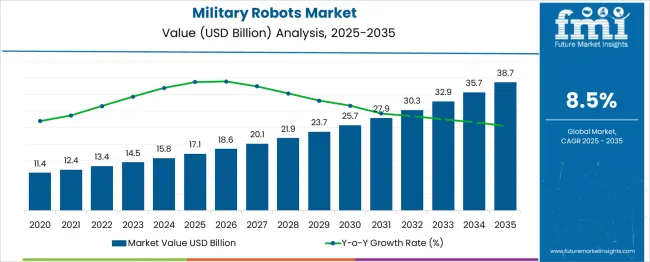
The Military Robots Market is estimated to be valued at USD 17.1 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 38.7 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.5% over the forecast period. Despite the 8.5% CAGR, the year-on-year growth pattern reveals moderate volatility. The early-phase gains between 2025 and 2029 range from USD 1.5 billion to USD 1.8 billion annually, while the later phase between 2030 and 2035 observes annual additions of USD 2.1 billion to USD 3 billion. This reflects moderate amplification in scale, though no erratic growth jumps appear. The market has exhibited steady pacing tied to structured adoption across ISR, unmanned combat systems, and logistics automation programs.
Volatility indexing shows a stable curve, with standard deviation across year-on-year increments confined within acceptable ranges for a high-value defense segment. Pricing revisions due to component cost stabilization, paired with predictable volume ramp-up from NATO-aligned and Asia-Pacific procurement, contribute to consistency.
Growth has not shown any reactive fluctuation to geopolitical escalations or temporary policy mandates. Instead, contractual defense orders, multiyear R&D frameworks, and restricted vendor ecosystems have produced a contained risk structure with low deviation from the core CAGR trajectory.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Military Robots Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 17.1 billion |
| Military Robots Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 38.7 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 8.5% |
The military robots market is undergoing rapid advancement, fueled by increasing defense modernization efforts, growing emphasis on soldier safety, and the need for real-time operational efficiency. Nations are deploying autonomous and semi-autonomous robotic systems to support complex battlefield environments, reduce human exposure to risk, and extend operational capabilities in surveillance, combat support, and logistics.
Technological progress in artificial intelligence, edge computing, and sensor fusion has enhanced the effectiveness of robotic systems in mission-critical tasks. Additionally, increasing geopolitical tensions and defense spending have expanded procurement programs worldwide. As integration with existing command and control infrastructure improves, the market is poised to scale with greater adaptability and interoperability across mission profiles.
The military robots market is segmented by platform, mode of operation, application, and geographic regions. The military robots market is divided into Land-based, Aerial, and Naval. In terms of the mode of operation, the military robots market is classified into automated and human-operated.
The application of the military robots market is segmented into Intelligence, Surveillance, And Reconnaissance (ISR), Search & rescue, Firefighting, Explosive Ordnance Disposal (EOD), Mine clearance, Transportation, Combat support, and others. Regionally, the military robots industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
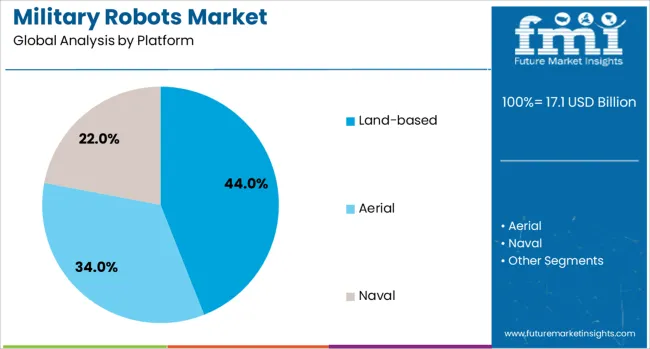
Land-based robots are projected to dominate the platform segment with a 44.00% revenue share in 2025. This segment’s lead stems from their versatile deployment across reconnaissance, explosive ordnance disposal, and logistics support missions.
These systems can navigate varied terrains, carry payloads, and integrate with unmanned ground control systems. Demand is rising for tracked and wheeled units capable of supporting infantry while operating autonomously or remotely in high-risk zones.
Their effectiveness in surveillance, convoy protection, and infrastructure inspection has led to strong adoption across major armed forces.
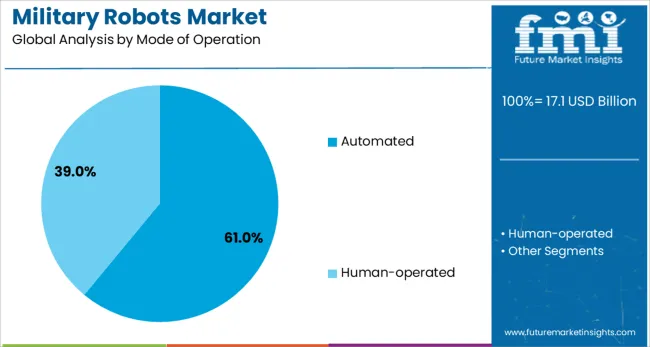
Automated systems are expected to account for 61.00% of the market share in 2025, making them the dominant mode of operation. The growth of this segment is fueled by AI-driven autonomy, reduced operator burden, and the ability to execute complex tasks without real-time human input.
Military organizations are increasingly investing in automated systems that can perform target recognition, route planning, and adaptive mission control.
Their reduced need for continuous supervision improves mission endurance and operational stealth, particularly in electronic warfare and reconnaissance operations.
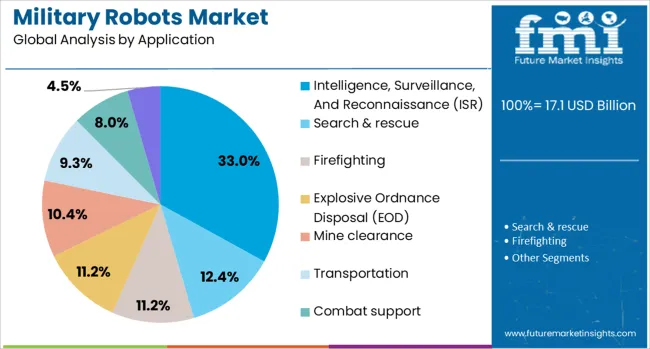
ISR is anticipated to lead the application category with a 33.00% share in 2025, driven by the increasing need for real-time situational awareness and data gathering in contested environments. Robotic systems equipped with advanced imaging, infrared, and LIDAR sensors are enhancing battlefield intelligence across land, air, and maritime domains.
These systems enable persistent surveillance and rapid threat detection, critical for both tactical and strategic operations. As threats become more asymmetric and dispersed, ISR-capable robots provide commanders with actionable insights while minimizing personnel exposure.
The military robots market is expanding swiftly due to increased deployment of unmanned systems across surveillance, logistics, combat, and explosive ordnance disposal operations. Uncrewed platforms, land, aerial, and maritime, are being used to reduce human risk while enhancing precision and mission coverage. Advances in autonomy, AI-driven swarm tactics, and ruggedized sensor integration are accelerating adoption. Both developed and emerging defense forces are redeploying resources toward robotic systems to augment traditional manned operations. Regulatory and ethical frameworks are evolving alongside field deployment, emphasizing machine reliability, human trust, and operational transparency in complex and contested environments.
Military robots are advancing from remotely operated platforms to semi-autonomous and fully autonomous systems. Airborne drones dominate usage share, with ground systems gaining traction through modular payloads for logistics, EOD, and frontline support. Techniques such as AI-driven target detection, edge computing, and swarm coordination are expanding mission complexity while reducing operator burden. Autonomous systems capable of navigating GPS-denied environments are being deployed in surveillance and search tasks. High-performance sensors—electro-optical, infrared, and electronic warfare modules—are becoming standard. These technological improvements are rapidly boosting mission impact, resilience, and adaptability in contested environments.
Global defense modernization has prioritized robotic systems across major regions. North America leads market revenue, driven by advanced procurement cycles and defense-industrial capabilities. Asia Pacific offers the fastest growth rates as nations such as China, India, South Korea, and Japan invest in domestically-produced robotic systems for border monitoring, maritime security, and force projection. Europe is bolstering NATO interoperability with modular robotics programs, while the Middle East, Africa, and Latin America are adopting entry-level systems for counterterrorism and border patrol. Budget constraints and infrastructure gaps, however, slow uniform adoption across less-resourced regions.
Despite rapid uptake, barriers persist around trust, regulation, and technical integration. Certification of autonomous weapon systems remains complex, requiring thorough testing under live-fire, operational stress, and durability scenarios. Cybersecurity threats, such as signal jamming and GPS spoofing, demand hardened communication links and resilience protocols. International debate continues on ethical frameworks, human oversight, and the accountable use of force by autonomous systems. Legacy force structures and mixed human-robot architectures require standardization. These challenges temper adoption, particularly in less commercially mature defense ecosystems.
North America led the market in 2024 with over 40% of global revenue, driven by advanced procurement pipelines and R&D infrastructure. Asia-Pacific was the fastest-growing region, supported by rising defense budgets, regional tensions, and civil-military innovation strategies. Europe maintained steady adoption through the modernization of NATO forces and interoperability programs. In Eastern Europe, Ukraine has notably expanded deployment, aiming to field thousands of ground robots by 2025. Armed ground robots, including gun-equipped UGVs, have been deployed for frontline operations, demonstrating real-time application of unmanned systems in combat zones.
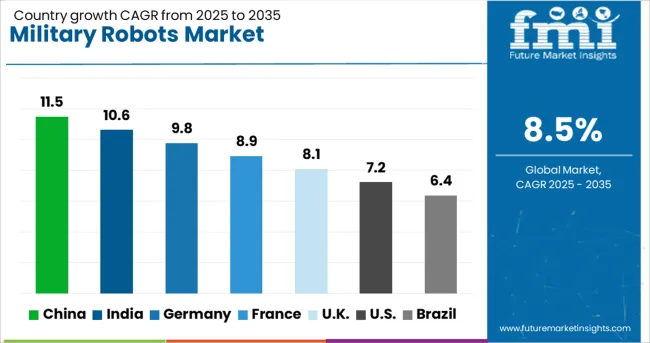
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 11.5% |
| India | 10.6% |
| Germany | 9.8% |
| France | 8.9% |
| UK | 8.1% |
| USA | 7.2% |
| Brazil | 6.4% |
The global military robots market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 8.5% from 2025 to 2035. China is expected to outperform with 11.5%, exceeding the global pace by 35%, supported by persistent automation across surveillance and combat applications. India follows at 10.6%, reflecting a 25% premium over the global rate, driven by active government funding and UAV integration within armed forces. Germany’s CAGR of 9.8% places it 15% higher than the global average due to rising defence robotics demand across NATO operations. The United Kingdom, at 8.1%, is nearing alignment with the global growth rate, while the United States, projected at 7.2%, trails by 15% owing to slower transition cycles and legacy system dependencies. OECD countries demonstrate moderate adoption, while ASEAN states continue to rely on imports.
China is forecast to expand at a CAGR of 11.5% through 2035, placing it 35% above the global average. Autonomous systems are being prioritized across ground, naval, and aerial platforms for reconnaissance, logistics, and perimeter defence. Local suppliers are scaling AI-driven sensor integration within combat-ready units. Unmanned platforms are replacing older surveillance systems in border areas and strategic installations. As domestic production volumes rise, exports of robotic subsystems are accelerating across Asia and Africa. Military procurement budgets have been adjusted to absorb rapid-scale automation needs across battalions, with concurrent development of support robotics for mobile weaponry and supply transport.
India is projected to grow at a CAGR of 10.6% through 2035, which is 25% higher than the global mean. Robotics programs are being integrated across all three armed services, supported by local development under defence indigenization policy mandates. Surveillance drones, bomb disposal units, and tactical robots are being manufactured by a mix of public and private entities. Cross-border tensions have prompted deployment of mobile sensor robots and night patrol bots. Procurement policy revisions are accelerating domestic trials of semi-autonomous weaponized platforms. State-owned labs are advancing machine learning integration for real-time terrain analysis, while cost-effective export variants are also under development.
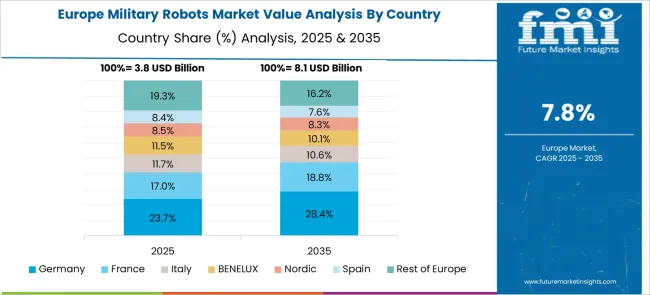
Germany is expected to achieve a CAGR of 9.8% during the forecast period, surpassing the global average by 15%. Tactical unmanned systems are being deployed for frontline surveillance and logistics support across NATO-aligned operations. Increased demand has been observed in modular autonomous vehicles suited for mine detection, casualty evacuation, and route clearance. Integration of cybersecurity and cross-platform communication protocols has been prioritized within procurement criteria. Domestic firms are scaling up dual-use robotic systems that serve both civil and military applications. EU-level funding is facilitating research into lightweight autonomous land systems optimized for Arctic and desert terrains.
The United Kingdom is expected to grow at a CAGR of 8.1% from 2025 to 2035, nearing the global benchmark. Integration of battlefield automation is advancing slowly, hindered by legacy systems and extended procurement cycles. Robotics use remains concentrated within reconnaissance and explosive ordnance disposal. Budget allocations for next-gen robotic programs have been steady, with limited breakthroughs in AI combat readiness. Collaborations with EU and NATO research programs have improved access to joint development platforms, especially in aerial surveillance units. Cybersecure data sharing between drones and command units has become a technical focus to enable multi-unit field deployment.
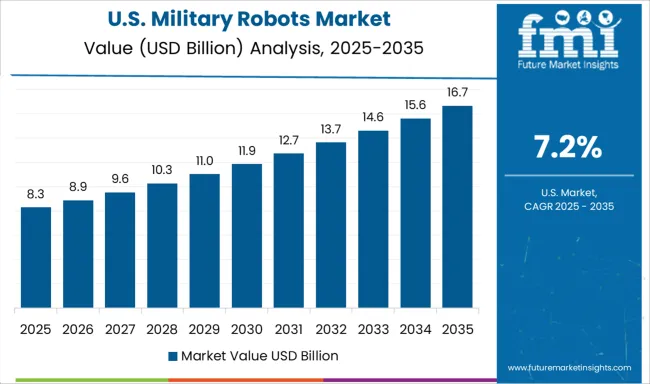
The United States is forecast to grow at a CAGR of 7.2%, falling 15% below the global average. Robotics deployment has remained cautious due to dependency on legacy combat systems and extended pilot testing protocols. Research continues in autonomous land systems and drone warfare applications, though commercialisation timelines have faced delays. Large military contractors are developing next-gen robotic units for multi-domain operations but face approval bottlenecks. Transition to fully autonomous units remains constrained by cybersecurity, ethics, and command compliance regulations. Tactical robots are deployed mainly for reconnaissance and remote explosive handling. Inter-service coordination on AI deployment has been ongoing but slow.
Between 2023 and 2025, military robots saw tactical integration into battlefield logistics, surveillance, and combat systems. Autonomous unmanned ground vehicles were enhanced with AI-driven threat detection and modular payloads. Satellite-servicing robots with robotic arms advanced space defense capabilities. Strategic collaborations supported weaponized robotic platforms for Middle East deployments. Reconnaissance vehicles equipped with C4/UAS systems entered field testing. Counter-drone robots featuring adaptive targeting algorithms were demonstrated in operational environments, reflecting a transition from concept-phase prototypes to actively deployed robotic defense units worldwide.
Autonomous unmanned ground vehicles were enhanced with AI-driven threat detection and modular payloads. Satellite-servicing robots with robotic arms advanced space defense capabilities. Strategic collaborations supported weaponized robotic platforms for Middle East deployments. Reconnaissance vehicles equipped with C4/UAS systems entered field testing. Counter-drone robots featuring adaptive targeting algorithms were demonstrated in operational environments, reflecting a transition from concept-phase prototypes to actively deployed robotic defense units worldwide.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 17.1 Billion |
| Platform | Land-based, Aerial, and Naval |
| Mode of Operation | Automated and Human-operated |
| Application | Intelligence, Surveillance, And Reconnaissance (ISR), Search & rescue, Firefighting, Explosive Ordnance Disposal (EOD), Mine clearance, Transportation, Combat support, and Others |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
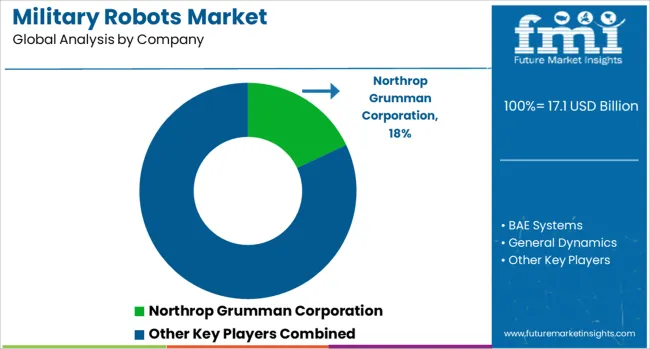
| Key Companies Profiled | Northrop Grumman Corporation, BAE Systems, General Dynamics, Lockheed Martin, and Thales Group |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by platform type (airborne, ground, naval) and application segment (ISR, combat support, EOD, logistics), demand dynamics in surveillance and battlefield autonomy, regional dominance of North America, innovation in AI-enabled autonomy and swarm tactics, environmental and operational resilience in electronic warfare environments, and emerging use cases in frontline logistics, robotic platoons, and swarm-enabled mission operations. |
The global military robots market is estimated to be valued at USD 17.1 billion in 2025.
The market size for the military robots market is projected to reach USD 38.7 billion by 2035.
The military robots market is expected to grow at a 8.5% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in military robots market are land-based, aerial and naval.
In terms of mode of operation, automated segment to command 61.0% share in the military robots market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Military Test Equipment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Military Textile Materials Testing Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Military Cyber Security Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Military Sensor Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Military Displays Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Military and Defense Ground Support Equipment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Military Radar Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Military Microgrid Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Military Cloud Computing Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Military Vehicle Electrification Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Military Wearables Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Military Trucks Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Military Embedded Systems Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Military Logistics Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Military Lighting Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Military Biometrics Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Military Electro-Optics Infrared (EO/IR) Systems Market Report – Growth & Trends 2025 to 2035
Military Hydration Products Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Military Vehicles and Aircraft Simulations Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Military Batteries Market Analysis & Forecast by Platform, Capacity, Type, End-Use and Region through 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA